Azure Plugin
The Deploy Azure plugin enables Deploy to work with the Microsoft Azure cloud computing service. You can provision Virtual Machines, Containers, and Deploy functionApp and WebApp from Deploy.
For information about requirements and the configuration items (CIs) that the Azure plugin provides, refer to the Azure Plugin Reference.
From version 10.2.0 Azure plugin is compatible with Digital.ai Deploy 10.2.0 or higher version.
Deploy Azure Plugin Features
- Create resource groups and storage accounts
- Define security groups and associated security rules
- Setup public IP addresses
- Define virtual networks (VNet) and their route tables
- Provision virtual machines associated to their network interface (NIC) and deploy applications to those virtual machines
- Support Windows Virtual Machines (VMs)
- Automatically destroy machines during undeployment
- Leverage the Blob Storage scalable object storage for unstructured data
- Create web apps with built-in auto-scale and load balancing
- Create function apps based on an event-driven, serverless compute experience
- Run containers (ACI) without managing virtual machines
- Safeguard cryptographic keys and other secrets using Key Vault
- Configure load balancer (Layer 4 TCP and UDP) to deliver high availability and network performance to your applications
- Deploy network configurations such as virtual networks (VNets), subnets, routing tables, network interfaces, and public IP addresses
- Deploy load balancing configurations such as load balancers and availability sets
- Deploy storage configurations such as storage accounts and blob containers
- Deploy content to blob containers
- Deploy security configurations such as security groups and associate security roles with them
- Configure app service plans and deploy web apps and web jobs
- Deploy functions to Azure Functions
- Deploy container groups and containers to Azure Container Instance
- Create artifact feeds and upload packages to the created feeds
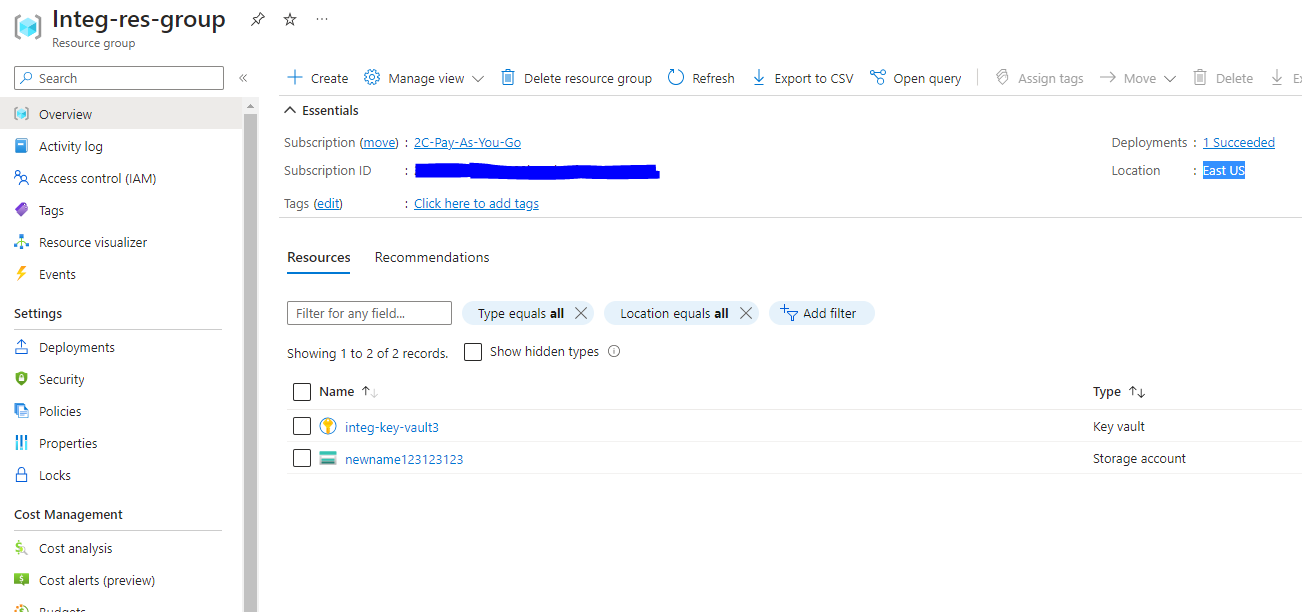
This is a diagram representing all the resource types Deploy Azure plugin supports and their dependencies:
Before You Get Started
Before you begin using the Azure plugin you must have:
- Access to a Microsoft Azure account.
- Digital.ai Deploy running with Azure plugin.
- Azure CLI (to create artifact feed and upload packages). For more information, see Azure CLI Installation Guide.
Make sure your Azure account is correctly configured, with the following elements:
- Subscription ID
- Service principal
- Tenant ID
- Client ID
- Client secret value
- Resource group to create
- An Azure region to create the resource group (e.g.
westus). - Name of the Azure app. This will also be used as the name of the Release and Deploy CIs.
- Username and password for the admin account.
Set Up an Azure Cloud Connection
To set up a connection to Azure Cloud:
- In the side navigation bar, click Explorer.
- Hover over Infrastructure, click
, and select New > Azure > Cloud.
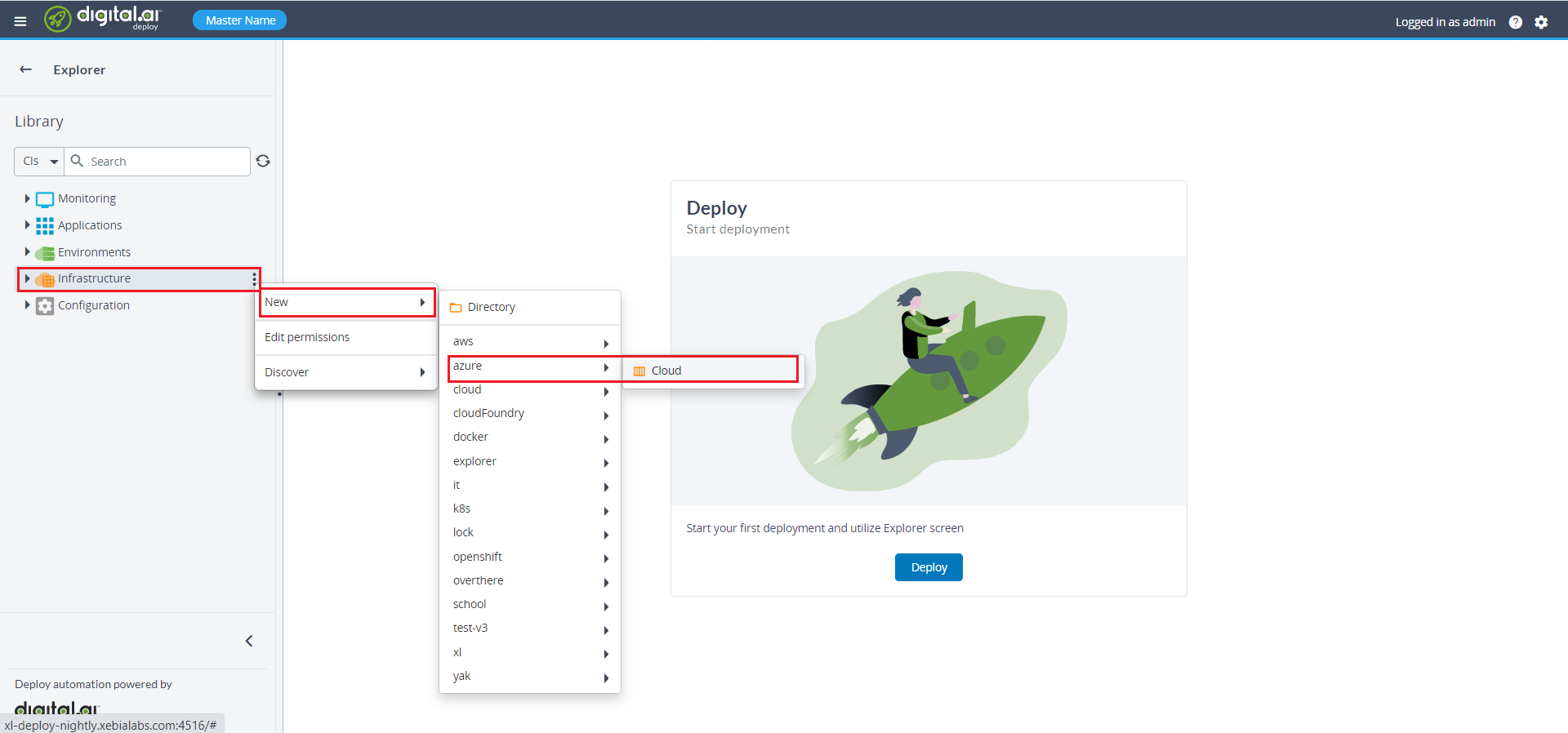
- Enter the subscription id (which you will found in Azure portal under subscriptions) in the Subscription ID field.
- Enter the user name in the User Name field.
- Enter the user password in the User Password field.
- Click Save or Save and close.
Verify the Azure Cloud Connectivity
To verify the connection with the azure.Cloud, do the following steps:
- In the side navigation bar, click Explorer.
- Expand the Infrastructure, hover over the newly created infrastructure and click
, and select Check Connection.
