Installing Release Using Kubernetes Operator
This section describes how to install the Release application on various Kubernetes platforms.
Supported Platforms
- Amazon EKS
- Azure Kubernetes Service
- Kubernetes On-premise
- OpenShift on AWS
- OpenShift on VMWare vSphere
- GCP GKE
Intended Audience
This guide is intended for administrators with cluster administrator credentials who are responsible for application deployment.
Before You Begin
The following are the prerequisites required to install Deploy using Kubernetes Operator installer:
- Docker version 17.03 or later
- The
kubectlcommand-line tool - Access to a Kubernetes cluster version 1.19 or later
- Kubernetes cluster configuration
- If you are installing Release on OpenShift cluster, you will need:
- The OpenShift oc tool
- Access to an OpenShift cluster version 4.5 or later
Keycloak as the Default Authentication Manager for Release
From Release 22.1, Keycloak is the default authentication manager for Release. This is defined by the spec.keycloak.install parameter that is set to true by default in the dairelease_cr.yaml file. If you want to disable Keycloak as the default authentication manager for Digitial.ai Release, set the spec.keycloak.install parameter to false. After you disable the Keycloak authentication, the default login credentials (admin/admin) will be applicable when you log in to the Digital.ai Release interface. For more information about how to configure Keycloak Configuration for Kubernetes Operator-based Installer for Release, see Keycloak Configuration for Kubernetes Operator Installer.
Installing Release on Amazon EKS
Follow the steps below to install Release on Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS).
Step 1—Create a folder for installation tasks
Create a folder on your workstation from where you will execute the installation tasks, for example, ReleaseInstallation.
Step 2—Download the Operator ZIP
- Download the release-operator-aws-eks-22.1.zip file from the Release Software Distribution site.
- Extract the ZIP file to the ReleaseInstallation folder.
Step 3—Update the Amazon EKS cluster information
To deploy the Release application on the Kubernetes cluster, update the infrastructure.yaml file parameters (Infrastructure File Parameters) in ReleaseInstallation folder with the parameters corresponding to the kubeconfig file (Amazon EKS Kubernetes Cluster Configuration File Parameters) as described in the table below. You can find the Kubernetes cluster information in the default location ~/.kube/config. Ensure the location of the kubeconfig configuration file is your home directory.
Note: The deployment will not proceed further if the infrastructure.yaml is updated with wrong details.
| Infrastructure File Parameters | Amazon EKS Kubernetes Cluster Configuration File Parameters | Steps to Follow |
|---|---|---|
| apiServerURL | server | Enter the server details of the cluster. |
| caCert | certificate-authority-data | Before updating the parameter value, decode to base64 format. |
| regionName | Region | Enter the AWS Region. |
| clusterName | cluster-name | Enter the name of the cluster. |
| accessKey | NA | This parameter defines the access key that allows the Identity and Access (IAM) user to access the AWS using CLI. Note: This parameter is not available in the Kubernetes configuration file. |
| accessSecret | NA | This parameter defines the secret password that the IAM user must enter to access the AWS using. Note: This parameter is not available in the Kubernetes configuration file. |
| isAssumeRole | NA | This parameter, when set to true, enables IAM user access to the cluster by using the AWS assumeRole. Note: When this parameter is set to true, the following fields—accountId, roleName, roleArn, durationSeconds, sessionToken—must be defined. |
| accountId* | NA | Enter the AWS account Id. |
| roleName* | NA | Enter the AWS IAM assume role name. |
| roleArn* | NA | Enter the roleArn of the IAM user role. Note: This field is required when roleArn has different principal policy than arn:aws:iam::'accountid':role/rolename |
| durationSeconds* | NA | Enter the duration in seconds of the role session(900 to max session duration). |
| sessionToken* | NA | Enter the temporary session token of the IAM user role. |
* These marked fields are required only when the parameter isAssumeRole is set to true.
Step 4—Convert license and repository keystore files to base64 format
-
Run the following command to get the storage class list:
kubectl get sc -
Run the keytool command below to generate the
RepositoryKeystore:keytool -genseckey {-alias alias} {-keyalg keyalg} {-keysize keysize} [-keypass keypass] {-storetype storetype} {-keystore keystore} [-storepass storepass]Example
keytool -genseckey -alias deployit-passsword-key -keyalg aes -keysize 128 -keypass deployit -keystore /tmp/repository-keystore.jceks -storetype jceks -storepass test123 -
Convert the Release license and the repository keystore files to the base64 format:
- To convert the xlrLicense into base64 format, run:
cat <License.lic> | base64 -w 0- To convert
RepositoryKeystoreto base64 format, run:
cat <repository-keystore.jceks> | base64 -w 0
The above commands are for Linux-based systems. For Windows, there is no built-in command to directly perform Base64 encoding and decoding. However, you can use the built-in command certutil -encode/-decode to indirectly perform Base64 encoding and decoding.
Step 5—Update the default Custom Resource Definitions
- Update
dairelease_cr.yamlfile with the mandatory parameters as described in the following table:
For deployments on test environments, you can use most of the parameters with their default values in the dairelease_cr.yaml file.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| KeystorePassphrase | The passphrase for the RepositoryKeystore. |
| Persistence.StorageClass | The storage class that must be defined as Amazon EKS cluster |
| RepositoryKeystore | Convert the repository keystore file for Digital.ai Release to the base64 format. |
| ingress.hosts | DNS name for accessing UI of Digital.ai Release. |
| postgresql.persistence.storageClass | The storage Class that needs to be defined as PostgreSQL |
| rabbitmq.persistence.storageClass | The storage class that must be defined as RabbitMQ |
| xlrLicense | Release license |
For deployments on production environments, you must configure all the parameters required for your Amazon EKS production setup, in the dairelease_cr.yaml file. The table in the next step lists these parameters and their default values, which can be overridden as per your requirements and workload.
To configure the Keycloak parameters for OIDC authentication, see Keycloak Configuration for Kubernetes Operator Installer.
- Update the default parameters as described in the following table:
The following table describes the default parameters in the Digital.ai dairelease_cr.yaml file. If you want to use your own database and messaging queue, refer to your external database and message queue documentation, and update the dairelease_cr.yaml file. For information on how to configure SSL/TLS with Digital.ai Release, see Configuring SSL/TLS.
