Webhook task
Automatic tasks often need to interact with an external system through a REST interface. Although you could use a Jython Script task to send an HTTP query and parse the response, the Webhook task type is a simpler option.
To configure a Webhook, specify the URL to call and the details of the request including HTTP method, request body, and authentication. The task will perform the query, parse the response, and optionally extract results and include them in release variables.
Webhooks are available in XML and JSON, depending on the format of the HTTP response. Each format has its own way of extracting a result from the response:
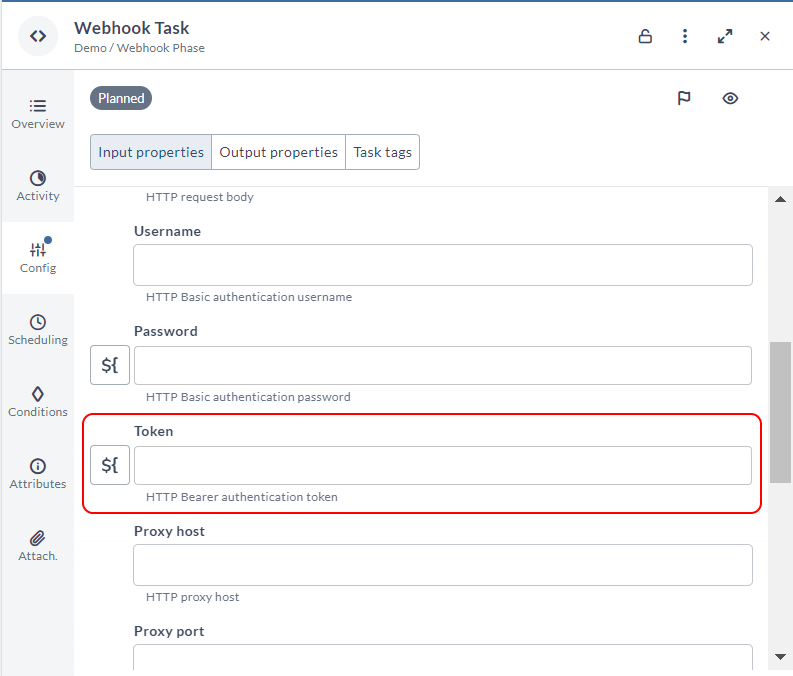
For more security and flexibility, Webhook tasks now have a new Token field to support HTTP bearer authentication token. It is added for both JSON and XML Webhook tasks.
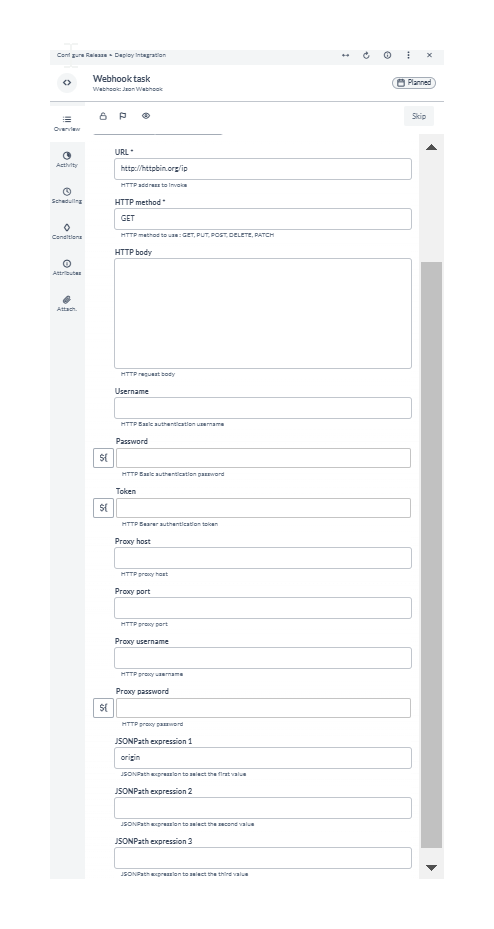
This example is based on HttpBin, a free service to test REST clients. It uses the /ip endpoint, which returns the IP of the caller in a JSON response with the following structure:
{
"origin": "xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx"
}
This is the configuration of the task in Release:
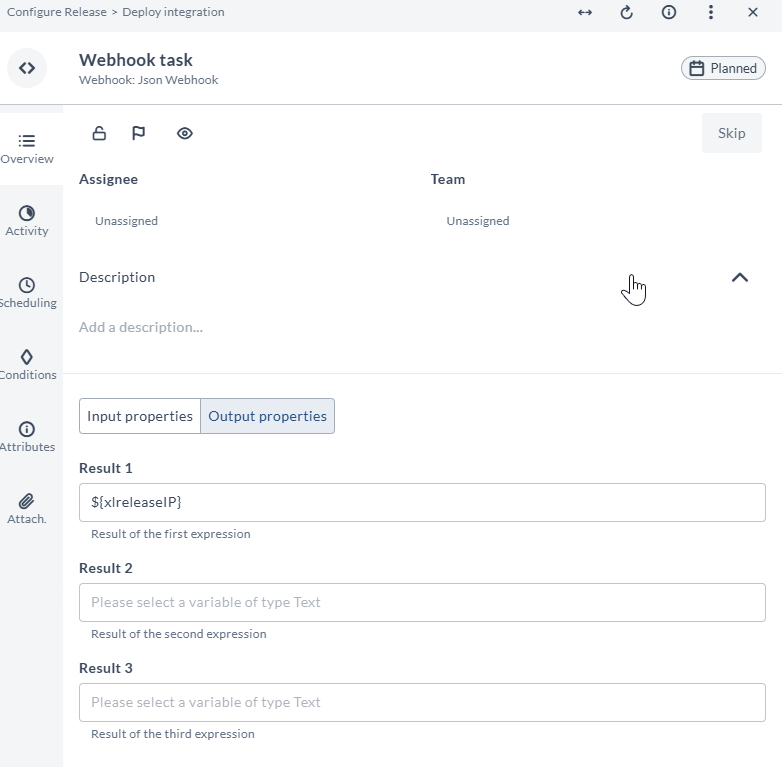
After the task is complete, the origin field is extracted from the response and stored in the ${xlreleaseIP} release variable, where it can be used by other tasks.
In the release flow editor, Webhook tasks have a blue border.