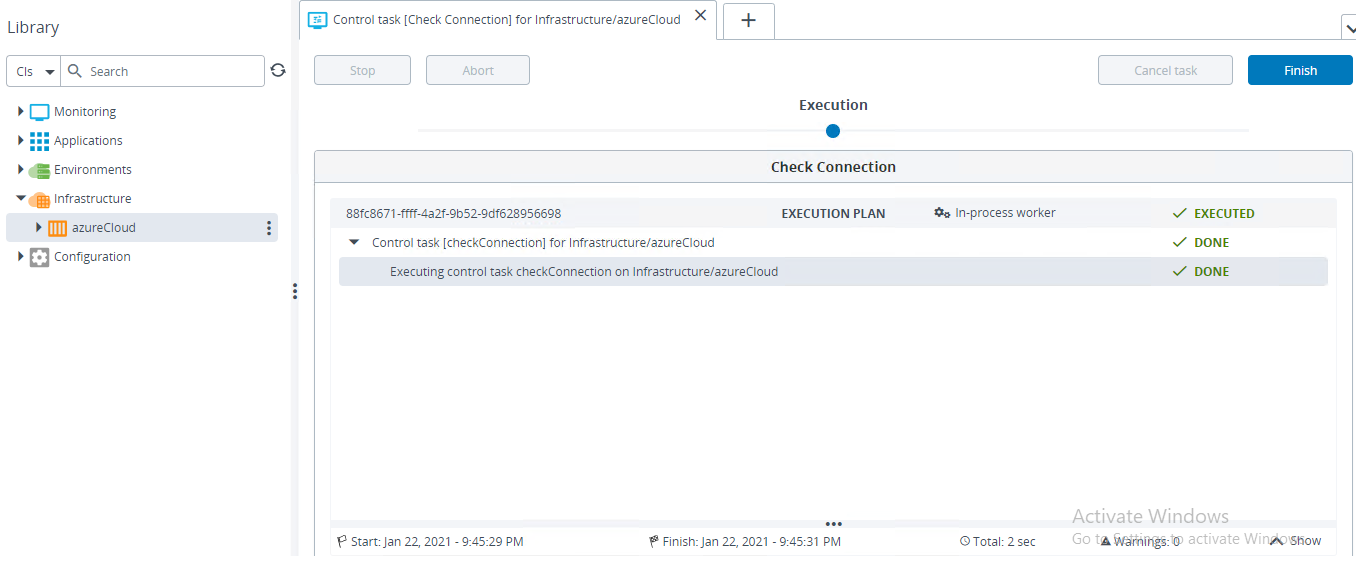
Execute the task. If the task succeeds, the connectivity is working fine and we are able to use Azure through Digital.ai Deploy.
This topic describes using a CI tool plugin to interact with Deploy. However, as a preferred alternative starting with version 9.0, you can utilize a wrapper script to bootstrap XL CLI commands on your Unix or Windows-based Continuous Integration (CI) servers without having to install the XL CLI executable itself. The script is stored with your project YAML files and you can execute XL CLI commands from within your CI tool scripts. For details, see the following topics:
Cloud Service Spec
To create a cloud service spec, do the following steps:
- In the side navigation bar, click Explorer.
- Hover over Applications, click
, then select New > Application. A new tab displays.
- Enter the name in the Name field.
- Click Save and close.
- Click
on the newly created then select New > Provisioning Package
- Enter the name in the Name field.
- Click Save and close.
Before creating Cloud Service create the following:
Set Up a Virtual Network
To set up a virtual network, do the following steps:
- In the side navigation bar, click Explorer.
- Under the Application, expand the newly created application.
- On the newly created package, click
then select New > azure > VirtualNetworkSpec. A new tab displays.
- Specify the required properties under the VirtualNetworkSpec.
- Click Save and close.
Set Up a Storage account
To set up a storage account, do the following steps:
- In the side navigation bar, click Explorer.
- Under the Application, expand the newly created application.
- On the newly created package, click
then select New > azure > StorageAccountSpec. A new tab displays.
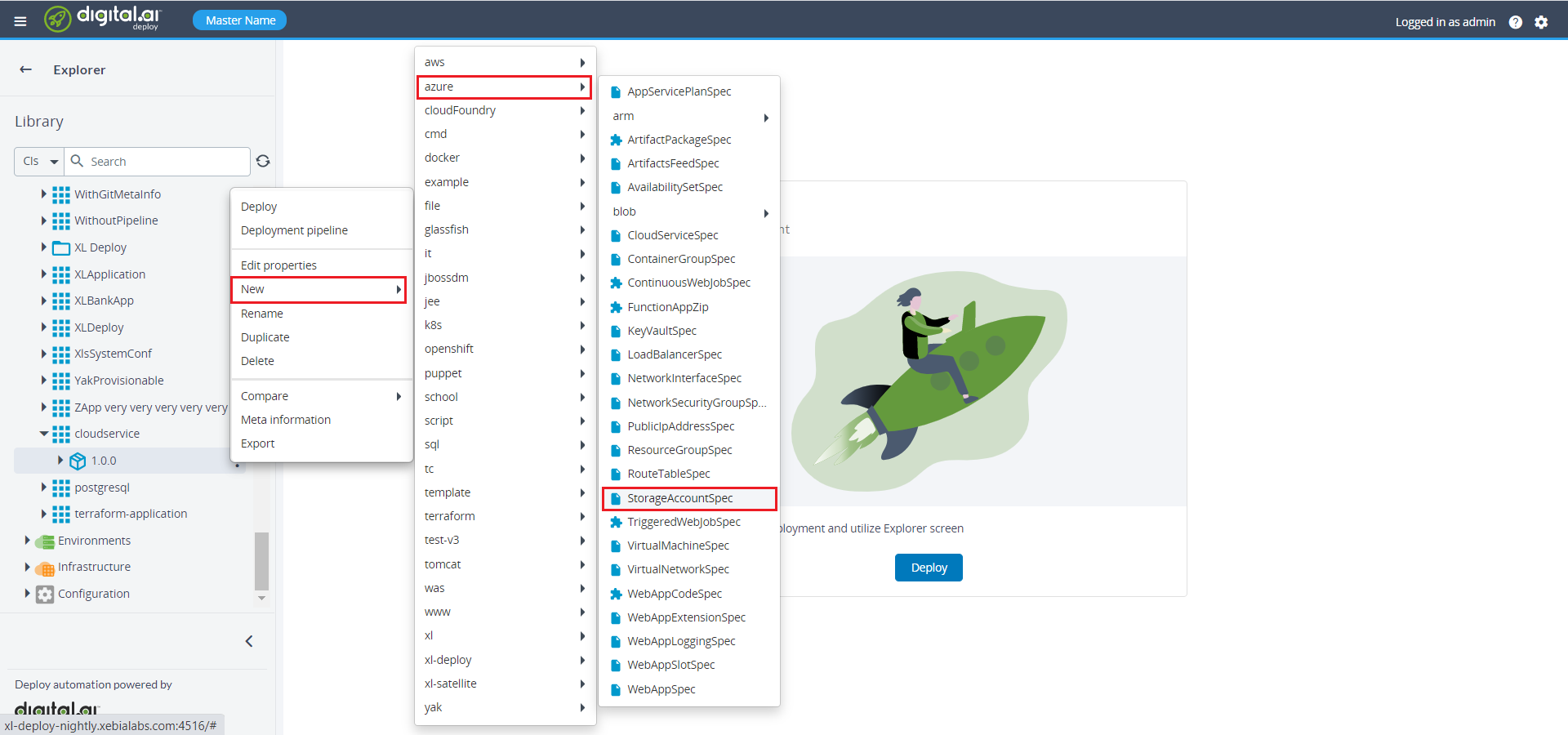
- Specify the required properties under the StorageAccountSpec.
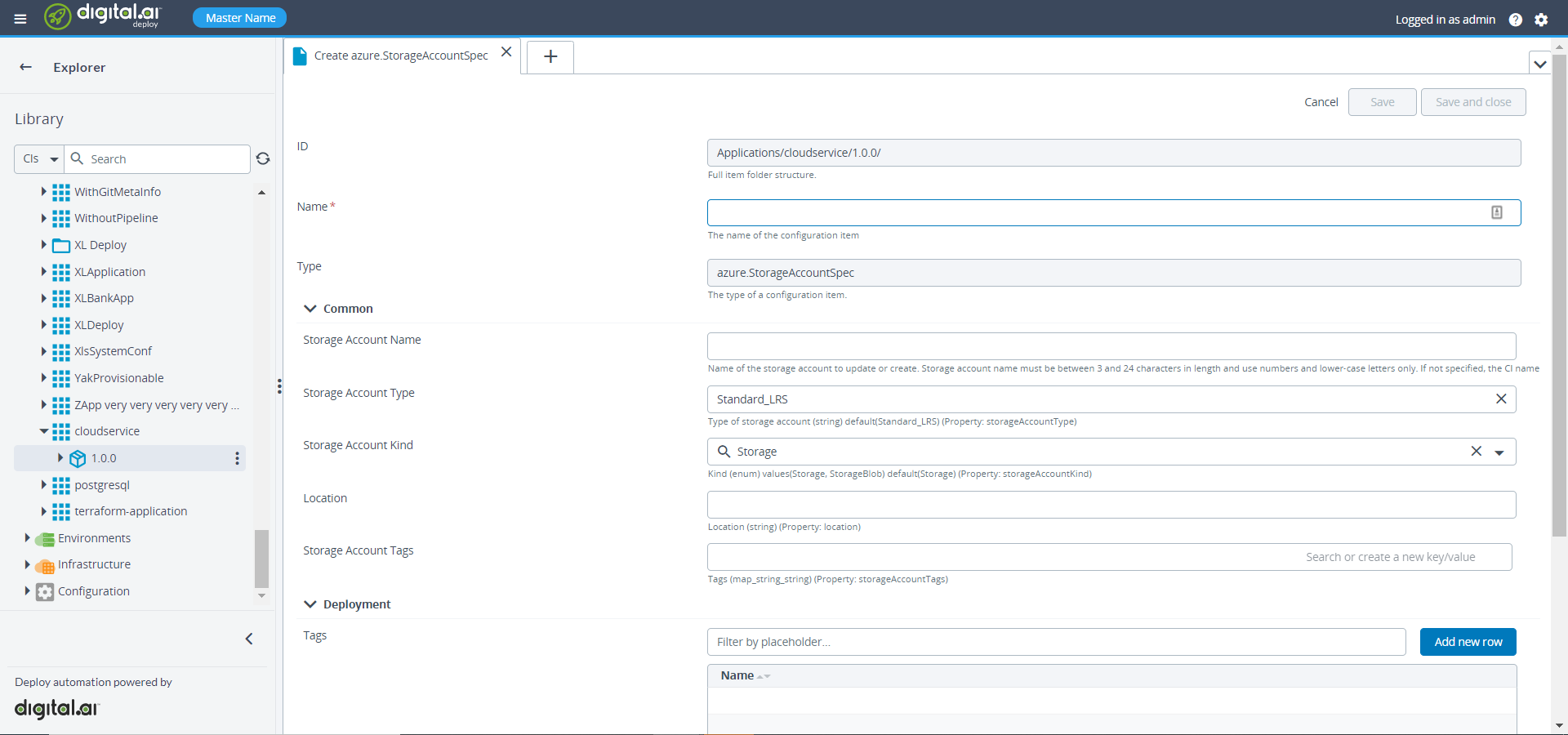
- Click Save and close.
