FAQs on Database/Datamart/ETL/Postgres/Oracle
CLI reports are not showing up on sites with Oracle database. What should I do?
Grant read privilege to the TeamForge reports read only user and also create synonyms in the TeamForge reports read only user schema.
Suppose the TeamForge reports read only username is ctfrptrouser213. The following commands and queries grant the user privileges to view CLI reports on sites that use the Oracle database.
grant drop any synonym to ctfrptrouser213;
grant create synonym to ctfrptrouser213;
BEGIN
FOR i IN (SELECT table_name FROM user_tables)
LOOP
EXECUTE IMMEDIATE('grant select on '|| i.table_name || ' to ctfrptrouser213');
END LOOP;
FOR i IN (SELECT view_name FROM user_views)
LOOP
EXECUTE IMMEDIATE('grant select on '|| i.view_name || ' to ctfrptrouser213');
END LOOP ;
END;
/
BEGIN
FOR i IN (select table_name from all_tables where owner='CTFRPTUSER213')
LOOP
EXECUTE IMMEDIATE('create synonym '|| i.table_name || ' for CTFRPTUSER213.' || i.table_name );
END LOOP;
FOR i IN (select view_name from all_views where owner='CTFRPTUSER213')
LOOP
EXECUTE IMMEDIATE('create synonym '|| i.view_name || ' for CTFRPTUSER213.' || i.view_name);
END LOOP ;
END;
/
What are the right PostgreSQL settings for my site?
Your site's PostgreSQL settings depend on the conditions your site is operating under, especially the number and size of projects and the number of users.
The default values in the site-options.conf file are designed for a TeamForge site running on a system with 8GB of RAM. This table contains recommended values for systems with various amounts of RAM, based on testing carried out in CollabNet's performance lab. Use your discretion in selecting the right values for your environment.
You must recreate the runtime environment after changing any value in the site-options.conf file.
Recommended values if PostgreSQL and TeamForge are on the same server
| site-options.conf Tokens | 8GB RAM | 16GB RAM | 32GB RAM | 64GB RAM | 128GB RAM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PGSQL_EFFECTIVE_CACHE_SIZE= | 4GB | 6GB | 12GB | 24GB | 48GB |
| PGSQL_SHARED_BUFFERS= | 1GB | 2GB | 4GB | 8GB | 8GB |
| PGSQL_WORK_MEM= | 64MB | 64MB | 64MB | 64MB | 64MB |
| PGSQL_WAL_BUFFERS= | 16MB | 32MB | 32MB | 32MB | 32MB |
| PGSQL_MAINTENANCE_WORK_MEM= | 256MB | 615MB | 615MB | 615MB | 615MB |
Recommended values if PostgreSQL is on a separate server
| site-options.conf Tokens | 8GB RAM | 16GB RAM | 32GB RAM | 64GB RAM | 128GB RAM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PGSQL_EFFECTIVE_CACHE_SIZE= | 6GB | 12GB | 24GB | 48GB | 96GB |
| PGSQL_SHARED_BUFFERS= | 2GB | 4GB | 8GB | 8GB | 8GB |
| PGSQL_WORK_MEM= | 64MB | 64MB | 64MB | 64MB | 64MB |
| PGSQL_WAL_BUFFERS= | 16MB | 32MB | 32MB | 32MB | 32MB |
| PGSQL_MAINTENANCE_WORK_MEM= | 256MB | 615MB | 615MB | 615MB | 615MB |
Why do ETL jobs fail post TeamForge upgrade?
ETL jobs can fail due to reasons such as incompatibility between the database and JDBC driver versions and ETL jobs not being able to connect to the Datamart. Try the following solutions.
Pentaho, used by TeamForge for data integration and transformation jobs, recommends using compatible JDBC drivers meant for specific database versions. See Pentaho's JDBC Drivers Reference for more information.
If ETL jobs fail post TeamForge upgrade due to incompatibility between the database and JDBC driver versions:
- Refer to Pentaho's JDBC Drivers Reference page.
- Click the JDBC driver reference URL corresponding to your database, Oracle or PostgreSQL.
- Identify and download the compatible JDBC driver for your database.
- Replace the JDBC driver found in the following directories with the one you downloaded. (The TeamForge ETL process refers to the JDBC driver available in these directories.)
/opt/collabnet/teamforge/dist/tomcat/commonlib//opt/collabnet/teamforge/runtime/tomcat_etl/webapps/etl/WEB-INF/lib
noteYou can also refer to this page for more information about Pentaho-special database issues and resolutions.
