Tree Map Chart
Tree maps are useful for giving business users quick views of large amounts of data to find trends and anomalies at-a-glance. It would be very difficult to view and comprehend information about 2,000 items in a pie chart; a heat map, however, makes this possible. Tree maps can show relationships among hundreds or thousands of items in hierarchies with rectangular spaces divided into regions. Each region is divided again to correspond to each level in the hierarchy. Business users easily interact with these hierarchical, colorful regions to get more information.
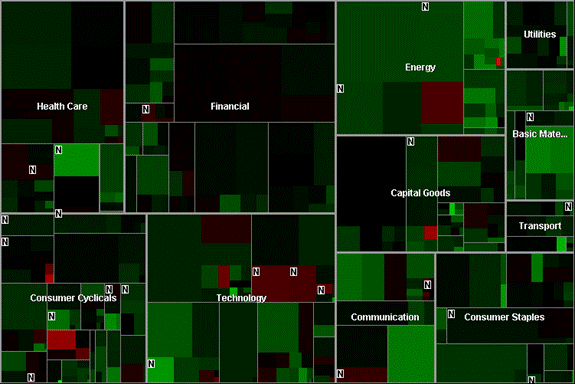
The Map of the Market tree map of daily stock quotes by SmartMoney.
Tree maps are especially useful when an organization has numerous facts to analyze, such as many sales regions, many manufacturing plants or hundreds of product lines and wants to monitor the complex activities among those many products, projects or salespeople.
Tree maps are comprised of multiple cells that have a varying size and color. Each cell has a specific label so that users can determine what each cell represents. The size, color and label for each cell are determined by values from three different points of data. In order to fully populate a heat map, select three distinct data columns for the label, cell size and cell color.
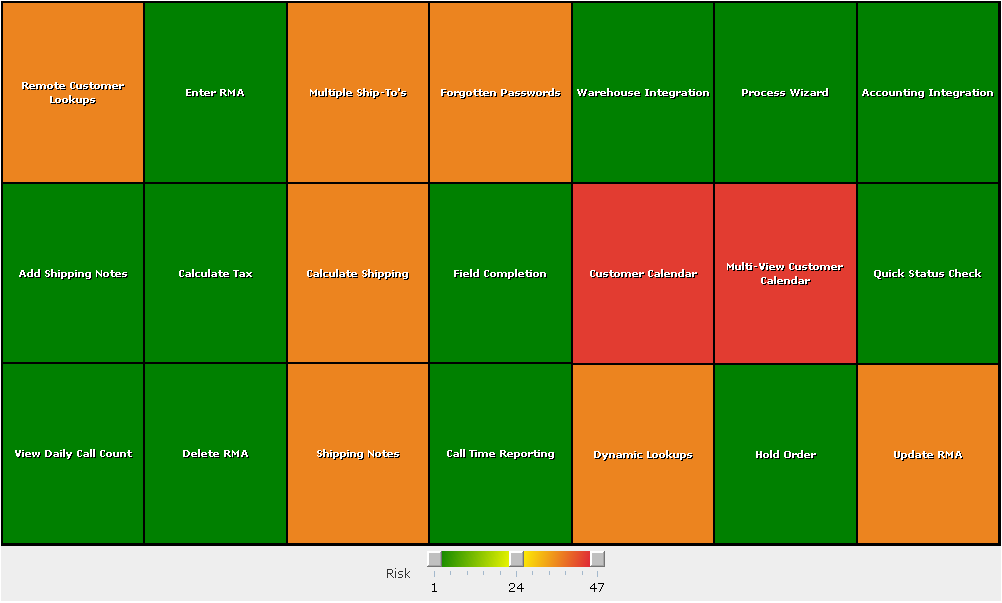
A tree map displaying the business value and risk from backlog item.
A cell is created for each item inthe product backlog. The size of the cell is determined by the business value attribute; larger values for business value produce larger cells. The color of the cell is determined by the risk of each item.
Note: Numeric data columns must be selected for the Cell Size and Cell Color columns.
The heat map color slider displays gradients of 3 different colors.
The Tree Map component also includes an interactive color slider that allows dynamic modification to the gradients of three distinct colors that correspond with values from the cell color column. The left color corresponds to low values, the center color corresponds to middle values, and the right color corresponds to high values. The gradients help establish the relationship each cell color value has to another. In the example, the highest values will get the purest shade of green. Slide the control to the left to single out the lowest value. Slide the control to the right to find the cell with the highest value.