Create a blob container inside the storage account
To create a blob container, do the following steps:
- On the newly created package, click
then select New > azure > blob > ContainerSpec. A new tab displays.
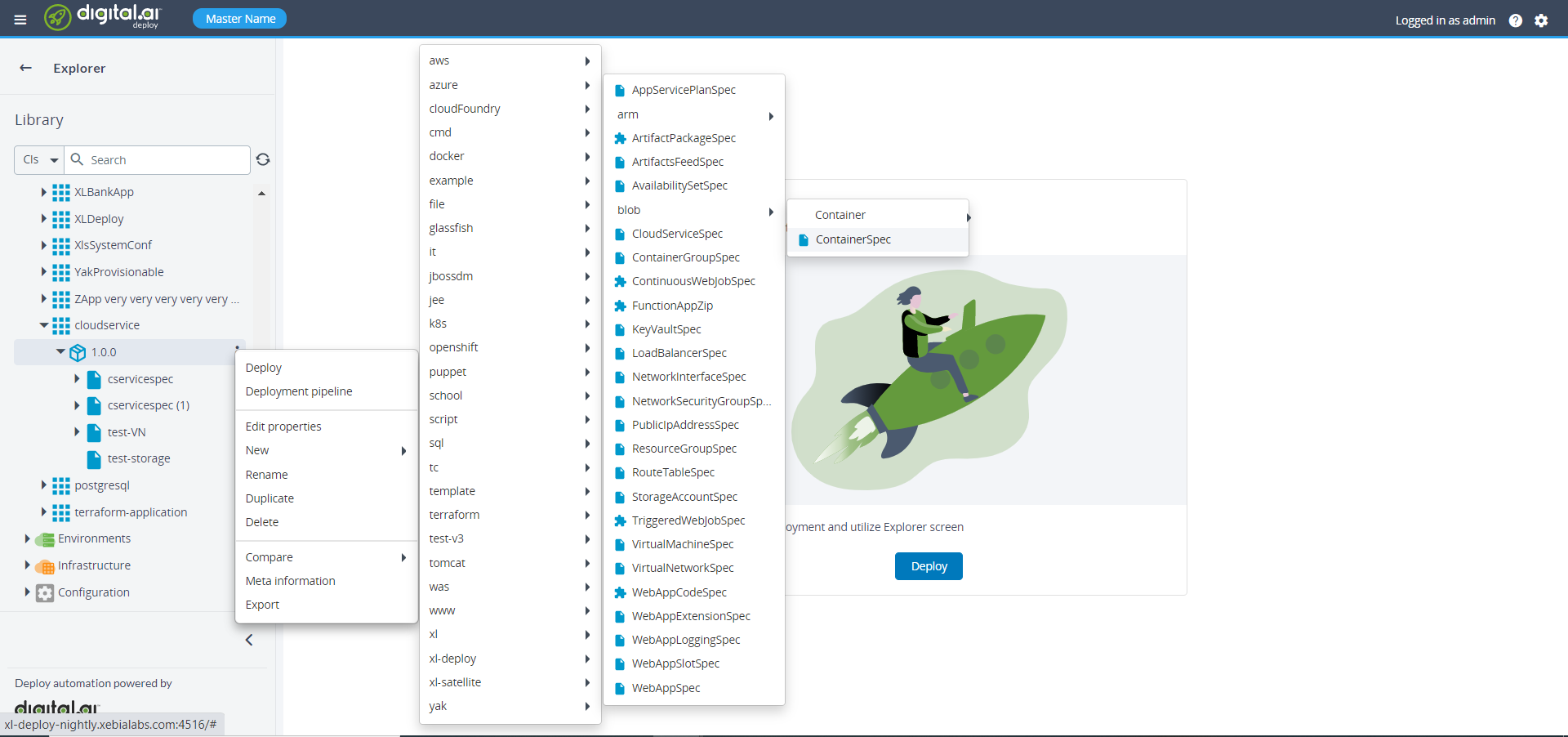
- Specify the required properties under the StorageAccountSpec.
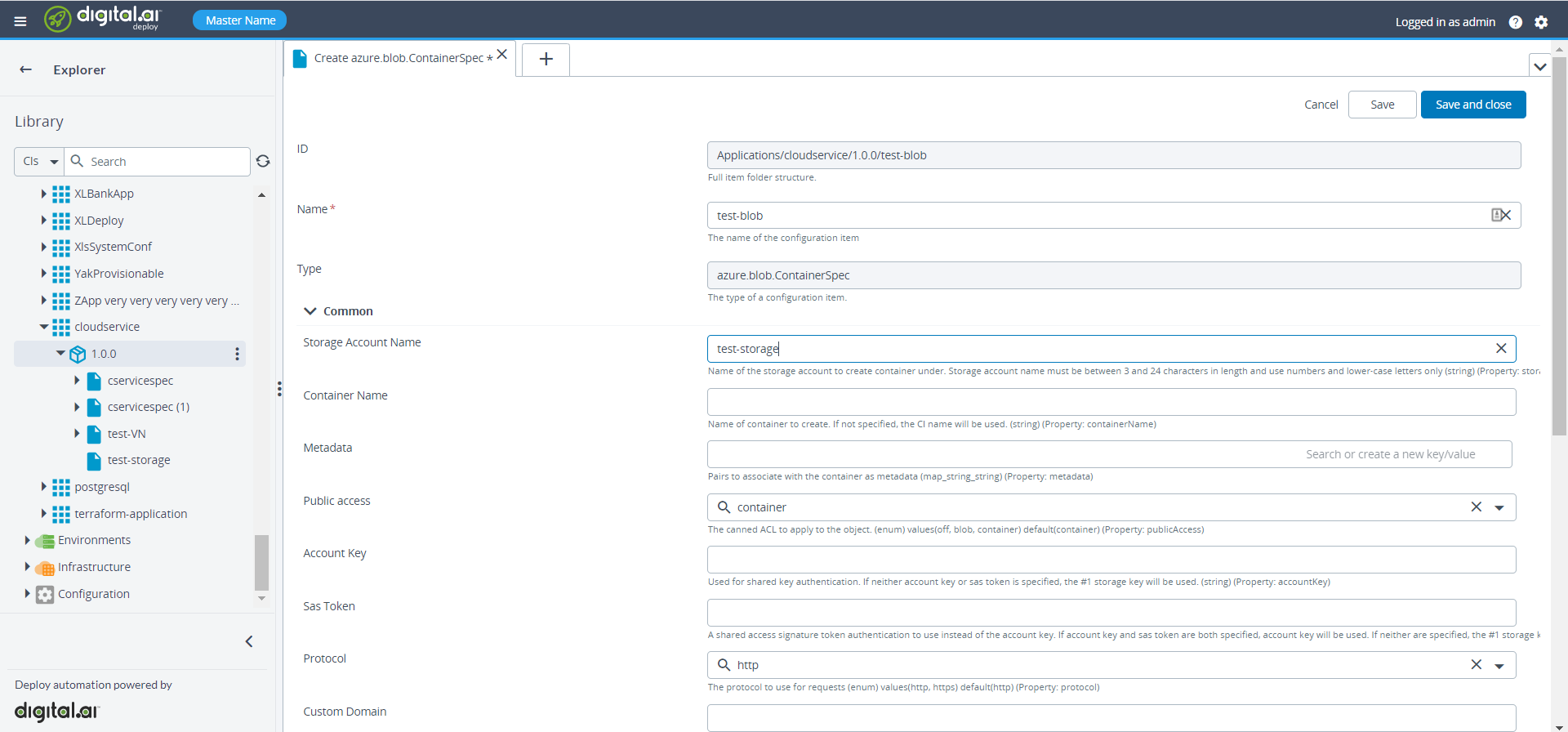
- Verify the newly created storage account and the blob container on the azure portal.
- Upload the required files (.cspkg, .csdef, and, .cscfg) in the newly created container by clicking Upload button from the Azure portal.
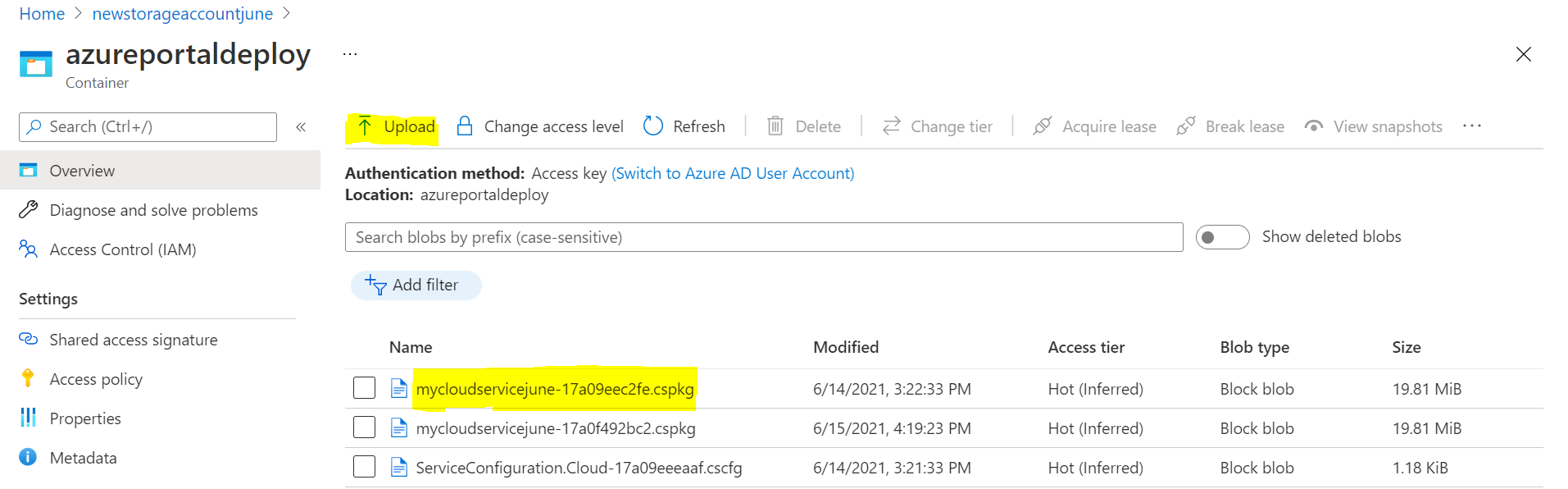 Note: To generate the package (.cspkg) file, Refer Create an Azure cloud service project and after making required changes in ServiceDefinition.csdef and ServiceConfig.cscfg files, run the application and then package it. See Package of Azure Cloud Service model for more information.