| Parameter | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| K8sSetup.Platform | The platform on which you install the chart. Allowed values are PlainK8s and AWSEKS | AWSEKS |
| ImageRepository | Image name | xebialabs/xl-release |
| ImageTag | Image tag | 10.2 |
| ImagePullPolicy | Image pull policy, Defaults to Always if image tag is latest, set to IfNotPresent | Always |
| ImagePullSecret | Specify docker-registry secret names. Secrets must be manually created in the namespace | None |
| haproxy-ingress.install | Install haproxy subchart. If you have haproxy already installed, set install to false | FALSE |
| haproxy-ingress.controller.kind | Type of deployment, DaemonSet or Deployment | Release |
| haproxy-ingress.controller.service.type | Kubernetes Service type for haproxy. It can be changed to LoadBalancer or NodePort | LoadBalancer |
| ingress.Enabled | Exposes HTTP and HTTPS routes from outside the cluster to services within the cluster | TRUE |
| ingress.annotations | Annotations for Ingress controller | kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/affinity: cookie nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-connect-timeout: "60" nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-read-timeout: "60" nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-send-timeout: "60" nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/rewrite-target: /$2 nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/session-cookie-name: SESSION_XLR nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-redirect: "false" |
| ingress.path | You can route an Ingress to different Services based on the path | /xl-release(/|$)(.*) |
| ingress.hosts | DNS name for accessing ui of Digital.ai Deploy | None |
| AdminPassword | Admin password for xl-release | admin |
| xlrLicense | Convert xl-release.lic files content to base64 | None |
| RepositoryKeystore | Convert repository-keystore.jceks files content to base64 | None |
| KeystorePassphrase | Passphrase for repository-keystore.jceks file | None |
| Resources | CPU/Memory resource requests/limits. User can change the parameter accordingly. | None |
| postgresql.install | postgresql chart with single instance. Install postgresql chart. If you have an existing database deployment, set install to false. | TRUE |
| postgresql.postgresqlUsername | PostgreSQL user (creates a non-admin user when postgresqlUsername is not specified as postgres) | postgres |
| postgresql.postgresqlPassword | PostgreSQL user password | postgres |
| postgresql.postgresqlExtendedConf.listenAddresses | Specifies the TCP/IP address(es) on which the server is to listen for connections from client applications | * |
| postgresql.postgresqlExtendedConf.maxConnections | Maximum total connections | 500 |
| postgresql.initdbScriptsSecret | Secret with initdb scripts contain sensitive information Note: This parameter can be used with initdbScriptsConfigMap or initdbScripts. The value is evaluated as a template. | postgresql-init-sql-xlr |
| postgresql.service.port | PostgreSQL port | 5432 |
| postgresql.persistence.enabled | Enable persistence using PVC | TRUE |
| postgresql.persistence.size | PVC Storage Request for PostgreSQL volume | 50Gi |
| postgresql.persistence.existingClaim | Provide an existing PersistentVolumeClaim, the value is evaluated as a template. | None |
| postgresql.resources.requests | CPU/Memory resource requests | requests: memory: 250m memory: cpu: 256m |
| postgresql.nodeSelector | Node labels for pod assignment | {} |
| postgresql.affinity | Affinity labels for pod assignment | {} |
| postgresql.tolerations | Toleration labels for pod assignment | [] |
| UseExistingDB.Enabled | If you want to use an existing database, change postgresql.install to false. | FALSE |
| UseExistingDB.XL_DB_URL | Database URL for xl-deploy | None |
| UseExistingDB.XL_DB_USERNAME | Database User for xl-deploy | None |
| UseExistingDB.XL_DB_PASSWORD | Database Password for xl-deploy | None |
| rabbitmq.install | Install rabbitmq chart. If you have an existing message queue deployment, set install to false. | TRUE |
| rabbitmq.extraPlugins | Additional plugins to add to the default configmap | rabbitmq_jms_topic_exchange |
| rabbitmq.replicaCount | Number of replica | 3 |
| rabbitmq.rbac.create | If true, create and use RBAC resources | TRUE |
| rabbitmq.service.type | Type of service to create | ClusterIP |
| UseExistingMQ.Enabled | If you want to use an existing Message Queue, change rabbitmq-ha.install to false | FALSE |
| UseExistingMQ.XLR_TASK_QUEUE_USERNAME | Username for xl-deploy task queue | None |
| UseExistingMQ.XLR_TASK_QUEUE_PASSWORD | Password for xl-deploy task queue | None |
| UseExistingMQ.XLR_TASK_QUEUE_URL | URL for xl-deploy task queue | None |
| UseExistingMQ.XLR_TASK_QUEUE_DRIVER_CLASS_NAME | Driver Class Name for xl-deploy task queue | None |
| HealthProbes | Would you like a HealthProbes to be enabled | TRUE |
| HealthProbesLivenessTimeout | Delay before liveness probe is initiated | 60 |
| HealthProbesReadinessTimeout | Delay before readiness probe is initiated | 60 |
| HealthProbeFailureThreshold | Minimum consecutive failures for the probe to be considered failed after having succeeded | 12 |
| HealthPeriodScans | How often to perform the probe | 10 |
| nodeSelector | Node labels for pod assignment | {} |
| tolerations | Toleration labels for pod assignment | [] |
| Persistence.Enabled | Enable persistence using PVC | TRUE |
| Persistence.StorageClass | PVC Storage Class for volume | None |
| Persistence.Annotations | Annotations for the PVC | {} |
| Persistence.AccessMode | PVC Access Mode for volume | ReadWriteOnce |
Step 6—Download and set up the XL CLI
-
Download the XL-CLI binaries.
wget https://dist.xebialabs.com/public/xl-cli/$VERSION/linux-amd64/xlNote: For
$VERSION, substitute with the version that matches your product version in the public folder. -
Enable
executepermissions.chmod +x xl -
Copy the XL binary in a directory that is on your
PATH.echo $PATHExample
cp xl /usr/local/bin -
Verify the release version.
xl version
Step 7—Set up the local Digital.ai Deploy Container instance
-
Run the following command to download and start the local Digital.ai Deploy instance:
docker run -d -e "ADMIN_PASSWORD=admin" -e "ACCEPT_EULA=Y" -p 4516:4516 --name xld xebialabs/xl-deploy:10.2 -
To access the Deploy interface, go to:
http://<host IP address>:4516/
Step 8—Activate the deployment process
Go to the root of the extracted file and run the following command:
xl apply -v -f digital-ai.yaml
Step 9—Verify the deployment status
- Check the deployment job completion using XL CLI.
The deployment job starts the execution of various tasks as defined in the digital-ai.yaml file in a sequential manner. If you encounter an execution error while running the scripts, the system displays error messages. The average time to complete the job is around 10 minutes.
Note: The running time depends on the environment.
To troubleshoot runtime errors, see Troubleshooting Operator Based Installer.
Step 10—Verify if the deployment was successful
To verify the deployment succeeded, do one of the following:
-
Open the local Deploy application, go to the Explorer tab, and from Library, click Monitoring > Deployment tasks
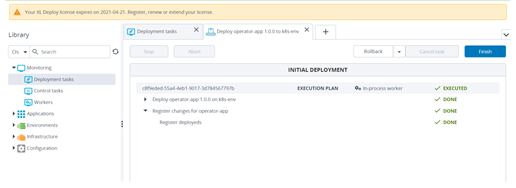
-
Run the following command in a terminal or command prompt:
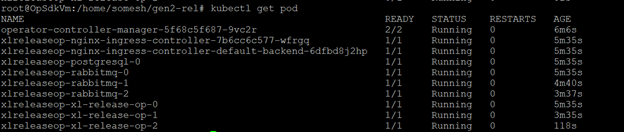
Step 11—Perform sanity checks
Open the newly installed Release application and perform the required sanity checks.
Post Installation Steps
After the installation, you must configure the user permissions for OIDC authentication using Keycloak. For more information about how to configure the user permissions, see Keycloak Configuration for Kubernetes Operator Installer.
Installing Release on Azure Kubernetes Service
Follow the steps below to install Release on Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS).
Step 1—Create a folder for installation tasks
Create a folder on your workstation from where you will execute the installation tasks, for example, ReleaseInstallation.
Step 2—Download the Operator ZIP
- Download the release-operator-azure-aks-22.1.zip file from the Deploy/Release Software Distribution site.
- Extract the ZIP file to the ReleaseInstallation folder.
Step 3—Update the Azure AKS Cluster Information
To deploy the Release application on the Kubernetes cluster, update the Infrastructure file parameters (infrastructure.yaml) in the location where you extracted the ZIP file with the parameters corresponding to the Azure AKS Kubernetes Cluster Configuration (kubeconfig) file as described in the table. You can find the Kubernetes cluster information in the default location ~/.kube/config.
Note: The deployment will not proceed further if the infrastructure.yaml is updated with wrong details.
| Infrastructure File Parameters | Azure AKS Kubernetes Cluster Configuration File Parameters | Steps to Follow |
|---|---|---|
| apiServerURL | server | Enter the server details of the cluster. |
| caCert | certificate-authority-data | Before updating the parameter value, decode to base 64 format. |
| tlsCert | client-certificate-data | Before updating the parameter value, decode to base 64 format. |
| tlsPrivateKey | client-key-data | Before updating the parameter value, decode to base 64 format. |
Step 4—Convert license and repository keystore files to base64 format
-
Run the following command to get the storage class list:
kubectl get sc -
Run the keytool command below to generate the
RepositoryKeystore:keytool -genseckey {-alias alias} {-keyalg keyalg} {-keysize keysize} [-keypass keypass] {-storetype storetype} {-keystore keystore} [-storepass storepass]Example
keytool -genseckey -alias deployit-passsword-key -keyalg aes -keysize 128 -keypass deployit -keystore /tmp/repository-keystore.jceks -storetype jceks -storepass test123 -
Convert the Release license and the repository keystore files to the base64 format:
- To convert the xlrLicense into base64 format, run:
cat <License.lic> | base64 -w 0- To convert
RepositoryKeystoreto base64 format, run:
cat <repository-keystore.jceks> | base64 -w 0
The above commands are for Linux-based systems. For Windows, there is no built-in command to directly perform Base64 encoding and decoding. However, you can use the built-in command certutil -encode/-decode to indirectly perform Base64 encoding and decoding.