If ETL jobs fail due to unavailable connections to the PostgreSQL Datamart:
Make sure that the following error message is found in etl.log
Invalid JNDI connection java:comp/env/jdbc/ReportsDS : FATAL: remaining connection slots are reserved for non-replication superuser connections
If yes, restart the ETL service and restart the failed ETL jobs manually using ./etl-client.py script in the /opt/collabnet/teamforge/runtime/scripts/ directory. The ETL jobs should be able to connect to the PostgreSQL Datamart after the restart.
If the problem persists even after restarting, contact Digital.ai Support.
What is ETL initial load job and when to run it?
You can run the initial load job any time after the site is upgraded to TeamForge 23.1. We recommend that you run it before you hand over the site to the users.
Why am I not able to see the charts for tracker metrics?
You may not be able to see the charts for the tracker metrics if the tracker initial load is not running correctly.
The incremental data collection is disabled until the initial load is run. You can check if the initial load is completed successfully by executing the query below from the Ad-hoc reporting page against the datamart.
select status from etl_job where job_name='tracker_initial_etl';
You must get the status value as 1 if the initial load is completed successfully. Otherwise, you must trigger the job manually by executing the command:
[RUNTIME_DIR]/scripts/etl-client.py -r TrackerInitialJob
Why am I getting a 'Not running' message when the Datamart service is stopped?
When TeamForge and Datamart are running in a single instance, the TeamForge database is stopped when you stop the Postgres services. The message, 'Not running' is displayed when you stop the Datamart service. You can ignore this message.
How do I enable the Postgresql log files archiving when the services are not started using the CollabNet startup script?
The Postgresql log files archiving can be enabled by running a simple command.
It is recommended you use the teamforge script to start and stop the Postgres services. However, if you use the Postgresql init script to start or stop the Postgres services, the postgresql log files are not archived by default.
To enable the Postgresql log files archiving, run the following command:
teamforge -s ctf-postgresql-13.11 start
Why am I getting an email specifying that the ETL job has failed?
You are getting this email because one of the Extract Transformation and Load (ETL) jobs has failed during the run.
You can see the etl.log for more details to find out the reason for the job failure.
The ETL job failure may happen because of the following reasons:
- Out of memory error.
- No response from the database.
If the ETL job failure is happening for the first time, you can restart the ETL ([RUNTIME_DIR]/scripts/collabnet restart etl) and check if the problem is occurring again. You can increase the JVM heap size by specifying the same in [ETL_JAVA_OPTS][siteoptiontokens.html#etljavaopts] if the problem keeps recurring. The default value is -Xms160m -Xmx256m. You can increase the heap size depending on the memory available in the box.
Check if both TeamForge and Datamart are up and responding to queries if there is no response from the database. Restart the ETL ([RUNTIME_DIR]/scripts/collabnet restart etl).
contact Digital.ai Support if the problem persists.
What does the "psql: could not connect to the server: No such file or directory" error message mean?
This error indicates that the PostgreSQL database server is not running. You need to restart the server.
Use the following command to start the server:
service postgresql start
Error while modifying custom reports via branding repository. How to fix?
When you create a custom report, change its category via the branding repository and then attempt to view the original report that you created (before modifying the category), you will encounter an error.
Run the following query to update the report:
update report set category=<category_name> where id = <report_id> and surrogate_id = <surrogate_id>;
In the above query category_name is the ID from the report_category table, which you can get by running the following query:
select id from report_category;
Ensure that the report type in the report belongs to the new category using the report_type_meta_data table by running the following query:
select type, category from report_type_meta_data;
Why do I get performance issues when retrieving flex field information from Datamart?
Flex fields are stored in XML format in the flex fields table. Due to the complexity involved in parsing the XML data and retrieving the relevant flex field information, you can see some performance issues. To overcome this, the XML to non-XML conversion based solution or feature has been implemented to store the flex fields in non-XML format. This approach has redefined the flex field storage and retrieval mechanism and thus has improved the performance of reporting queries while retrieving flex field information from Datamart.
How to enable or disable this feature in Datamart?
To enable or disable this feature respectively, update the field “attribute_value” to either true or false for the record where entity_name is 'flex_field_xml_to_nonxml_etl' and attribute_name is 'ALLOW_FLEXFIELD_XML_TO_NONXML' in ETL Attributes table.
update etl_attributes set attribute_value='true' where entity_name = 'flex_field_xml_to_nonxml_etl'
and attribute_name = 'ALLOW_FLEXFIELD_XML_TO_NONXML';
Does a new job have to be executed to get the benefits of this feature?