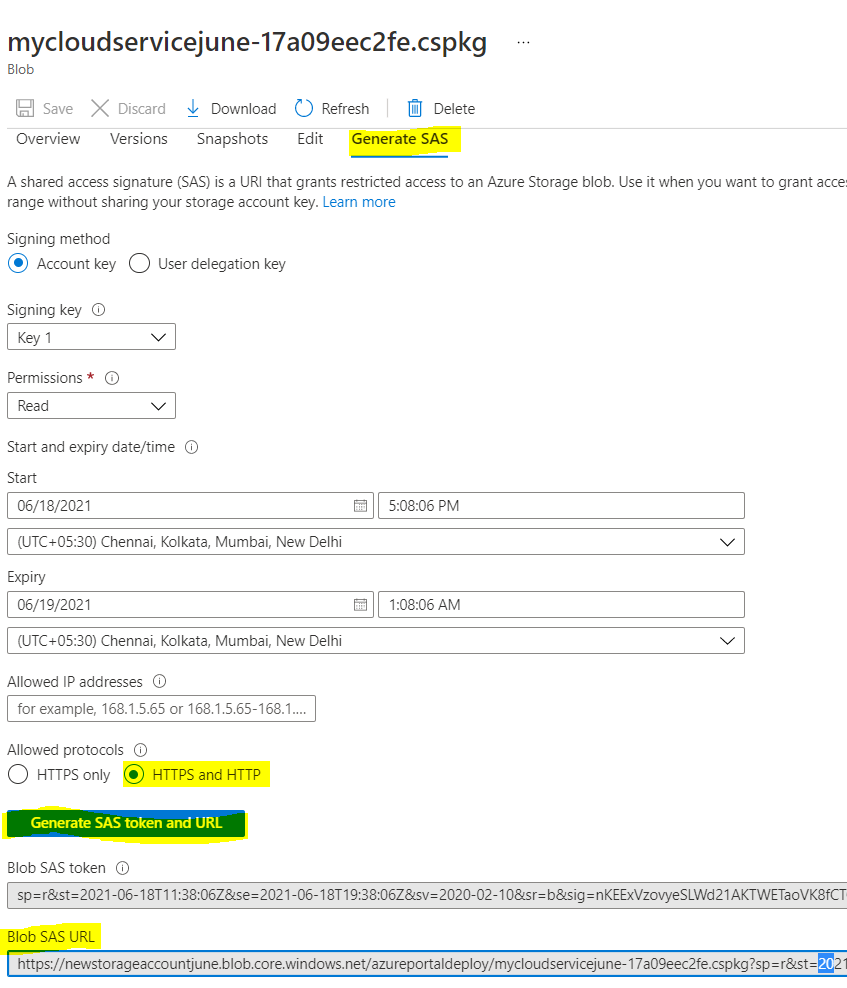
Note: To generate the package (.cspkg) file, Refer Create an Azure cloud service project and after making required changes in ServiceDefinition.csdef and ServiceConfig.cscfg files, run the application and then package it. See Package of Azure Cloud Service model for more information. - Click on
.cspkgfile and then click on Generate SAS. - Select HTTPS and HTTP in Allowed protocal.
- Copy the Blob SAS URL and paste it in the required fields of cloudservicespec.
Create a Public IP address
To create a public IP address, do the following steps:
- In the side navigation bar, click Explorer.
- Under the Application, expand the newly created application.
- On the newly created package, click
then select New > azure > PublicIpAdressSpec. A new tab displays.
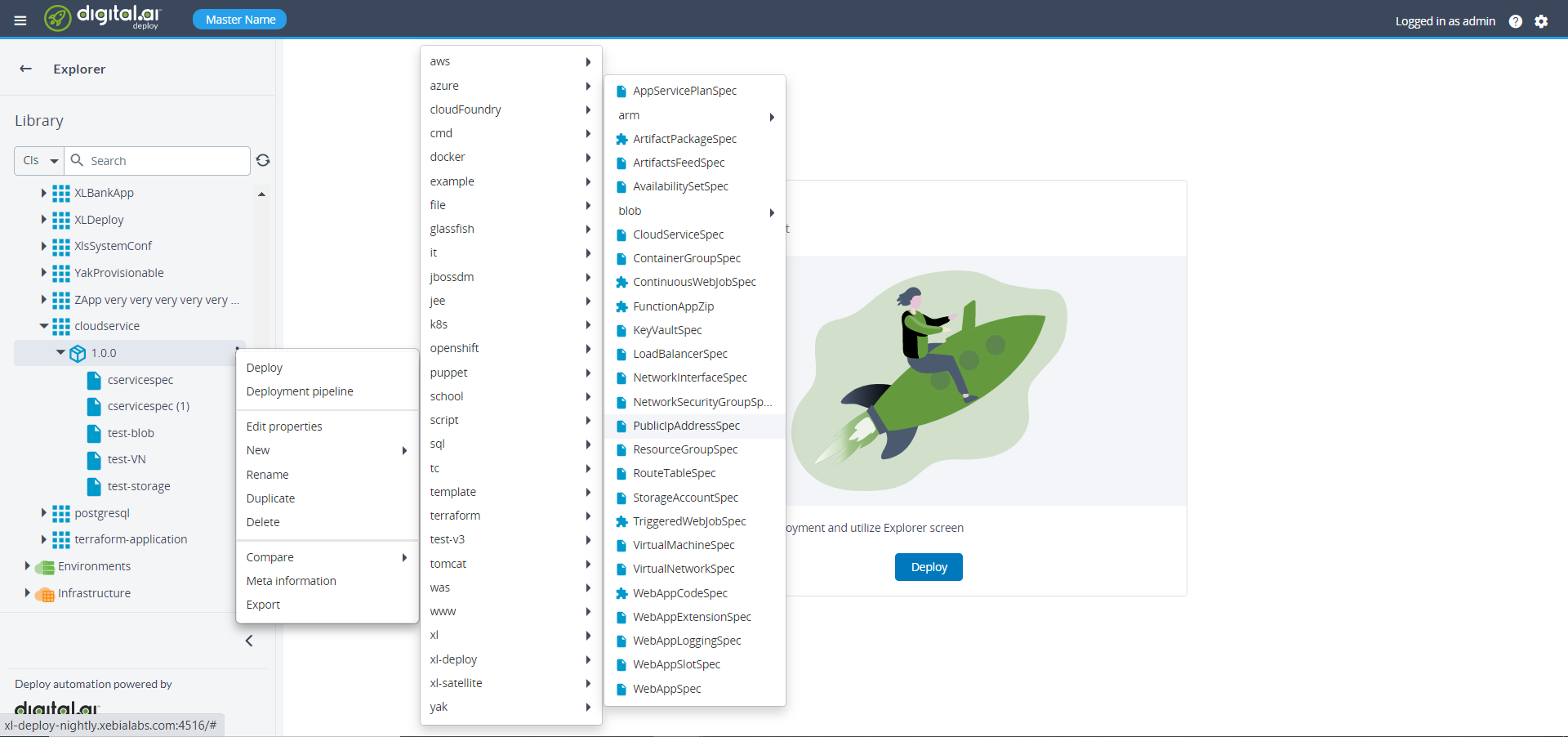
- Specify the required properties under the StorageAccountSpec.

Create Cloud Service Spec
To create cloud service spec, do the following steps:
- In the side navigation bar, click Explorer.
- Under the Application, expand the newly created application.
- On the newly created package, click
then select New > azure > CloudServiceSpec. A new tab displays.