Step 5—Update the default Digitial.ai Release Custom Resource Definitions.
- Update the mandatory parameters as described in the following table:
For deployments on test environments, you can use most of the parameters with their default values in the dairelease_cr.yaml file.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| KeystorePassphrase | The passphrase for the RepositoryKeystore. |
| Persistence.StorageClass | The storage class that must be defined as Azure AKS cluster. |
| RepositoryKeystore | Convert the repository keystore file for Digital.ai Release to the base64 format. |
| ingress.hosts | DNS name for accessing UI of Digital.ai Release. |
| postgresql.persistence.storageClass | Storage Class to be defined as PostgreSQL. |
| rabbitmq.persistence.storageClass | Storage Class to be defined as RabbitMQ. |
| xlrLicense | Release license |
For deployments on production environments, you must configure all the parameters required for your Azure AKS AKS production setup in the dairelease_cr.yaml file. The table in [Step 5.2] lists these parameters and their default values, which can be overridden as per your requirements and workload.
To configure the Keycloak parameters for OIDC authentication, see Keycloak Configuration for Kubernetes Operator Installer.
- Update the default parameters as described in the following table:
The following table describes the default parameters in the Digital.ai dairelease_cr.yaml file.
| Parameter | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| K8sSetup.Platform | The platform on which you install the chart. Allowed values are PlainK8s and AzureAKS | AWSEKS |
| replicaCount | Number of replicas | 3 |
| ImageRepository | Image name | xebialabs/xl-release |
| ImageTag | Image tag | 10.2 |
| ImagePullPolicy | Image pull policy, Defaults to Always if image tag is ’latest’,set to IfNotPresent | Always |
| ImagePullSecret | Specifies docker-registry secret names. Secrets must be manually created in the namespace | NA |
| haproxy-ingress.install | Install haproxy subchart. If you have haproxy already installed, set install to false | TRUE |
| haproxy-ingress.controller.kind | Type of deployment, DaemonSet or Deployment | DaemonSet |
| haproxy-ingress.controller.service.type | Kubernetes Service type for haproxy. It can be changed to LoadBalancer or NodePort | NodePort |
| ingress.Enabled | Exposes HTTP and HTTPS routes from outside the cluster to services within the cluster | TRUE |
| ingress.annotations | Annotations for ingress controller | ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-redirect:falsekubernetes.io/ingress.class: haproxyingress.kubernetes.io/rewrite-target: /ingress.kubernetes.io/affinity: cookieingress.kubernetes.io/session-cookie-name: JSESSIONIDingress.kubernetes.io/session-cookie-strategy: prefixingress.kubernetes.io/config-backend: option httpchk GET /ha/health HTTP/1.0 |
| ingress.path | You can route an Ingress to different Services based on the path | /xl-release/ |
| ingress.tls.secretName | Secret file that contains the tls private key and certificate | example-secretsName |
| ingress.tls.hosts | DNS name for accessing ui of Digital.ai Release using tls. | example.com |
| AdminPassword | Admin password for xl-release | If user does not provide password, random 10 character alphanumeric string will be generated |
| resources | CPU/Memory resource requests/limits. User can change the parameter accordingly | NA |
| postgresql.install | postgresql chart with single instance. Install postgresql chart. If you have an existing database deployment, set install to false. | TRUE |
| postgresql.postgresqlUsername | PostgreSQL user (creates a non-admin user when postgresqlUsername is not postgres) | postgres |
| postgresql.postgresqlPassword | PostgreSQL user password | random 10 character alphanumeric string |
| postgresql.replication.enabled | Enable replication | FALSE |
| postgresql.postgresqlExtendedConf.listenAddresses | Specifies the TCP/IP address(es) on which the server is to listen for connections from client applications | * |
| postgresql.postgresqlExtendedConf.maxConnections | Maximum total connections | 500 |
| postgresql.initdbScriptsSecret | Secret with initdb scripts contain sensitive informationNote: This parameter can be used with initdbScriptsConfigMap or initdbScripts. The value is evaluated as a template. | postgresql-init-sql-xlr |
| postgresql.service.port | PostgreSQL port | 5432 |
| postgresql.persistence.enabled | Enable persistence using PVC | TRUE |
| postgresql.persistence.size | PVC Storage Request for PostgreSQL volume | 50Gi |
| postgresql.persistence.existingClaim | Provide an existing PersistentVolumeClaim, the value is evaluated as a template. | NA |
| postgresql.resources.requests | CPU/Memory resource requests | requests: memory: 1Gi memory: cpu: 250m |
| postgresql.resources.limits | Limits | limits: memory: 2Gi, limits: cpu: 1 |
| postgresql.nodeSelector | Node labels for pod assignment | {} |
| postgresql.affinity | Affinity labels for pod assignment | {} |
| postgresql.tolerations | Toleration labels for pod assignment | [] |
| UseExistingDB.Enabled | If you want to use an existing database, change postgresql.install to false. | FALSE |
| UseExistingDB.XLR_DB_URL | Database URL for xl-release | NA |
| UseExistingDB.XLR_DB_USERNAME | Database User for xl-release | NA |
| UseExistingDB.XLR_DB_PASSWORD | Database Password for xl- | NA |
| UseExistingDB.XLR_REPORT_DB_URL | Database URL for xlr_report | NA |
| UseExistingDB.XLR_REPORT_DB_USER | Database User for xlr_report | NA |
| UseExistingDB.XLR_REPORT_DB_PASS | Database Password for xlr_report | NA |
| rabbitmq.install | Install rabbitmq chart. If you have an existing message queue deployment, set install to false. | TRUE |
| rabbitmq.rabbitmqUsername | RabbitMQ application username | guest |
| rabbitmq.rabbitmqPassword | RabbitMQ application password | random 24 character long alphanumeric string |
| rabbitmq.rabbitmqErlangCookie | Erlang cookie | RELEASERABBITMQCLUSTER |
| rabbitmq.rabbitmqMemoryHighWatermark | Memory high watermark | 500MB |
| rabbitmq.rabbitmqNodePort | Node port | 5672 |
| rabbitmq.extraPlugins | Additional plugins to add to the default configmap | rabbitmq_shovel,rabbitmq_shovel_management,rabbitmq_federation,rabbitmq_federation_management,rabbitmq_amqp1_0,rabbitmq_management |
| rabbitmq.replicaCount | Number of replicas | 3 |
| rabbitmq.rbac.create | If true, create & use RBAC resources | TRUE |
| rabbitmq.service.type | Type of service to create | ClusterIP |
| rabbitmq.persistentVolume.enabled | If set to True, persistent volume claims are created | TRUE |
| rabbitmq.persistentVolume.size | Persistent volume size | 20Gi |
| rabbitmq.persistentVolume.annotations | Persistent volume annotations | {} |
| rabbitmq.persistentVolume.resources | Persistent Volume resources | {} |
| rabbitmq.persistentVolume.requests | CPU/Memory resource requests | requests: memory: 250Mi memory: cpu: 100m |
| rabbitmq.persistentVolume.limits | Limits | limits: memory: 550Mi, limits: cpu: 200m |
| rabbitmq.definitions.policies | HA policies to add to definitions.json | {”name”: ”ha-all”,”pattern”: .*,vhost:/,definition: {ha-mode: all,ha-sync-mode:automatic, ha-sync-batch-size`: 1}} |
| rabbitmq-ha.definitions.globalParameters | Pre-configured global parameters | {name:cluster_name,value: ``} |
| rabbitmq-ha.prometheus.operator.enabled | Enabling Prometheus Operator | FALSE |
| UseExistingMQ.Enabled | If you want to use an existing Message Queue change rabbitmq-ha.instal to false | FALSE |
| UseExistingMQ.XLR_T\ASK_QUEUE_USERNAME | Username for xl-task queue | NA |
| UseExistingMQ.XLR_TASK_QUEUE_PASSWORD | Password for xl-task queue | NA |
| UseExistingMQ.XLR_TASK_QUEUE_NAME | Name for xl-task queue | NA |
| HealthProbes | Would you like a HealthProbes to be enabled? | TRUE |
| HealthProbesLivenessTimeout | Delay before liveness probe is initiated | 90 |
| HealthProbesReadinessTimeout | Delay before readiness probe is initiated | 90 |
| HealthProbeFailureThreshold | Minimum consecutive failures for the probe to be considered failed after having succeeded | 12 |
| HealthPeriodScans | How often to perform the probe | 10 |
| nodeSelector | Node labels for pod assignment | {} |
| tolerations | Toleration labels for pod assignment | [] |
| affinity | Affinity labels for pod assignment | {} |
| Persistence.Enabled | Enable persistence using PVC | true |
| Persistence.Annotations | Annotations for the PVC | {} |
| Persistence.AccessMode | PVC Access Mode for volume | ReadWriteOnce |
| Persistence.Size | XLR PVC Storage Request for volume. For production grade setup, size must be changed | 5Gi |
Step 6—Download and set up the XL CLI
-
Download the XL-CLI binaries.