No, the existing tracker initial job and tracker incremental job will do the required data processing.
How are invalid XML records handled during XML to non-XML conversion?
Earlier, if any corrupted XML records were found being stored during the XML to Non-XML conversion, the administrators need to manually correct them and store the corrected data into the new flex field bridge tables. To save this manual effort, an automated healing approach was implemented. This auto healing process rectifies the invalid XML records from the audit tables, populates the new flex field bridge tables with the rectified records, and the status of these rectified records are marked as processed in their tables of origin.
What are the changes related to custom reports development on flex fields?
The custom report developers need to query the new flex field bridge tables to get the benefits from the XML to non-XML conversion feature implementation.
How to handle the ETL job failure due to OutofMemoryError: GC overhead limit exceeded?
For a permanent fix, see Why am I getting an email specifying that the ETL job has failed?
To fix this issue during runtime, perform these steps:
-
Stop the ETL service.
kill -9 <etl process id> -
Open the file
/opt/collabnet/teamforge/runtime/conf/set-env.sh. -
Increase the JVM heap size in ETL_JAVA_OPTS to
Xms512andXmx2048m.ETL_JVM_OPTS="-Xms512m -Xmx2048m -server -XX:+HeapDumpOnOutOfMemoryError -
XX:HeapDumpPath=/tmp -verbose:gc -XX:+PrintGCTimeStamps -XX:+PrintGCDetails -
Dsun.rmi.dgc.client.gcInterval=600000 -Dsun.rmi.dgc.server.gcInterval=600000 -
Djava.awt.headless=true -
Dsourceforge.home=/opt/collabnet/teamforge/runtime/sourceforge_home -
Dsourceforge.logdir=/opt/collabnet/teamforge/log/etl -
Dapp.data=/opt/collabnet/teamforge/var -
Dapp.runtime=/opt/collabnet/teamforge/runtime -
Dapp.distribution=/opt/collabnet/teamforge/dist -
Dapp.log=/opt/collabnet/teamforge/log" -
Start the ETL service.
-
Run this command to make sure that you see the updated memory setting in the command output.
ps -ef | grep etl | grep -v jboss -
Run the ETL job again.
How to redo the entire XML to non-XML conversion if required for some reason?
Workaround 1: Bootstrap the reporting service and execute the tracker initial job. As XML to non-XML conversion is part of initial job as well, this would redo the conversion process.
Workaround 2: Truncate the relevant tables and reset the previously processed artifact flex field key to 0. This would reinitiate the XML to non-XML conversion while executing the tracker incremental job.
Relevant SQL process:
truncate table stage_flex_fields_bridge;
truncate table text_flex_fields_bridge;
truncate table user_flex_fields_bridge;
truncate table ms_flex_fields_bridge;
truncate table ss_flex_fields_bridge;
truncate table date_flex_fields_bridge;
truncate table bad_xml_records;
update etl_attributes set attribute_value = 0 where attribute_name = 'PREV_RUN_ARTIFACT_FLEX_FIELDS_KEY' ;
commit;
What kind of objects can I create reports on?
Reports can report on data from trackers, tasks, planning folders, and repositories.
Task reports can report on data in a single project or across multiple projects. Tracker reports can report on data in a single tracker or across multiple trackers in a project or multiple projects. Task and Tracker reports are in tabular format and grouped under Table reports. You can also create reports on data in planning folders and on data in source code repositories.
How do I change the time to run the ETL jobs?
The ETL_JOB_TRIGGER_TIME can be modified to specify a different time.
By default, the ETL job runs at 2:30 AM (local time) everyday. It is recommended to run this once a day to avoid any performance degradation of the Teamforge site. See ETL_JOB_TRIGGER_TIME for more information.
How can I check the status of ETL?
The following command displays the status of the ETL process.