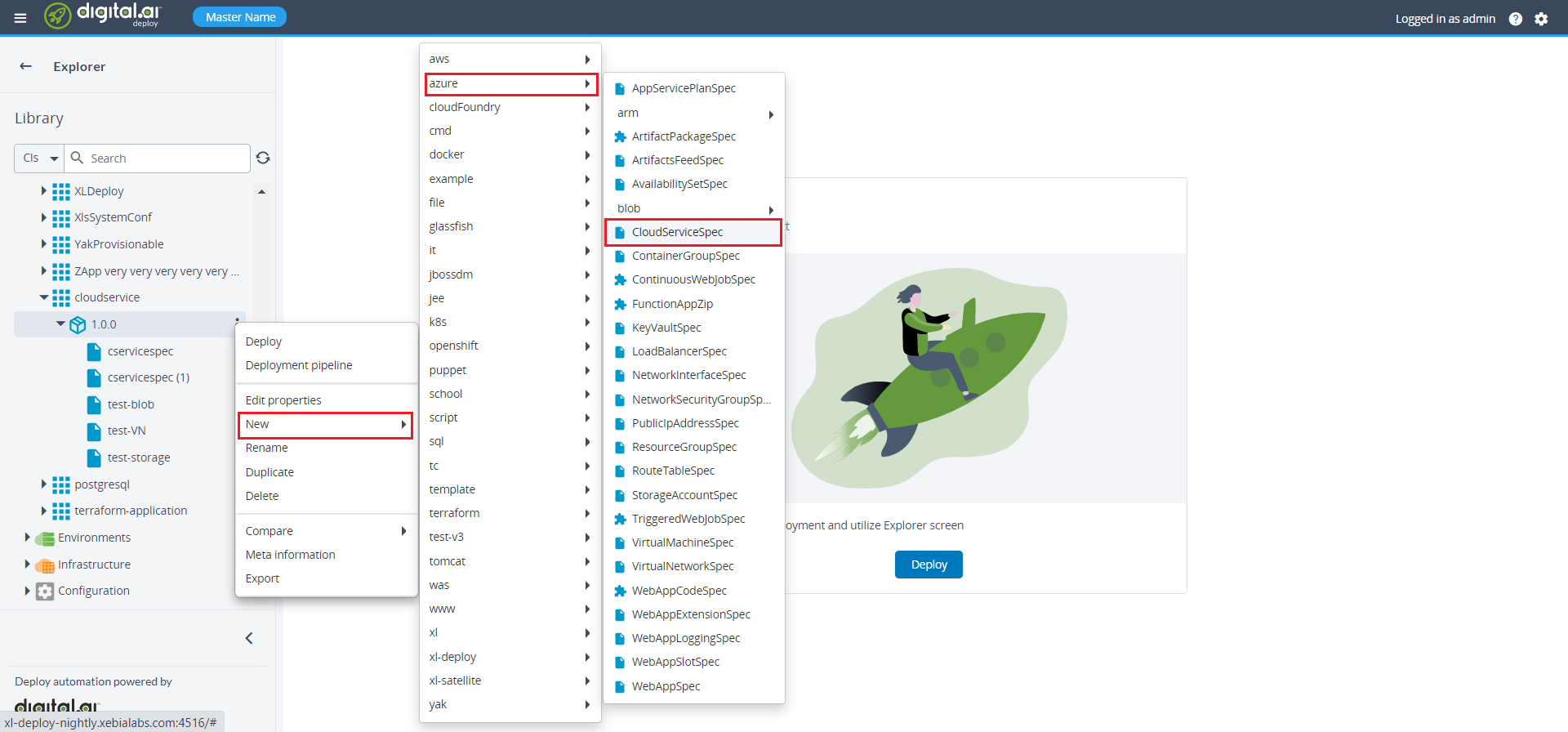
- Specify the required properties including virtual network, storage account, and public ip address under the CloudServiceSpec.
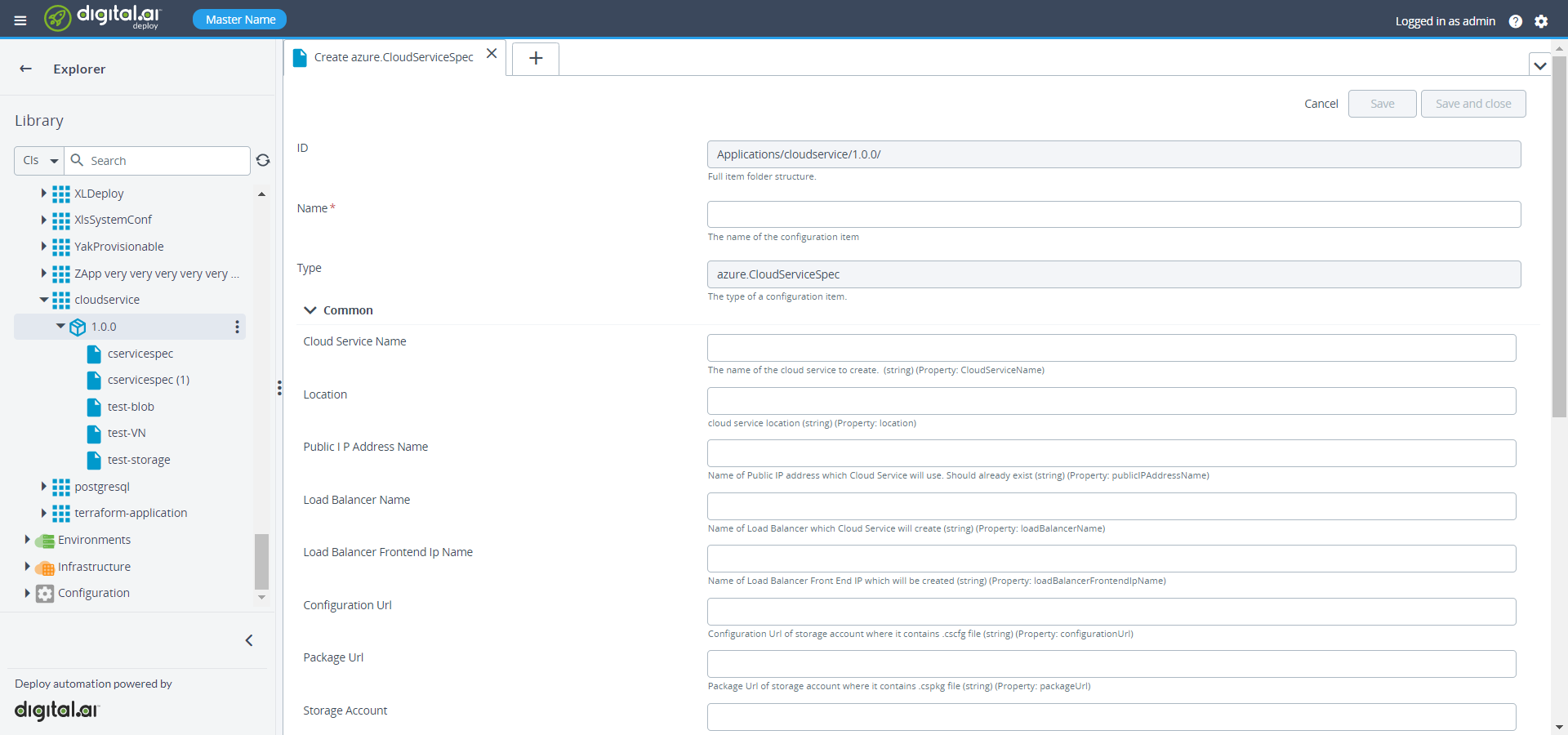
Deploy the Cloud Service Spec
Deploy the CloudServiceSpec file from the Applications. After successful deployment of CloudServiceSpec on Digital.ai Deploy, verify the same on Azure portal.
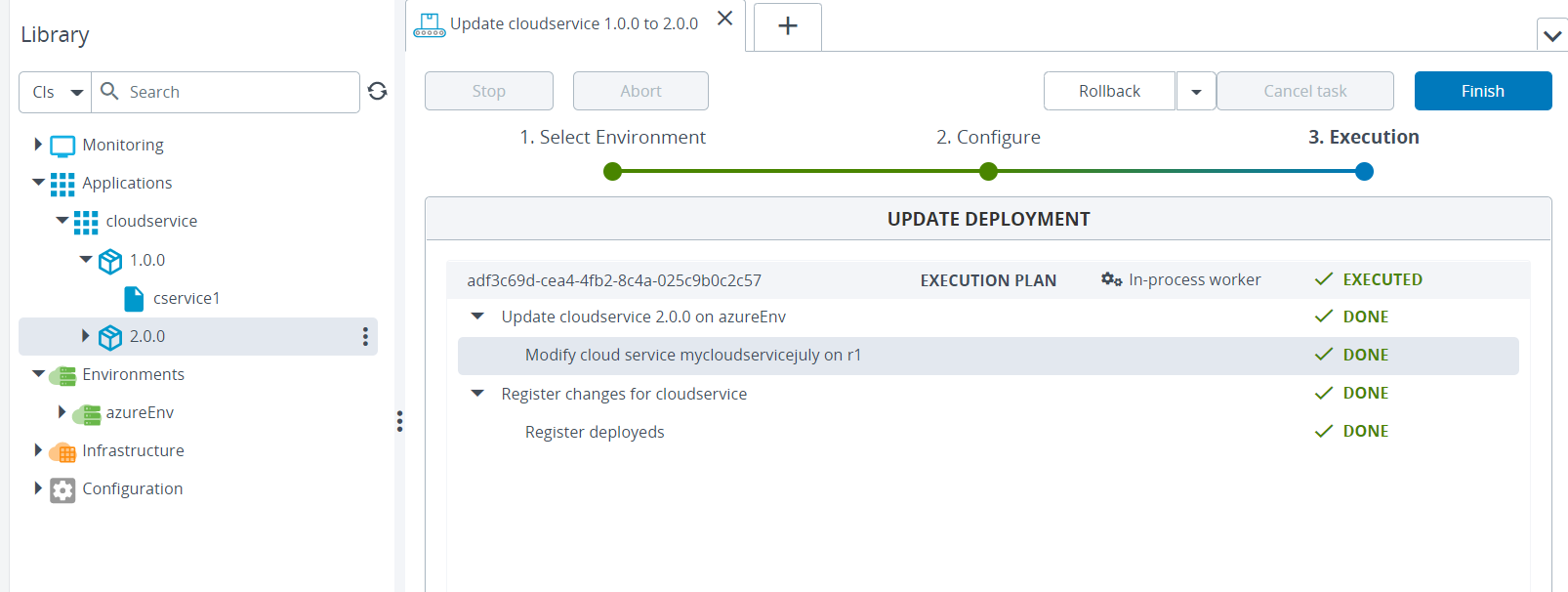
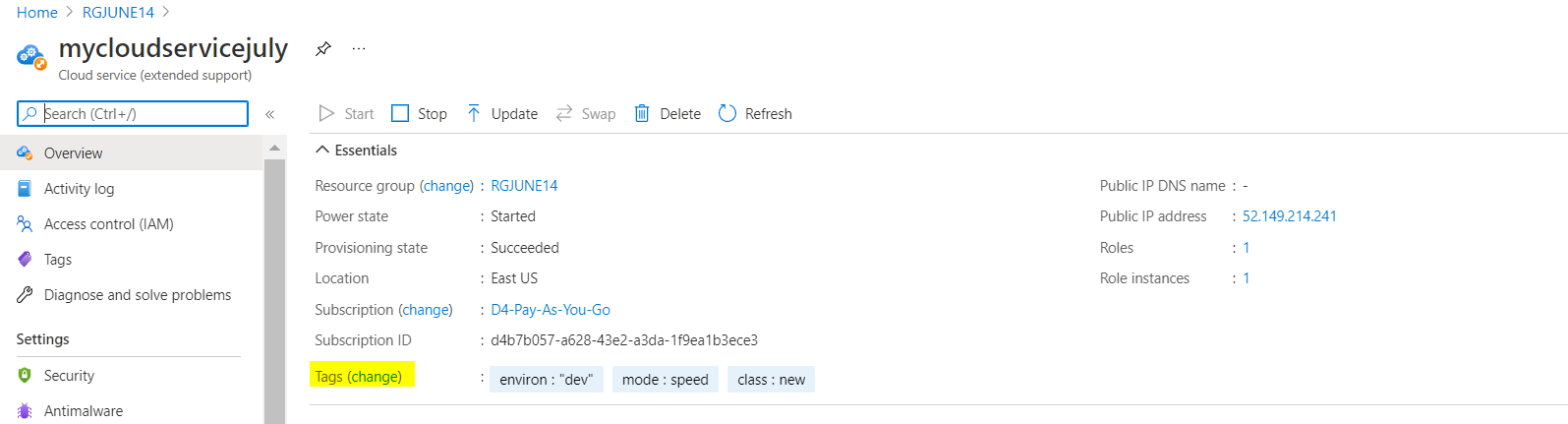
Azure Blueprints
The Azure blueprints allow you to define deployments and releases in YAML templates, simplifying the process of provisioning resources with the Azure plugin. Azure Resource Manager (ARM) templates can also be used to easily define the Azure resource deployments. For more information, see Deploy to Azure with using the ARM template blueprint
The available Azure blueprints are:
- Basic AKS Cluster
- Azure App Service
- Microservice application on Azure Kubernetes service
- Basic ARM Template
For more information on the blueprints, see Deploy/Release Blueprints. This tutorial will help you to for deploy resources to Azure using ARM templates: Deploy to Azure with using the ARM template blueprint.