wget https://dist.xebialabs.com/public/xl-cli/$VERSION/linux-amd64/xlNote: For
$VERSION, substitute with the version that matches your product version in the public folder. -
Enable
executepermissions.chmod +x xl -
Copy the XL binary in a directory that is on your
PATH.echo $PATHExample
cp xl /usr/local/bin -
Verify the release version.
xl version
Step 7—Set up the Digital.ai Deploy container instance
-
Run the following command to download and start the Digital.ai Deploy instance:
docker run -d -e "ADMIN_PASSWORD=admin" -e "ACCEPT_EULA=Y" -p 4516:4516 --name xld xebialabs/xl-deploy:10.2 -
To access the Deploy interface, go to:
http://<host IP address>:4516/
Step 8—Activate the deployment process
Go to the root of the extracted file and run the following command:
xl apply -v -f digital-ai.yaml
Step 9—Verify the deployment status
-
Check the deployment job completion using XL CLI.
The deployment job starts the execution of various tasks as defined in thedigital-ai.yamlfile in a sequential manner. If you encounter an execution error while running the scripts, the system displays error messages. The average time to complete the job is around 10 minutes.Note: The running time depends on the environment.
To troubleshoot runtime errors, see Troubleshooting Operator Based Installer.
Step 10—Verify if the deployment was successful
To verify the deployment succeeded, do one of the following:
- Open the local Deploy application, go to the Explorer tab, and from Library, click Monitoring > Deployment tasks

- Run the following command in a terminal or command prompt:

Step 11—Perform sanity checks
Open the Release application and perform the required sanity checks.
Post Installation Steps
After the installation, you must configure the user permissions for OIDC authentication using Keycloak. For more information about how to configure the user permissions, see Keycloak Configuration for Kubernetes Operator Installer.
Installing Release on Kubernetes On-premise Platform
Follow the steps below to install Release on Kubernetes On-premise platform.
Step 1—Create a folder for installation tasks
Create a folder on your workstation from where you will execute the installation tasks, for example, ReleaseInstallation.
Step 2—Download the Operator ZIP
- Download the release-operator-onprem-22.1.zip file from the Deploy/Release Software Distribution site.
- Extract the ZIP file to the ReleaseInstallation folder.
Step 3—Update the Kubernetes on-premise cluster information
To deploy the Release application on the Kubernetes cluster, update the Infrastructure file parameters (infrastructure.yaml) in the location where you extracted the ZIP file with the parameters corresponding to the Kubernetes On-premise Cluster Configuration (kubeconfig) file as described in the table. You can find the Kubernetes cluster information in the default location ~/.kube/config. Ensure the location of the kubeconfig configuration file is your home directory.
Note: The deployment will not proceed further if the infrastructure.yaml is updated with wrong details.
| Infrastructure File Parameters | Kubernetes On-premise Cluster Configuration File Parameters | Parameter Value |
|---|---|---|
| apiServerURL | server | Enter the server parameter value. |
| caCert | certificate-authority-data | Enter the server details of the cluster. |
| tlsCert | client-certificate-data | Before updating the parameter value, decode to base64 format. |
| tlsPrivateKey | client-key-data | Before updating the parameter value, decode to base64 format. |
Step 4—Convert license and repository keystore files to base64 format
Update the Values file with the license and keystore details.
-
Run the following command to get the storage class list:
kubectl get sc -
Run the keytool command below to generate the
RepositoryKeystore:keytool -genseckey {-alias alias} {-keyalg keyalg} {-keysize keysize} [-keypass keypass] {-storetype storetype} {-keystore keystore} [-storepass storepass]Example
keytool -genseckey -alias deployit-passsword-key -keyalg aes -keysize 128 -keypass deployit -keystore /tmp/repository-keystore.jceks -storetype jceks -storepass test123 -
Convert the Release license and the repository keystore files to the base 64 format.
- To convert the xlrLicense into base 64 format, run:
cat <License.lic> | base64 -w 0 - To convert
RepositoryKeystoreto base64 format, run:cat <keystore.jks> | base64 -w 0
- To convert the xlrLicense into base 64 format, run:
The above commands are for Linux-based systems. For Windows, there is no built-in command to directly perform Base64 encoding and decoding. But you can use the built-in command certutil -encode/-decode to indirectly perform Base64 encoding and decoding.
Step 5—Update the default Digitial.ai Release Custom Resource Definitions.
- Update
dairelease_crfile in the\digitalai-release\kubernetespath of the extracted zip file. - Update the mandatory parameters as described in the following table:
For deployments on test environments, you can use most of the parameters with their default values in the dairelease_cr file.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| K8sSetup.Platform | Platform on which to install the chart. For the Kubernetes on-premise cluster, you must set the value to PlainK8s |
| ingress.hosts | DNS name for accessing UI of Digital.ai Release. |
| xlrLicense | Convert the Digital.ai Release Repository Keystore file to the base64 format. |
| RepositoryKeystore | Convert the Digital.ai Release Repository Keystore file to the base64 format. |
| KeystorePassphrase | The passphrase for the RepositoryKeystore. |
| postgresql.persistence.storageClass | Storage Class to be defined for PostgreSQL |
| rabbitmq.persistence.storageClass | Storage Class to be defined for RabbitMQ |
| Persistence.StorageClass | The storage class that must be defined as Kubernetes On-premise cluster |
For deployments on production environments, you must configure all the parameters required for your Kubernetes On-premise production setup, in the dairelease_cr.yaml file. The table in lists these parameters and their default values, which can be overridden as per your requirements and workload. You must override the default parameters, and specify the parameter values with those from the custom resource file.
To configure the Keycloak parameters for OIDC authentication, see Keycloak Configuration for Kubernetes Operator Installer.
- Update the default parameters as described in the following table:
The following table describes the default parameters in the Digital.ai dairelease_cr.yaml file. If you want to use your own database and messaging queue, refer to respective external database and messaging queue documentation, and update the dairelease_cr.yaml file.
