Exercise 5 Query your Story
This topic explains how to query for a story in Agility.
Overview
This tutorial will help you query the Story created in Exercise 4 using the Rest API.
Prerequisites
-
Access to a Digital.ai 7.0 instance or newer. We are using 'https://www16.v1host.com/api-examples from our previous exercises.
-
We assume that you understand all material found in the following previous exercises:
-
Agility Sync REST API Tutorial
-
Exercise 1: Basic Use of the API Console
-
Exercise 2: Find a Scope (Project) OID Token in the U
-
Exercise 3: Query a Scope (Project) for Specific Attribute
-
Exercise 4: Create your own Story (Backlog Item) within a Scope
-
-
Knowledge of the VersionOne API Console.
-
Basic Knowledge of XML.
What you'll learn
This exercise walks you through querying a Story using the rest-1.v1 endpoint, understanding OIDs and Moments, using the query.v1 endpoint as an alternative, and working with basic query parameters like sel and where.
Be aware that prior to doing the next operation (GET or POST), make sure that you are on the Request tab. Keep this in mind as you work through the exercises.
Step 1: Recall the OID of the newly created Story.
Recall that we saved the previous OID returned in the response from the output from Exercise 4 below. Line 4 contains the Story:1045:1058. Its OID is Story:1045.
Did you notice this OID Story:1045 has an appendage of 1058? This is what is called a Moment.
A Moment is a chronologically-increasing integer assigned to every change in the Agility system. When you created your story in Exercise 4, it generated moment 1058. Each action against any asset creates a new moment.
Format breakdown:
- Story:1045 is the OID, which represents the current state of the story
- Story:1045:1058 is the OID with a Moment, representing the story at a specific point in history
You can use Moments to query historical data and track how assets changed over time. For more details, see Moment documentation.
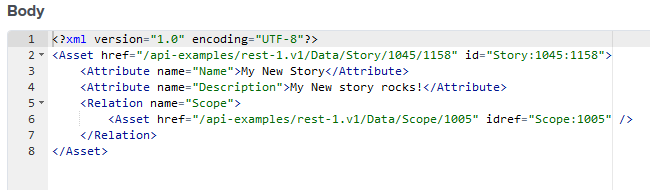
Step 2: Use the OID to query the Story.
Enter this into the URL boxrest-1.v1/Data/Story/1045and click Send.
Observe a similar results to the output below.
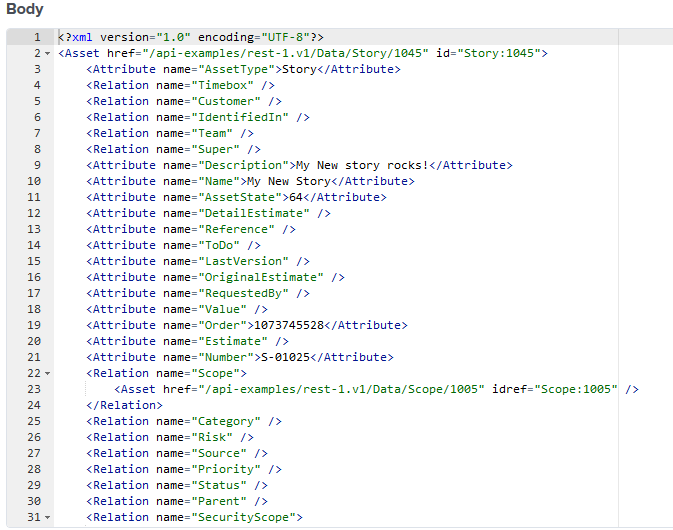
Step 3: Query with Specific Attributes
Instead of retrieving all default attributes, use the sel parameter to select only what you need.
Enter this into the URL box:
rest-1.v1/Data/Story/1045?sel=Name,Number,Estimate,Description
Click Send.
This returns only the selected attributes (Name, Number, Estimate, Description) in the response.
Use the where Parameter
You can also filter results. For example, to query stories in a specific scope:
rest-1.v1/Data/Story?sel=Name,Estimate&where=Scope='Scope:1005'
Learn more: Queries comparison
Step 4: Alternative Approach Using query.v1
The query.v1 endpoint offers a more readable way to write queries using YAML or JSON format.
query.v1 Advantages
query.v1 has several advantages over rest-1.v1:
- Query syntax is more readable (YAML or JSON)
- Returns JSON by default (XML is also supported based on request headers)
- Supports multiple queries in one request
- Works better for complex, nested queries
Example with query.v1
Change the request type to POST, enter this URL:
query.v1
In the request body, enter this YAML:
from: Story
select:
- Name
- Number
- Estimate
where:
ID: Story:1045
Click Send.
The response is in JSON format:
[
[
{
"_oid": "Story:1045",
"Name": "My New Story",
"Number": "S-01045",
"Estimate": "5"
}
]
]
Learn more: Tour of query.v1 | query.v1 endpoint
Review
-
Queried a Story using its OID with the rest-1.v1 endpoint.
-
Understood the difference between OID (Story:1045) and OID with Moment (Story:1045:1058).
-
Used the
selparameter to select specific attributes. -
Used the
whereparameter to filter results. -
Learned about the query.v1 endpoint as an alternative approach.
Next Steps: Continue to Exercise 6: Update your Story
Quiz
Question 1: What is the difference between Story:1045 and Story:1045:1058?
- A) They are identical
- B) The second includes a Moment number for historical data
- C) The first is invalid syntax
- D) They refer to different stories
Question 2: Which parameter selects specific attributes in rest-1.v1?
- A) select
- B) sel
- C) attributes
- D) fields
Question 3: What is an advantage of using query.v1 over rest-1.v1?
- A) It returns XML
- B) It requires no authentication
- C) It supports more readable syntax
- D) It's faster for simple queries
Answers: 1-B, 2-A+B, 3-C