Azure WebApp
The Deploy Azure WebApp provides a host service to create and deploy web apps. To create Webapp on your Azure environment, you can configure the Azure WebApp Tags.
You can also configure the following using Deploy:
Azure WebApp Tags
This section describes how to configure Azure WebApp tags using Deploy.
Before you create Azure WebApp tags, you must have the following:
- Azure Cloud Infrastructure configured with a valid resource group
- Environment CI that points to the Azure resource group configured
- Webapptag and app service plan packages created or imported into the Deploy server
- Webapp configured with the required apps service plan in your resource group
Step 1 – Create the asp service app on Azure portal
Configure the asp service plan on your Azure environment.
After the deployment is successful, the serviceapp is displayed in the Azure portal.
Step 2 – Create the webapptag on Azure portal
Configure the webapptag 1.0.0 package on your Azure environment.
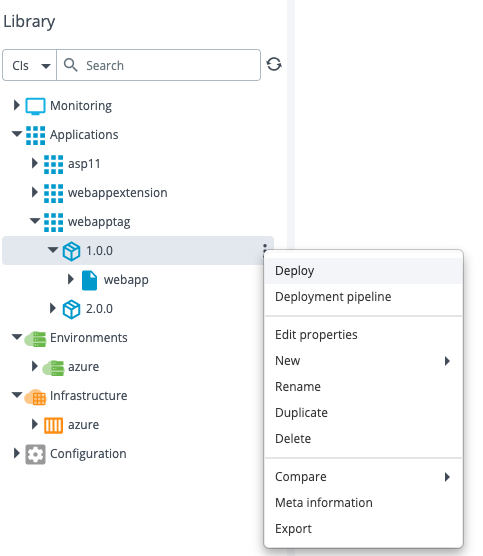
After the deployment is successful, the webapp tags are displayed in the Azure portal.
Step 3 – Update the webapptag Deployment
Update the webapptag deployment to version 2.0.0.
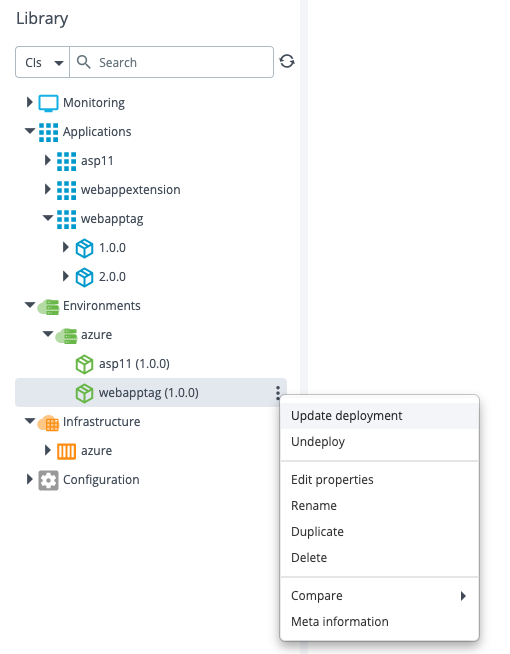
After the update is successful, the new tags are displayed in the Azure portal.
To undeploy the webapp tag, do the following:
- From Environments, click azure > webapptag 2.0.0 and perform a rollback to the earlier deployment version. After the rollback is successful, the original tags from webapptag 1.0.0 are displayed in the Azure portal.
- Right-click webapptag 2.0.0 and click Undeploy to remove webapp from Azure portal.
Azure WebApp Slots
This section describes how to configure Azure WebApp slots using Deploy.
Step 1 – Perform the deployment of web app slot on Azure portal
Deploy the webappslot app on your Azure environment.
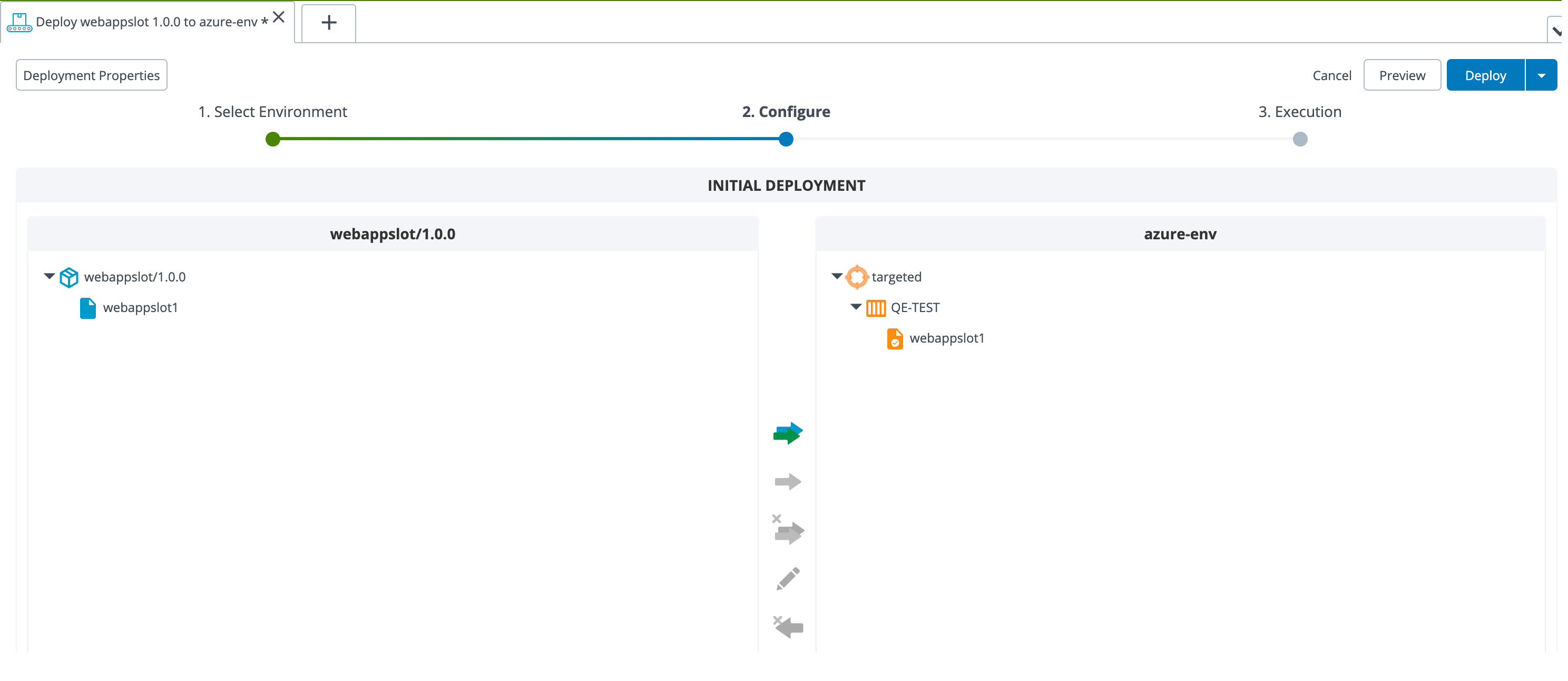
After the deployment is successful, verify the new deployment slot in the Azure portal.
Azure WebApp Logging
This section describes how to configure Azure logging using Deploy.
Step 1 – Ensure the serviceapp and webapptag are deployed successfully
See Azure WebApp Tags steps 1 and 2.
Step 2 – Perform the deployment of webapplogging on Azure portal
Configure the webapplogging 1.0.0 package on your Azure environment.