| Parameter | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| K8sSetup.Platform | Platform on which to install the chart. Allowed values are PlainK8s and AWSEKS | PlainK8s |
| XldMasterCount | Number of master replicas | 3 |
| XldWorkerCount | Number of worker replicas | 3 |
| ImageRepository | Image name | Truncated |
| ImageTag | Image tag | 10.1 |
| ImagePullPolicy | Image pull policy, Defaults to 'Always' if image tag is 'latest',set to 'IfNotPresent' | Always |
| ImagePullSecret | Specify docker-registry secret names. Secrets must be manually created in the namespace | nil |
| haproxy-ingress.install | Install haproxy subchart. If you have haproxy already installed, set 'install' to 'false' | true |
| haproxy-ingress.controller.kind | Type of deployment, DaemonSet or Deployment | DaemonSet |
| haproxy-ingress.controller.service.type | Kubernetes Service type for haproxy. It can be changed to LoadBalancer or NodePort | NodePort |
| nginx-ingress-controller.install | Install nginx subchart to false, as we are using haproxy as a ingress controller | false (for HAProxy) |
| nginx-ingress.controller.install | Install nginx subchart. If you have nginx already installed, set 'install' to 'false' | true |
| nginx-ingress.controller.image.pullSecrets | pullSecrets name for nginx ingress controller | myRegistryKeySecretName |
| nginx-ingress.controller.replicaCount | Number of replica | 1 |
| nginx-ingress.controller.service.type | Kubernetes Service type for nginx. It can be changed to LoadBalancer or NodePort | NodePort |
| haproxy-ingress.install | Install haproxy subchart to false as we are using nginx as a ingress controller | false (for NGINX) |
| ingress.Enabled | Exposes HTTP and HTTPS routes from outside the cluster to services within the cluster | true |
| ingress.annotations | Annotations for ingress controller | ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-redirect: "false"kubernetes.io/ingress.class: haproxyingress.kubernetes.io/rewrite-target: /ingress.kubernetes.io/affinity: cookieingress.kubernetes.io/session-cookie-name: JSESSIONIDingress.kubernetes.io/session-cookie-strategy: prefixingress.kubernetes.io/config-backend: |
| ingress.path | You can route an Ingress to different Services based on the path | /xl-release/ |
| ingress.hosts | DNS name for accessing ui of Digital.ai Release | example.com |
| ingress.tls.secretName | Secret file which holds the tls private key and certificate | example-secretsName |
| ingress.tls.hosts | DNS name for accessing ui of Digital.ai Release using tls | example.com |
| AdminPassword | Admin password for xl-release | If user does not provide password, random 10 character alphanumeric string will be generated |
| xldLicense | Convert xl-release.lic files content to base64 | nil |
| RepositoryKeystore | Convert keystore.jks files content to base64 | nil |
| KeystorePassphrase | Passphrase for keystore.jks file | nil |
| resources | CPU/Memory resource requests/limits. User can change the parameter accordingly | nil |
| postgresql.install | postgresql chart with single instance. Install postgresql chart. If you have an existing database deployment, set 'install' to 'false'. | true |
| postgresql.postgresqlUsername | PostgreSQL user (creates a non-admin user when postgresqlUsername is not postgres) | postgres |
| postgresql.postgresqlPassword | PostgreSQL user password | random 10 character alphanumeric string |
| postgresql.postgresqlExtendedConf.listenAddresses | Specifies the TCP/IP address(es) on which the server is to listen for connections from client applications | '*' |
| postgresql.postgresqlExtendedConf.maxConnections | Maximum total connections | 500 |
| postgresql.initdbScriptsSecret | Secret with initdb scripts that contain sensitive information (Note: can be used with initdbScriptsConfigMap or initdbScripts). The value is evaluated as a template. | postgresql-init-sql-xld |
| postgresql.service.port | PostgreSQL port | 5432 |
| postgresql.persistence.enabled | Enable persistence using PVC | true |
| postgresql.persistence.size | PVC Storage Request for PostgreSQL volume | 50Gi |
| postgresql.persistence.existingClaim | Provide an existing PersistentVolumeClaim, the value is evaluated as a template. | nil |
| postgresql.resources.requests | CPU/Memory resource requests | requests: memory: 1Gi memory: cpu: 250m |
| postgresql.resources.limits | Limits | limits: memory: 2Gi, limits: cpu: 1 |
| postgresql.nodeSelector | Node labels for pod assignment | {} |
| postgresql.affinity | Affinity labels for pod assignment | {} |
| postgresql.tolerations | Toleration labels for pod assignment | [] |
| UseExistingDB.Enabled | If you want to use an existing database, change 'postgresql.install' to 'false'. | false |
| UseExistingDB.XL_DB_URL | Database URL for xl-release | nil |
| UseExistingDB.XL_DB_USERNAME | Database User for xl-release | nil |
| UseExistingDB.XL_DB_PASSWORD | Database Password for xl-release | nil |
| rabbitmq-ha.install | Install rabbitmq chart. If you have an existing message queue deployment, set 'install' to 'false'. | true |
| rabbitmq-ha.rabbitmqUsername | RabbitMQ application username | guest |
| rabbitmq-ha.rabbitmqPassword | RabbitMQ application password | random 24 character long alphanumeric string |
| rabbitmq-ha.rabbitmqErlangCookie | Erlang cookie | RELEASERABBITMQCLUSTER |
| rabbitmq-ha.rabbitmqMemoryHighWatermark | Memory high watermark | 500MB |
| rabbitmq-ha.rabbitmqNodePort | Node port | 5672 |
| rabbitmq-ha.extraPlugins | Additional plugins to add to the default configmap | rabbitmq_shovel,rabbitmq_shovel_management,rabbitmq_federation,rabbitmq_federation_management,rabbitmq_jms_topic_exchange,rabbitmq_management, |
| rabbitmq-ha.replicaCount | Number of replica | 3 |
| rabbitmq-ha.rbac.create | If true, create & use RBAC resources | true |
| rabbitmq-ha.service.type | Type of service to create | ClusterIP |
| rabbitmq-ha.persistentVolume.enabled | If true, persistent volume claims are created | false |
| rabbitmq-ha.persistentVolume.size | Persistent volume size | 20Gi |
| rabbitmq-ha.persistentVolume.annotations | Persistent volume annotations | {} |
| rabbitmq-ha.persistentVolume.resources | Persistent Volume resources | {} |
| rabbitmq-ha.persistentVolume.requests | CPU/Memory resource requests | requests: memory: 250Mi memory: cpu: 100m |
| rabbitmq-ha.persistentVolume.limits | Limits | limits: memory: 550Mi, limits: cpu: 200m |
| rabbitmq-ha.definitions.policies | HA policies to add to definitions.json | {"name": "ha-all","pattern": ".*","vhost": "/","definition": {"ha-mode": "all","ha-sync-mode": "automatic","ha-sync-batch-size": 1}} |
| rabbitmq-ha.definitions.globalParameters | Pre-configured global parameters | {"name": "cluster_name","value": ""} |
| rabbitmq-ha.prometheus.operator.enabled | Enabling Prometheus Operator | false |
| UseExistingMQ.Enabled | If you want to use an existing Message Queue, change 'rabbitmq-ha.install' to 'false' | false |
| UseExistingMQ.XLD_TASK_QUEUE_USERNAME | Username for xl-release task queue | nil |
| UseExistingMQ.XLD_TASK_QUEUE_PASSWORD | Password for xl-release task queue | nil |
| UseExistingMQ.XLD_TASK_QUEUE_URL | URL for xl-release task queue | nil |
| UseExistingMQ.XLD_TASK_QUEUE_DRIVER_CLASS_NAME | Driver Class Name for xl-release task queue | nil |
| HealthProbes | Would you like a HealthProbes to be enabled | true |
| HealthProbesLivenessTimeout | Delay before liveness probe is initiated | 90 |
| HealthProbesReadinessTimeout | Delay before readiness probe is initiated | 90 |
| HealthProbeFailureThreshold | Minimum consecutive failures for the probe to be considered failed after having succeeded | 12 |
| HealthPeriodScans | How often to perform the probe | 10 |
| nodeSelector | Node labels for pod assignment | {} |
| tolerations | Toleration labels for pod assignment | [] |
| affinity | Affinity labels for pod assignment | {} |
| Persistence.Enabled | Enable persistence using PVC | true |
| Persistence.StorageClass | PVC Storage Class for volume | nil |
| Persistence.Annotations | Annotations for the PVC | {} |
| Persistence.AccessMode | PVC Access Mode for volume | ReadWriteOnce |
| Persistence.XldExportPvcSize | XLD Master PVC Storage Request for volume. For production grade setup, size must be changed | 10Gi |
| Persistence. XldWorkPvcSize | XLD Worker PVC Storage Request for volume. For production grade setup, size must be changed | 5Gi |
| satellite.Enabled | Enable the satellite support to use it with Digital.ai Release | false |
Step 6—Download and set up the XL CLI
Download the XL-CLI binaries.
wget https://dist.xebialabs.com/public/xl-cli/$VERSION/linux-amd64/xl
Note: For $VERSION, substitute with the version that matches your product version in the public folder.