[RUNTIME_DIR]/scripts/collabnet status etl
You can get additional information about the various ETL jobs that are configured using the command:
[RUNTIME_DIR]/scripts/etl-client.py -a
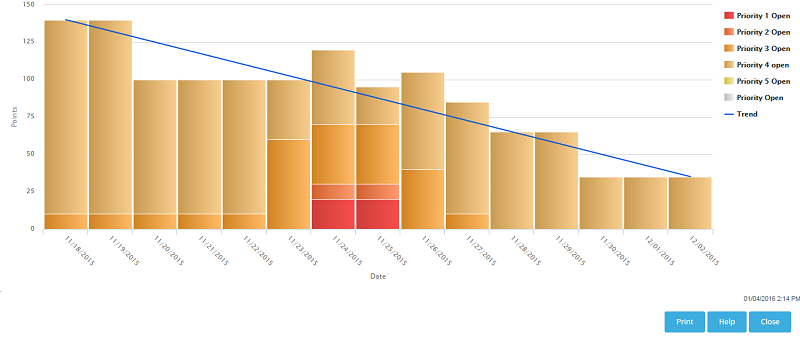
What can I learn from a burndown chart?
Burndown is the estimated amount of work that remains to be done in an iteration or a release, compared with the work originally estimated.
At any time, you can click on a planning folder (release, iteration or standard) and view the burndown chart which shows the work to be completed in terms of story points within the given time frame. This helps you see how the team is progressing towards "done". In the burndown chart of a standard planning folder ('Folder') you can see how the sum of the estimated and remaining effort and points (story points) for all contained and descendant features is changing within a given time frame by choosing the options available in the View Mode.
In both 'Release' and 'Folder' burndown charts, you can use the trend line shown in your burndown chart to do some useful things:
-
Project the time when all the work for this iteration will be completed.
-
Predict the amount of work your team can expect to complete during any given iteration.
'Folder' burndown chart which has the View Mode

'Iteration' burndown chart
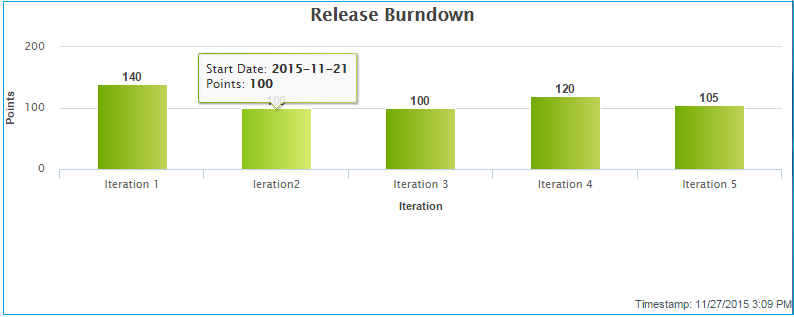
Release Burndown Chart
A release burndown chart shows an iteration-wise breakup of the work to be completed, that is, it shows how much work (in terms of points) is remaining at the start of each iteration.
The information you derive from your burndown chart will help revise the product scope, make accurate planning decisions, and refine implementation details.
In general, a burndown chart trends downward until it reaches zero. In practice, some events can reverse the downward trend of your burndown chart. For example, development work frequently uncovers a greater scope for a user story than was initially estimated. As a result, you'll revise your estimate of remaining work on that story, and your burndown figure may be pushed upwards.
The burndown chart uses whatever effort units you are using in the planning folder.
The story told in your burndown chart is only as reliable as the underlying data. The owners of individual task artifacts can help keep the burndown chart accurate by regularly updating their remaining effort and points (story points).
What can I learn from a capacity chart?
The capacity chart shows the project team's judgment of how much work can be done with the resources available and the time period represented in the planning folder.
-
When you compare average capacity with individual users' assignments, you can see which team members are relatively over- or under-assigned. You can also see how much of the estimated and remaining effort is unassigned.
-
Comparing average capacity with the relative priorities of artifacts is one way to gauge your team's ability to deliver the work that the product owner has defined.
-
When you view average capacity against the count of open and closed artifacts, you have another way to assess your team's likelihood of meeting its sprint commitment.
The data behind the capacity chart is updated in real time, so that your team can respond quickly to changes in effort estimates or relative priorities.
Capacity is expressed as a numeric value, using the same scale as you are using for estimated, remaining, actual effort accounts.
You can see the capacity of a planning folder in the planning folder summary view.
A planning folder's capacity must be equal to or greater than the total estimated effort (or total remaining effort) for the artifacts in the planning folder. To avoid confusion, you may want to wait for estimates to emerge before setting the planning folder's capacity.
What can I learn from an "Open by Priority" chart?
Dynamic planning is most effective when you know the relative priorities of work items you are tracking. The Open by Priority chart helps you check that your team is working on the optimal mix of artifacts.
Use the Open by Priority chart for a quick overview of the type of work your project is working with. A glance at this chart can suggest some broad generalizations, which you'll then want to test by examining your planning folder contents more closely.