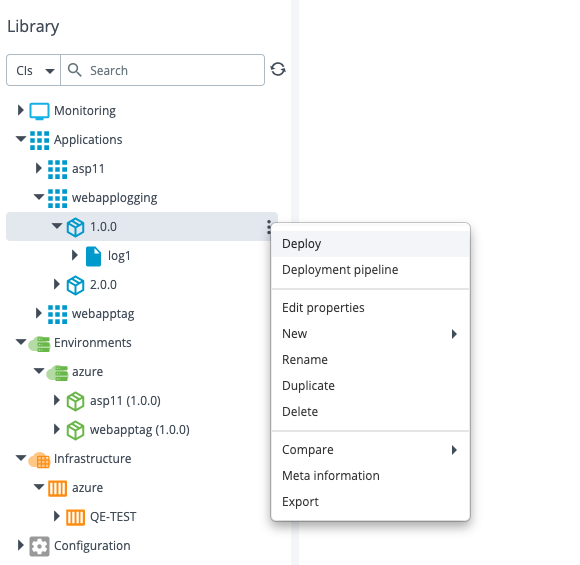
After the deployment is successful, the App Service Logs settings are updated in the Azure portal.
Step 3 – Update the webapplogging Deployment
Update the webapplogging deployment to version 2.0.0.
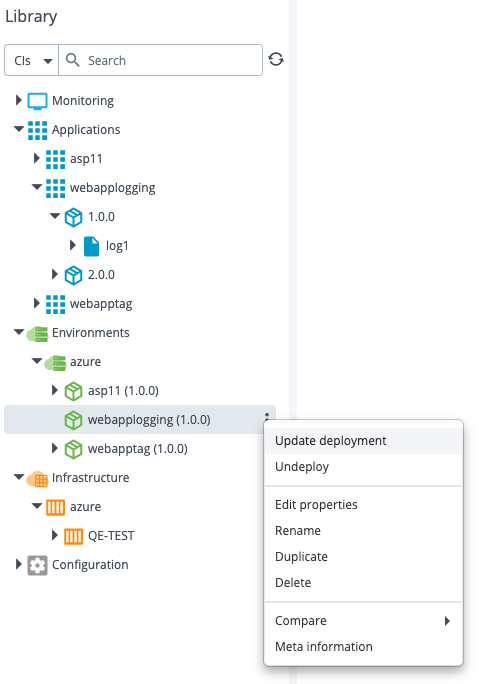
After the update is successful, the App Service Logs settings are updated in the Azure portal.
Azure WebApp Extensions
This section describes how to configure WebApp Extensions using Deploy.
Step 1 – Ensure the serviceapp and webapptag are deployed successfully
See Azure WebApp Tags steps 1 and 2.
Step 2 – Perform the deployment of webappextension on Azure portal
Configure the webappextension 1.0.0 package on your Azure environment.
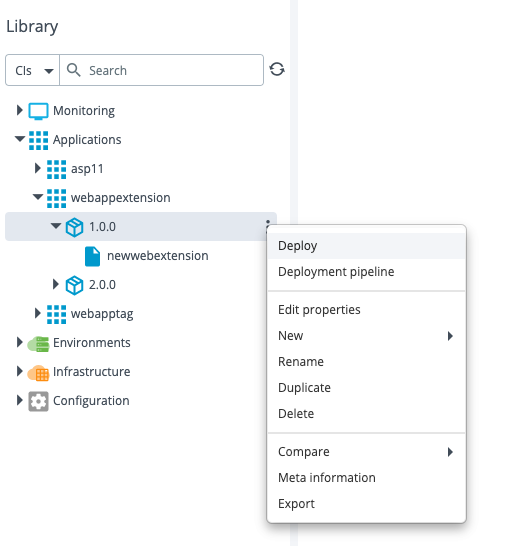
After the deployment is successful, the .NET Raygun APM extension for the web app is displayed in the Azure portal.
Step 3 – Update the webappextension Deployment
Update the webappextension deployment to version 2.0.0.
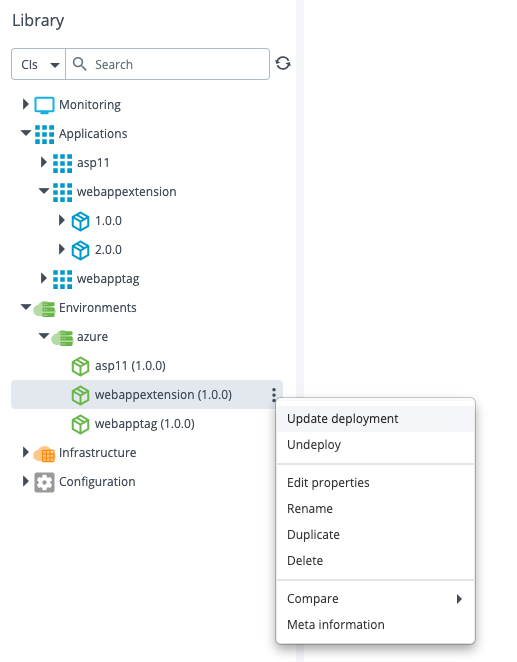
After the update is successful, the extensions for the web app are removed from the Azure portal.
Azure FunctionApp
The Deploy Azure FunctionApp provides functionality in Digital.ai Deploy to create and deploy FunctionApp in specified Resource Group.
Before you create Azure FunctionApp, you must have the following:
- Azure Cloud Infrastructure configured with a valid resource group
- Environment CI that points to the Azure resource group configured
Azure FunctionApp Using an Image
This section describes how to configure Azure FunctionApp using image stored in a repository.
Step 1 – Configure the required Prerequisites.
Step 2 – Fill the required fields in the azure.FunctionAppImage configuration item.
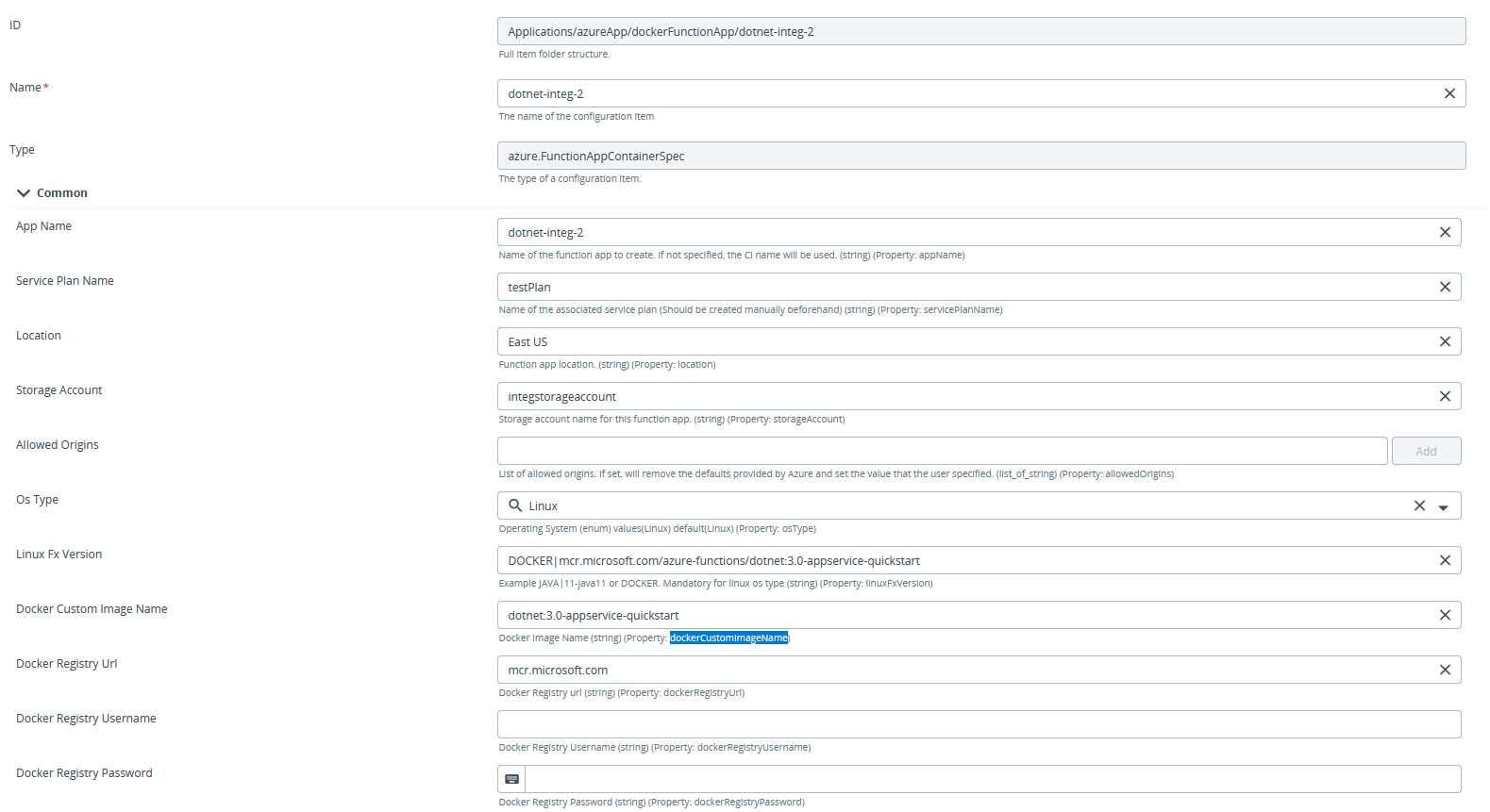
Step 3 – Deploy the Configuration Item to the Deployable.
Deploy the FunctionApp on your Azure environment.