-
Enable
executepermissions.chmod +x xl -
Copy the XL binary in a directory that is on your
PATH.echo $PATHExample
cp xl /usr/local/bin -
Verify the Release version.
xl version
Step 7—Set up the Digital.ai Deploy container instance
-
Run the following command to download and start the local Digital.ai Deploy instance:
docker run -d -e "ADMIN_PASSWORD=admin" -e "ACCEPT_EULA=Y" -p 4516:4516 --name xld xebialabs/xl-deploy:10.2 -
To access the Deploy interface, go to:
http://<host IP address>:4516/
Step 8—Activate the deployment process
Go to the root of the extracted file and run the following command:
xl apply -v -f digital-ai.yaml
Step 9—Verify the deployment status
- Check the deployment job completion using XL CLI.
The deployment job starts the execution of various tasks as defined in the digital-ai.yaml file in a sequential manner. If you encounter an execution error while running the scripts, the system displays error messages. The average time to complete the job is around 10 minutes.
Note: The running time depends on the environment.

To troubleshoot runtime errors, see Troubleshooting Operator Based Installer.
Step 10—Verify if the deployment was successful
To verify the deployment succeeded, do one of the following:
-
Open the local Deploy application, go to the Explorer tab, and from Library, click Monitoring > Deployment tasks

-
Run the following commands in a terminal or command prompt:

Step 11—Perform sanity checks
Open the Deploy application and perform the required deployment sanity checks.
Post Installation Steps
After the installation, you must configure the user permissions for OIDC authentication using Keycloak. For more information about how to configure the user permissions, see Keycloak Configuration for Kubernetes Operator Installer.
Installing Release on OpenShift Cluster
Follow the steps below to install Release on Kubernetes On-premise platform.
You can install Deploy on the following platforms:
- OpenShift cluster on AWS
- OpenShift cluster on VMWare vSphere
Follow the steps below to install Deploy on one of the platforms.
Step 1—Create a folder for installation tasks
Create a folder on your workstation from where you will execute the installation tasks, for example, ReleaseInstallation.
Step 2—Download the Operator ZIP
- Download the release-operator-openshift-22.1.zip file from the Deploy/Release Software Distribution site.
- Extract the ZIP file to the ReleaseInstallation folder.
Step 3—Update the platform information
To deploy the Release application on the OpenShift cluster, update the Infrastructure file parameters (infrastructure.yaml) in the folder where you extracted the ZIP file with the parameters corresponding to the OpenShift Cluster Configuration (kubeconfig) file as described in the table. You can find the OpenShift cluster information in the default location ~/.kube/config. Ensure the location of the kubeconfig configuration file is your home directory.
Note: The deployment will fail if the infrastructure.yaml is updated with wrong details.
| Infrastructure File Parameters | OpenShift Cluster Configuration File Parameters | Parameter Value |
|---|---|---|
| serverUrl | server | Enter the server URL. |
| openshiftToken | openshiftToken | This parameter defines the access token to access your OpenShift cluster. |
Step 4—Convert license and repository keystore files to base64 format
-
Run the following command to retrieve
StorageClassvalues for Server, Postgres and Rabbitmq:oc get sc -
Run the keytool command below to generate the
RepositoryKeystore:keytool -genseckey {-alias alias} {-keyalg keyalg} {-keysize keysize} [-keypass keypass] {-storetype storetype} {-keystore keystore} [-storepass storepass]Example
keytool -genseckey -alias deployit-passsword-key -keyalg aes -keysize 128 -keypass deployit -keystore /tmp/repository-keystore.jceks -storetype jceks -storepass test123 -
Convert the Release license and the repository keystore files to the base64 format:
- To convert the xlrLicense into base64 format, run:
cat <License.lic> | base64 -w 0- To convert
RepositoryKeystoreto base64 format, run:
cat <repository-keystore.jceks> | base64 -w 0Example
keytool -genseckey -alias deployit-passsword-key -keyalg aes -keysize 128 -keypass deployit -keystore /tmp/repository-keystore.jceks -storetype jceks -storepass test123
The above commands are for Linux-based systems. For Windows, there is no built-in command to directly perform Base64 encoding and decoding. However, you can use the built-in command certutil -encode/-decode to indirectly perform Base64 encoding and decoding.
Step 5—Update the Custom Resource Definitions (dairelease_cr.yaml)
- Update the
dairelease_crfile with the mandatory parameters as described in the following table:
For deployments on test environments, you can use most of the parameters with their default values in the dairelease_cr.yaml file.
| Parameters | Description |
|---|---|
| KeystorePassphrase | The passphrase for repository-keystore file |
| Persistence.StorageClass | PVC Storage Class for volume |
| RepositoryKeystore | Convert the repository-keystore file content to Base 64 format. |
| ingress.hosts | DNS name for accessing UI of Digital.ai Release. |
| postgresql.Persistence.StorageClass | PVC Storage Class for Postgres |
| rabbitmq.Persistence.StorageClass | PVC Storage Class for Rabbitmq |
| xlrLicense | Release license |
For deployments on production environments, you must configure all the parameters required for your Openshift production setup in the dairelease_cr.yaml file. The table in in the next step lists these parameters and their default values, which can be overridden as per your requirements and workload.
To configure the Keycloak parameters for OIDC authentication, see Keycloak Configuration for Kubernetes Operator Installer.
- Update the default parameters as described in the following table based on your requirements:
The following table describes the default parameters in the Digital.ai dairelease_cr.yaml file. If you want to use your own database and messaging queue, refer to respective database and message queue documentation, and update the dairelease_cr.yaml file.
Fields to be updated in dairelease_cr.yaml | Description | Default Values |
|---|---|---|
| AdminPassword | The administrator password for Release | admin |
| ImageRepository | Image name | xebialabs/xl-release |
| ImageTag | Image tag | 10.2 |
| Resources | CPU/Memory resource requests/limits. User can change the parameter accordingly. | NA |
| postgresql.install | postgresql chart with single instance. Install postgresql chart. If you have an existing database deployment, set install to false. | TRUE |
| postgresql.postgresqlUsername | PostgreSQL user (creates a non-admin user when postgresqlUsername is not postgres) | postgres |
| postgresql.postgresqlPassword | PostgreSQL user password | postgres |
| postgresql.replication.enabled | Enable replication | false |
| postgresql.postgresqlExtendedConf.listenAddresses | Specifies the TCP/IP address(es) on which the server is to listen for connections from client applications | * |
| postgresql.postgresqlExtendedConf.maxConnections | Maximum total connections | 500 |
| postgresql.initdbScriptsSecret | Secret with initdb scripts contain sensitive information Note: The parameter can be used with initdbScriptsConfigMap or initdbScripts. The value is evaluated as a template. | postgresql-init-sql-xld |
| postgresql.service.port | PostgreSQL port | 5432 |
| postgresql.persistence.enabled | Enable persistence using PVC | TRUE |
| postgresql.persistence.size | PVC Storage Request for PostgreSQL volume | 50Gi |
| postgresql.persistence.existingClaim | Provide an existing PersistentVolumeClaim, the value is evaluated as a template. | NA |
| postgresql.resources.requests | CPU/Memory resource requests/limits. User can change the parameter accordingly. | cpu: 250m |
| Memory: 256Mi | ||
| postgresql.nodeSelector | Node labels for pod assignment | {} |
| postgresql.affinity | Affinity labels for pod assignment | {} |
| postgresql.tolerations | Toleration labels for pod assignment | [] |
| UseExistingDB.Enabled | If you want to use an existing database, change postgresql.install to false. | false |
| UseExistingDB.XL_DB_URL | Database URL for xl-release | NA |
| UseExistingDB.XL_DB_USERNAME | Database User for xl-release | NA |
| UseExistingDB.XL_DB_PASSWORD | Database Password for xl-release | NA |
| rabbitmq.install | Install rabbitmq chart. If you have an existing message queue deployment, set install to false. | TRUE |
| rabbitmq.extraPlugins | Additional plugins to add to the default configmap | rabbitmq_jms_topic_exchange |
| rabbitmq.replicaCount | Number of replica | 3 |
| rabbitmq.rbac.create | If true, create & use RBAC resources | TRUE |
| rabbitmq.service.type | Type of service to create | ClusterIP |
| rabbitmq.persistence.enabled | If true, persistent volume claims are created | TRUE |
| rabbitmq.persistence.size | Persistent volume size | 8Gi |
| UseExistingMQ.Enabled | If you want to use an existing Message Queue, change rabbitmq-ha.install to false | false |
| UseExistingMQ.XLD_TASK_QUEUE_USERNAME | Username for xl-deploy task queue | NA |
| UseExistingMQ.XLD_TASK_QUEUE_PASSWORD | Password for xl-deploy task queue | NA |
| UseExistingMQ.XLD_TASK_QUEUE_URL | URL for xl-deploy task queue | NA |
| UseExistingMQ.XLD_TASK_QUEUE_DRIVER_CLASS_NAME | Driver Class Name for xl-deploy task queue | NA |
| HealthProbes | Would you like a HealthProbes to be enabled | TRUE |
| HealthProbesLivenessTimeout | Delay before liveness probe is initiated | 60 |
| HealthProbesReadinessTimeout | Delay before readiness probe is initiated | 60 |
| HealthProbeFailureThreshold | Minimum consecutive failures for the probe to be considered failed after having succeeded | 12 |
| HealthPeriodScans | How often to perform the probe | 10 |
| nodeSelector | Node labels for pod assignment | {} |
| tolerations | Toleration labels for pod assignment | [] |
| Persistence.Enabled | Enable persistence using PVC | TRUE |
| Persistence.Annotations | Annotations for the PVC | {} |
| Persistence.AccessMode | PVC Access Mode for volume | ReadWriteOnce |
| Persistence.XldMasterPvcSize | XLD Master PVC Storage Request for volume. For production grade setup, size must be changed | 10Gi |
| Persistence. XldWorkPvcSize | XLD Worker PVC Storage Request for volume. For production grade setup, size must be changed | 10Gi |
| satellite.Enabled | Enable the satellite support to use it with Deploy | false |
Step 6—Set up the CLI
-
Download the XL-CLI libraries.