-
When the darker bars on the left side of the chart are high, you are probably working on the high-impact issues that come up earlier in a work cycle. Don't be surprised if the trend line in your Burndown chart is not yet sloping steeply downward to the right.
-
When the lighter bars on the right side of the chart are high, you are likely to be working on cleanup issues and refinements. You may be approaching the end of the work cycle you defined in this planning folder. At this stage, the Closed slice of the Open vs. Closed chart is likely to be equal to or larger than the Open proportion.
The Open by Priority chart won't tell you how much work is involved in the artifacts that it measures. For that, check the Burndown chart.
What can I learn from an "Open vs. Closed" chart?
Sometimes you just want a raw count of the number of work items you are looking at.
Use the Open vs. Closed chart for a quick overview of your team's progress in purely numerical terms. A glance at this chart can suggest some broad generalizations, which you'll then want to test by examining your other charts and your planning folder contents more closely.
The Open vs. Closed chart is good for some basic summary information. You may want to share this chart with executive sponsors who need to know how things are going in quantitative terms, but don't need a lot of detail about the types of work being addressed.
How does TeamForge deliver activity reports?
The data in your reports comes from a special database that extracts live site data from the production database at intervals you specify.
You can specify the time at which the reporting data is refreshed from the production database. By default, the extraction takes place daily at 2:30 a.m. in the TeamForge application server's time zone. See Schedule Data extraction for Reporting.
The reporting database can be deployed on a separate machine to help channel load away from the application server. Historical data is available even if the application server no longer stores it.
Where does the reporting data come from?
An ETL application extracts data from the live production PostgreSQL or Oracle database where the TeamForge site stores most of its critical data. (Information about reporting configurations is also stored in the production database.) Some data is also gathered from the file system.
How is the production data converted into reporting data?
TeamForge extracts a snapshot of the production data, transforms it into a format that supports reporting requirements, and loads it into the datamart, which is optimized for fast retrieval. The Extract-Transform-Load (ETL) application is a Tomcat JVM running as a TeamForge service under the TeamForge integration server architecture.
Where is the reporting data kept?
After the ETL app collects and processes the live site data, it is stored in a separate database called the datamart. If the TeamForge site uses a PostgreSQL database, then the datamart is also a PostgreSQL database; likewise for Oracle. The datamart uses a Star Schema-based design for tables.
How are the reports shown in the TeamForge user interface?
The reports are rendered in the TeamForge UI using Adobe Flex.
When a site is upgraded, there will be a delay before reporting data is available to users, until the scheduled ETL run has occurred. Performing a manual ETL run immediately after an upgrade is not advisable, since it could consume a lot of system resources leading to performance problems.
Why do I get duplicate records in a tracker report?
Yes, this is a known limitation.
For a tracker report, when you select more than one value from a multi-select, user-defined field as filter and if an artifact is associated with all of the selected values, then that artifact's record is duplicated for each of the selected values.
For example, assume that you have a 'Select User' multi-select, user-defined field with values 'User 1', 'User 2' and 'User 3' in a tracker report. All these three values are associated with 'artifact 1001'. Select all three values as filter and generate the tracker report. You will see 'artifact 1001' record being duplicated, that is, you will see three individual 'artifact 1001' records created for each of the three users.
What is the difference between a stagger and normal header in query result heading settings?
The normal and the stagger header preference setting allows you to set a standard header for your query view or a staggered header.
For more information about queries in Issue Tracker, see: Query database of issues.
Can the query result be listed without the issue id?
No. Query results can never be listed without the issue id because issue id is the only field which identifies each issue uniquely.
Why do PostgreSQL deployment fail during provision?
If a previous PostgreSQL instance was not shut down properly, the PostgreSQL upgrade gets aborted and the deployment fails during provision.
To fix this, follow these steps:
-
Check the state of the database cluster.
/usr/pgsql-9.6/bin/pg_controldata /opt/collabnet/teamforge/var/pgsql/9.6/data/ | grep 'Database cluster state' -
Run these commands if the Database cluster state doesn't return
shutdown. This step makes sure that PostgreSQL is shut down properly.su - postgres -c "/usr/pgsql-9.6/bin/pg_ctl start -D /opt/collabnet/teamforge/var/pgsql/9.6/data/"
su - postgres -c "/usr/pgsql-9.6/bin/pg_ctl stop -D /opt/collabnet/teamforge/var/pgsql/9.6/data/" -
Repeat step 1 to check whether the Database cluster state returns
shutdownand then continue with the upgrade.