wget https://dist.xebialabs.com/public/xl-cli/$VERSION/linux-amd64/xlNote: For
$VERSION, substitute with the version that matches your product version in the public folder. -
Enable
executepermissions.chmod +x xl -
Copy the XL binary to a directory in your
PATH.echo $PATH
cp xl /usr/local/bin -
Verify the Deploy application release version.
xl version
Step 7—Set up the Deploy container instance
-
Run the following command to download and run the Digital.ai Deploy instance:
docker run -d -e "ADMIN_PASSWORD=admin" -e "ACCEPT_EULA=Y" -p 4516:4516 --name xld xebialabs/xl-deploy:10.2 -
Go the following URL to access the Deploy application:
http://<host IP address>:4516/
Step 8—Activate the Release Deployment process
-
Go to the root of the extracted file and run the following command to activate the Release deployment process:
xl apply -v -f digital-ai.yaml
Step 9—Verify the deployment status
-
Check the deployment job completion using XL CLI.
The deployment job starts the execution of various tasks as defined in thedigital-ai.yamlfile in a sequential manner. If you encounter an execution error while running the scripts, the system displays error messages. The average time to complete the job is around 1 minute.Note: The running time depends on the environment.
To troubleshoot runtime errors, see Troubleshooting Operator Based Installer
Step 10—Verify if the deployment was successful
To verify the deployment succeeded, do one of the following:
-
Open the local Deploy application, go to the Explorer tab, and from Library, click Monitoring > Deployment tasks
-
Run the following command in a terminal or command prompt:

To check the deployment status using CLI, run the following command:
oc get pod
Step 11—Perform sanity checks
Open the Release application and perform the required deployment sanity checks.
Post Installation Steps
After the installation, you must configure the user permissions for OIDC authentication using Keycloak. For more information about how to configure the user permissions, see Keycloak Configuration for Kubernetes Operator Installer.
Installing Release on GCP GKE
Follow the steps below to install Release on Google Cloud Platform (GCP) Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE).
Step 1—Create a folder for installation tasks
Create a folder on your workstation from where you will execute the installation tasks, for example, ReleaseInstallation.
Step 2—Download the Operator ZIP
- Download the release-operator-gcp-gke-22.1.zip file from the Deploy/Release Software Distribution site.
- Extract the ZIP file to the ReleaseInstallation folder.
Step 3—Update the GCP GKE Cluster Information
To deploy the Deploy application on the Kubernetes cluster, update the infrastructure.yaml file parameters (Infrastructure File Parameters) in DeployInstallation folder with the parameters corresponding to the kubeconfig file (GCP GKE Kubernetes Cluster Configuration File Parameters) as described in the table below. You can find the Kubernetes cluster information in the default location ~/.kube/config. Ensure the location of the kubeconfig configuration file is your home directory.
Note: The deployment will not proceed further if the infrastructure.yaml is updated with wrong details.
| Infrastructure File Parameters | GCP GKE Kubernetes Cluster Configuration File Parameters | Steps to Follow |
|---|---|---|
| apiServerURL | server | Enter the server details of the cluster. |
| caCert | certificate-authority-data | Before updating the parameter value, decode to base 64 format. |
| token | access token | Enter the access token details. |
Step 4—Update the daideploy_cr.yaml file with the license and keystore details
-
Run the following command to get the storage class list:
kubectl get sc -
Convert the Release license and the repository keystore files to the base 64 format.
-
Run the following commands:
- To convert the xlrLicense into base 64 format, run:
cat <License.lic> | base64 -w 0 - To convert
RepositoryKeystoreto base64 format, run:cat <keystore.jks> | base64 -w 0
The above commands are for Linux-based systems. For Windows, there is no built-in command to directly perform Base64 encoding and decoding. But you can use the built-in command certutil -encode/-decode to indirectly perform Base64 encoding and decoding.
Step 5—Update the default Digitial.ai Deploy Custom Resource Definitions.
- Update the mandatory parameters as described in the following table:
For deployments on test environments, you can use most of the parameters with their default values in the daideploy_cr.yaml file.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| postgresql.persistence.storageClass | Storage Class to be defined as PostgreSQL. |
| rabbitmq.persistence.storageClass | Storage Class to be defined as RabbitMQ. |
| Persistence.StorageClass | The storage class that must be defined as GCP GKE cluster. |
For deployments on production environments, you must configure all the parameters required for your GCP GKE production setup in the daideploy_cr.yaml file. The table in [Step 5.2] lists these parameters and their default values, which can be overridden as per your requirements and workload. You must override the default parameters, and specify the parameter values with those from the custom resource file.
To configure the Keycloak parameters for OIDC authentication, see Keycloak Configuration for Kubernetes Operator Installer.
- Update the default parameters as described in the following table:
Note: The following table describes the default parameters in the Digital.ai dairelease_cr.yaml file. If you want to use your own database and messaging queue, refer to respective external database and message queue documentation, and update the dairelease_cr.yaml file.
| Parameter | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| replicaCount | Number of replicas | 3 |
| ImageRepository | Image name | xebialabs/xl-release |
| ImageTag | Image tag | 22.1 |
| ImagePullPolicy | Image pull policy, Defaults to Always if image tag is ’latest’,set to IfNotPresent | Always |
| ImagePullSecret | Specifies docker-registry secret names. Secrets must be manually created in the namespace | NA |
| haproxy-ingress.install | Install haproxy subchart. If you have haproxy already installed, set install to false | TRUE |
| haproxy-ingress.controller.kind | Type of deployment, DaemonSet or Deployment | DaemonSet |
| haproxy-ingress.controller.service.type | Kubernetes Service type for haproxy. It can be changed to LoadBalancer or NodePort | NodePort |
| ingress.Enabled | Exposes HTTP and HTTPS routes from outside the cluster to services within the cluster | TRUE |
| ingress.annotations | Annotations for ingress controller | ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-redirect:falsekubernetes.io/ingress.class: haproxyingress.kubernetes.io/rewrite-target: /ingress.kubernetes.io/affinity: cookieingress.kubernetes.io/session-cookie-name: JSESSIONIDingress.kubernetes.io/session-cookie-strategy: prefixingress.kubernetes.io/config-backend: option httpchk GET /ha/health HTTP/1.0 |
| ingress.path | You can route an Ingress to different Services based on the path | /xl-release/ |
| ingress.hosts | DNS name for accessing ui of Digital.ai Release | example.com |
| ingress.tls.secretName | Secret file that contains the tls private key and certificate | example-secretsName |
| ingress.tls.hosts | DNS name for accessing ui of Digital.ai Release using tls. | example.com |
| AdminPassword | Admin password for xl-release | If user does not provide password, random 10 character alphanumeric string will be generated |
| xlrLicense | Convert xl-release.lic files content to base64 | NA |
| RepositoryKeystore | Convert keystore.jks files content to base64 | NA |
| KeystorePassphrase | Passphrase for keystore.jks file | NA |
| resources | CPU/Memory resource requests/limits. User can change the parameter accordingly | NA |
| postgresql.install | postgresql chart with single instance. Install postgresql chart. If you have an existing database deployment, set install to false. | TRUE |
| postgresql.postgresqlUsername | PostgreSQL user (creates a non-admin user when postgresqlUsername is not postgres) | postgres |
| postgresql.postgresqlPassword | PostgreSQL user password | random 10 character alphanumeric string |
| postgresql.replication.enabled | Enable replication | FALSE |
| postgresql.postgresqlExtendedConf.listenAddresses | Specifies the TCP/IP address(es) on which the server is to listen for connections from client applications | * |
| postgresql.postgresqlExtendedConf.maxConnections | Maximum total connections | 500 |
| postgresql.initdbScriptsSecret | Secret with initdb scripts contain sensitive informationNote: This parameter can be used with initdbScriptsConfigMap or initdbScripts. The value is evaluated as a template. | postgresql-init-sql-xlr |
| postgresql.service.port | PostgreSQL port | 5432 |
| postgresql.persistence.enabled | Enable persistence using PVC | TRUE |
| postgresql.persistence.size | PVC Storage Request for PostgreSQL volume | 50Gi |
| postgresql.persistence.existingClaim | Provide an existing PersistentVolumeClaim, the value is evaluated as a template. | NA |
| postgresql.resources.requests | CPU/Memory resource requests | requests: memory: 1Gi memory: cpu: 250m |
| postgresql.resources.limits | Limits | limits: memory: 2Gi, limits: cpu: 1 |
| postgresql.nodeSelector | Node labels for pod assignment | {} |
| postgresql.affinity | Affinity labels for pod assignment | {} |
| postgresql.tolerations | Toleration labels for pod assignment | [] |
| UseExistingDB.Enabled | If you want to use an existing database, change postgresql.install to false. | FALSE |
| UseExistingDB.XLR_DB_URL | Database URL for xl-release | NA |
| UseExistingDB.XLR_DB_USERNAME | Database User for xl-release | NA |
| UseExistingDB.XLR_DB_PASSWORD | Database Password for xl- | NA |
| UseExistingDB.XLR_REPORT_DB_URL | Database URL for xlr_report | NA |
| UseExistingDB.XLR_REPORT_DB_USER | Database User for xlr_report | NA |
| UseExistingDB.XLR_REPORT_DB_PASS | Database Password for xlr_report | NA |
| rabbitmq.install | Install rabbitmq chart. If you have an existing message queue deployment, set install to false. | TRUE |
| rabbitmq.rabbitmqUsername | RabbitMQ application username | guest |
| rabbitmq.rabbitmqPassword | RabbitMQ application password | random 24 character long alphanumeric string |
| rabbitmq.rabbitmqErlangCookie | Erlang cookie | RELEASERABBITMQCLUSTER |
| rabbitmq.rabbitmqMemoryHighWatermark | Memory high watermark | 500MB |
| rabbitmq.rabbitmqNodePort | Node port | 5672 |
| rabbitmq.extraPlugins | Additional plugins to add to the default configmap | rabbitmq_shovel,rabbitmq_shovel_management,rabbitmq_federation,rabbitmq_federation_management,rabbitmq_amqp1_0,rabbitmq_management |
| rabbitmq.replicaCount | Number of replicas | 3 |
| rabbitmq.rbac.create | If true, create & use RBAC resources | TRUE |
| rabbitmq.service.type | Type of service to create | ClusterIP |
| rabbitmq.persistentVolume.enabled | If set to True, persistent volume claims are created | TRUE |
| rabbitmq.persistentVolume.size | Persistent volume size | 20Gi |
| rabbitmq.persistentVolume.annotations | Persistent volume annotations | {} |
| rabbitmq.persistentVolume.resources | Persistent Volume resources | {} |
| rabbitmq.persistentVolume.requests | CPU/Memory resource requests | requests: memory: 250Mi memory: cpu: 100m |
| rabbitmq.persistentVolume.limits | Limits | limits: memory: 550Mi, limits: cpu: 200m |
| rabbitmq.definitions.policies | HA policies to add to definitions.json | {”name”: ”ha-all”,”pattern”: .*,vhost:/,definition: {ha-mode: all,ha-sync-mode:automatic, ha-sync-batch-size`: 1}} |
| rabbitmq-ha.definitions.globalParameters | Pre-configured global parameters | {name:cluster_name,value: ``} |
| rabbitmq-ha.prometheus.operator.enabled | Enabling Prometheus Operator | FALSE |
| UseExistingMQ.Enabled | If you want to use an existing Message Queue change rabbitmq-ha.instal to false | FALSE |
| UseExistingMQ.XLR_T\ASK_QUEUE_USERNAME | Username for xl-task queue | NA |
| UseExistingMQ.XLR_TASK_QUEUE_PASSWORD | Password for xl-task queue | NA |
| UseExistingMQ.XLR_TASK_QUEUE_NAME | Name for xl-task queue | NA |
| HealthProbes | Would you like a HealthProbes to be enabled? | TRUE |
| HealthProbesLivenessTimeout | Delay before liveness probe is initiated | 90 |
| HealthProbesReadinessTimeout | Delay before readiness probe is initiated | 90 |
| HealthProbeFailureThreshold | Minimum consecutive failures for the probe to be considered failed after having succeeded | 12 |
| HealthPeriodScans | How often to perform the probe | 10 |
| nodeSelector | Node labels for pod assignment | {} |
| tolerations | Toleration labels for pod assignment | [] |
| affinity | Affinity labels for pod assignment | {} |
| Persistence.Enabled | Enable persistence using PVC | true |
| Persistence.Annotations | Annotations for the PVC | {} |
| Persistence.AccessMode | PVC Access Mode for volume | ReadWriteOnce |
| Persistence.Size | XLR PVC Storage Request for volume. For production grade setup, size must be changed | 5Gi |
Step 6—Download and set up the XL CLI
-
Download the XL-CLI binaries.
wget https://dist.xebialabs.com/public/xl-cli/$VERSION/linux-amd64/xlNote: For
$VERSION, substitute with the version that matches your product version in the public folder. -
Enable
executepermissions.chmod +x xl -
Copy the XL binary in a directory that is on your
PATH.echo $PATHExample
cp xl /usr/local/bin -
Verify the release version.
xl version
Step 7—Set up the Digital.ai Deploy Container instance
-
Run the following command to download and start the Digital.ai Deploy instance:
Note: A local instance of Digital.ai Deploy is used to automate the product installation on the Kubernetes cluster.
docker run -d -e "ADMIN_PASSWORD=admin" -e "ACCEPT_EULA=Y" -p 4516:4516 --name xld xebialabs/xl-deploy:10.2 -
To access the Deploy interface, go to:
http://<host IP address>:4516/
Step 8—Activate the deployment process
Go to the root of the extracted file and run the following command:
xl apply -v -f digital-ai.yaml
Step 9—Verify the deployment status
-
Check the deployment job completion using XL CLI.
The deployment job starts the execution of various tasks as defined in thedigital-ai.yamlfile in a sequential manner. If you encounter an execution error while running the scripts, the system displays error messages. The average time to complete the job is around 10 minutes.Note: The runtime depends on the environment.

To troubleshoot runtime errors, see Troubleshooting Operator Based Installer.
Step 10—Verify if the deployment was successful
To verify the deployment succeeded, do one of the following:
-
Open the local Deploy application, go to the Explorer tab, and from Library, click Monitoring > Deployment tasks

-
Run the following command in a terminal or command prompt:

Step 11—Perform sanity checks
Open the Deploy application and perform the required deployment sanity checks.
Post Installation Steps
After the installation, you must configure the user permissions for OIDC authentication using Keycloak. For more information about how to configure the user permissions, see Keycloak Configuration for Kubernetes Operator Installer.