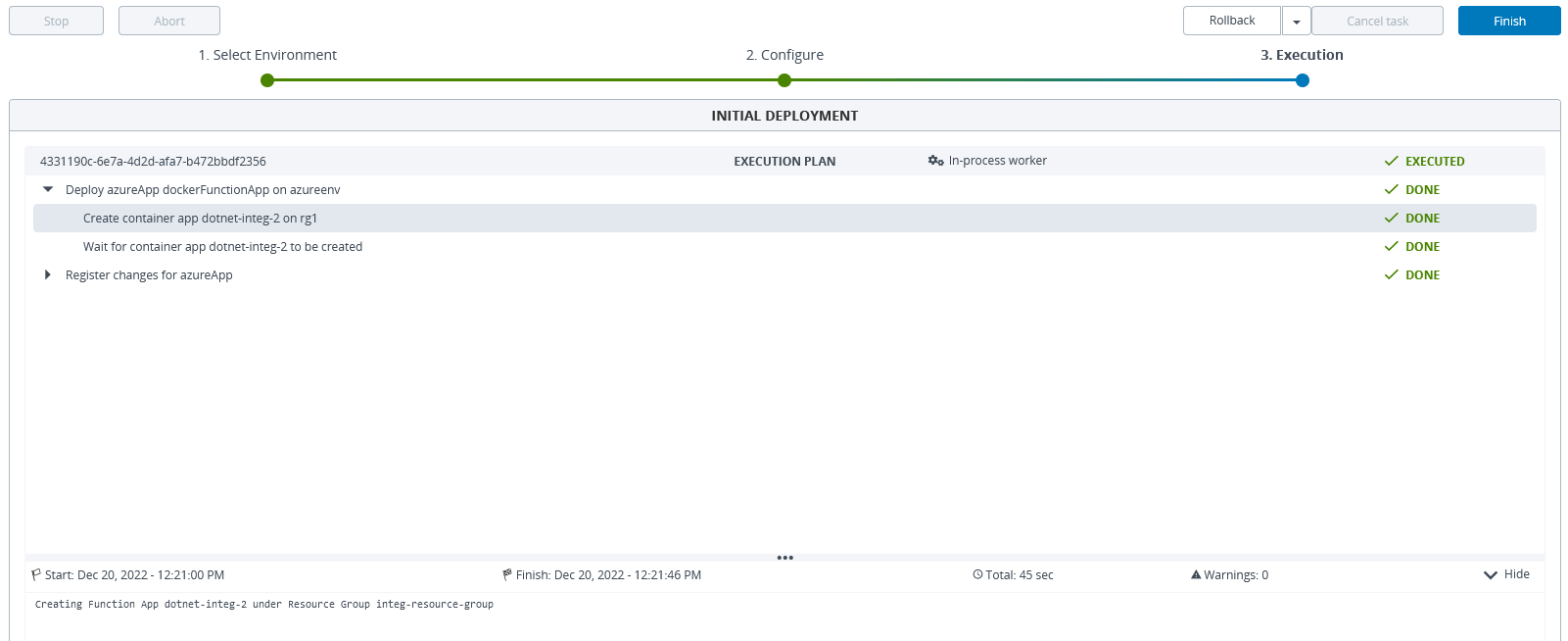
Azure FunctionApp Using a Zip file
This section describes how to configure Azure FunctionApp using zip file as artifact.
Step 1 – Configure the required Prerequisites.
Step 2 – Fill the required fields in the azure.FunctionAppZip configuration item.
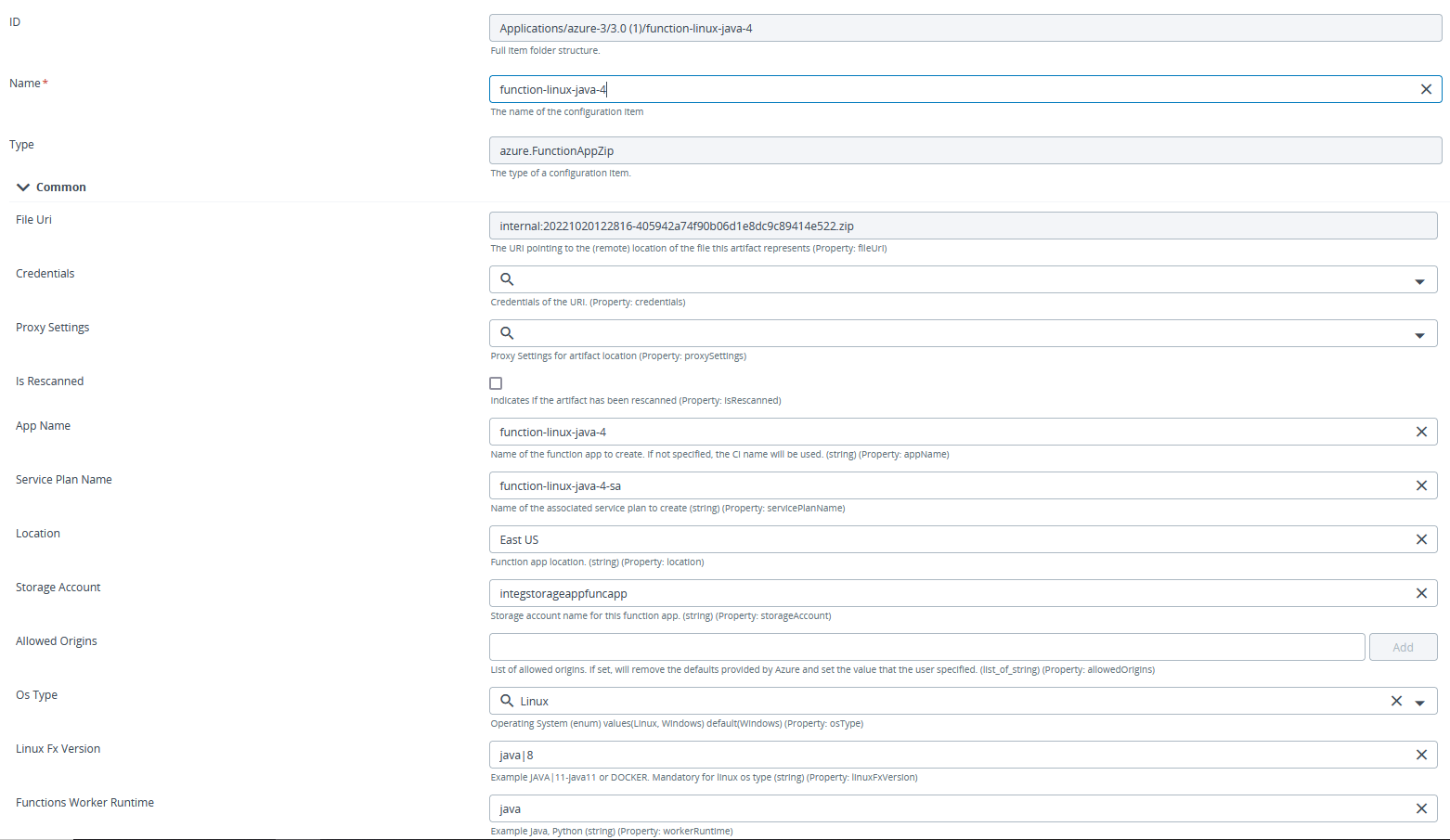
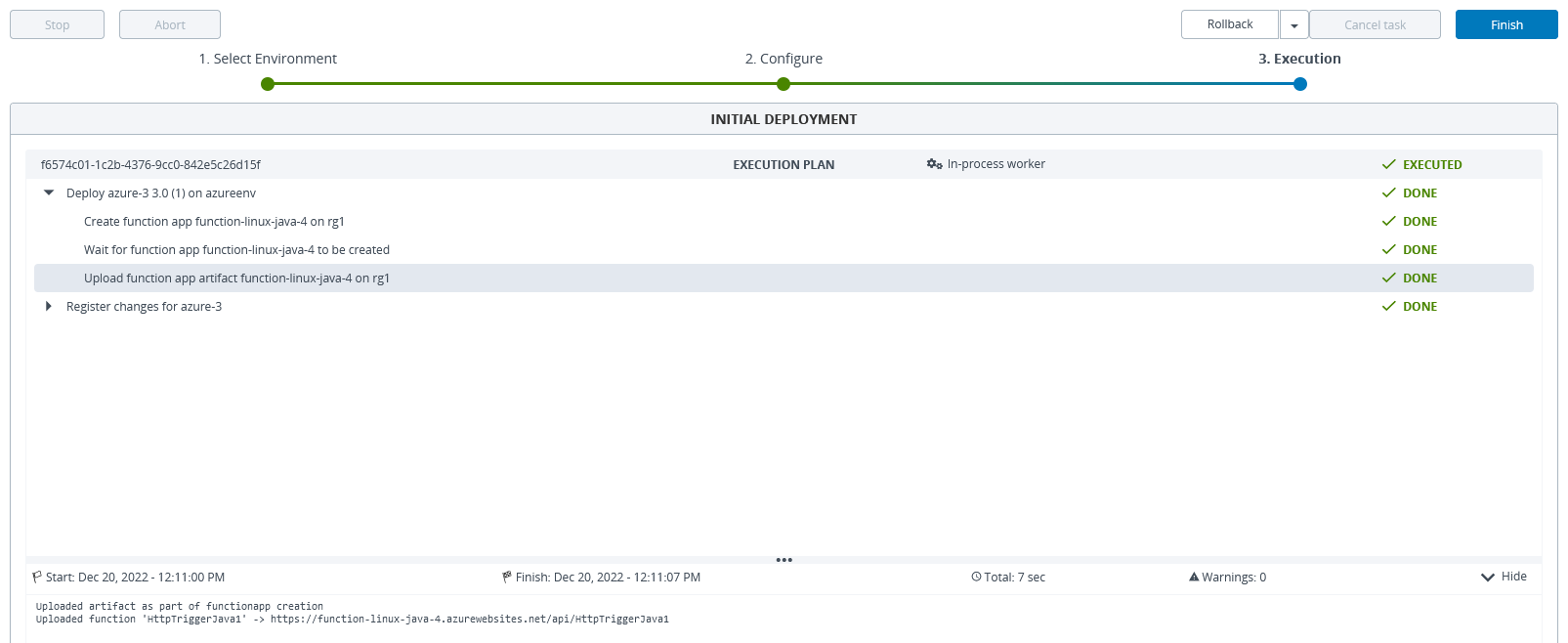
Step 3 – Deploy the Configuration Item to the Deployable.
Deploy the FunctionApp on your Azure environment.
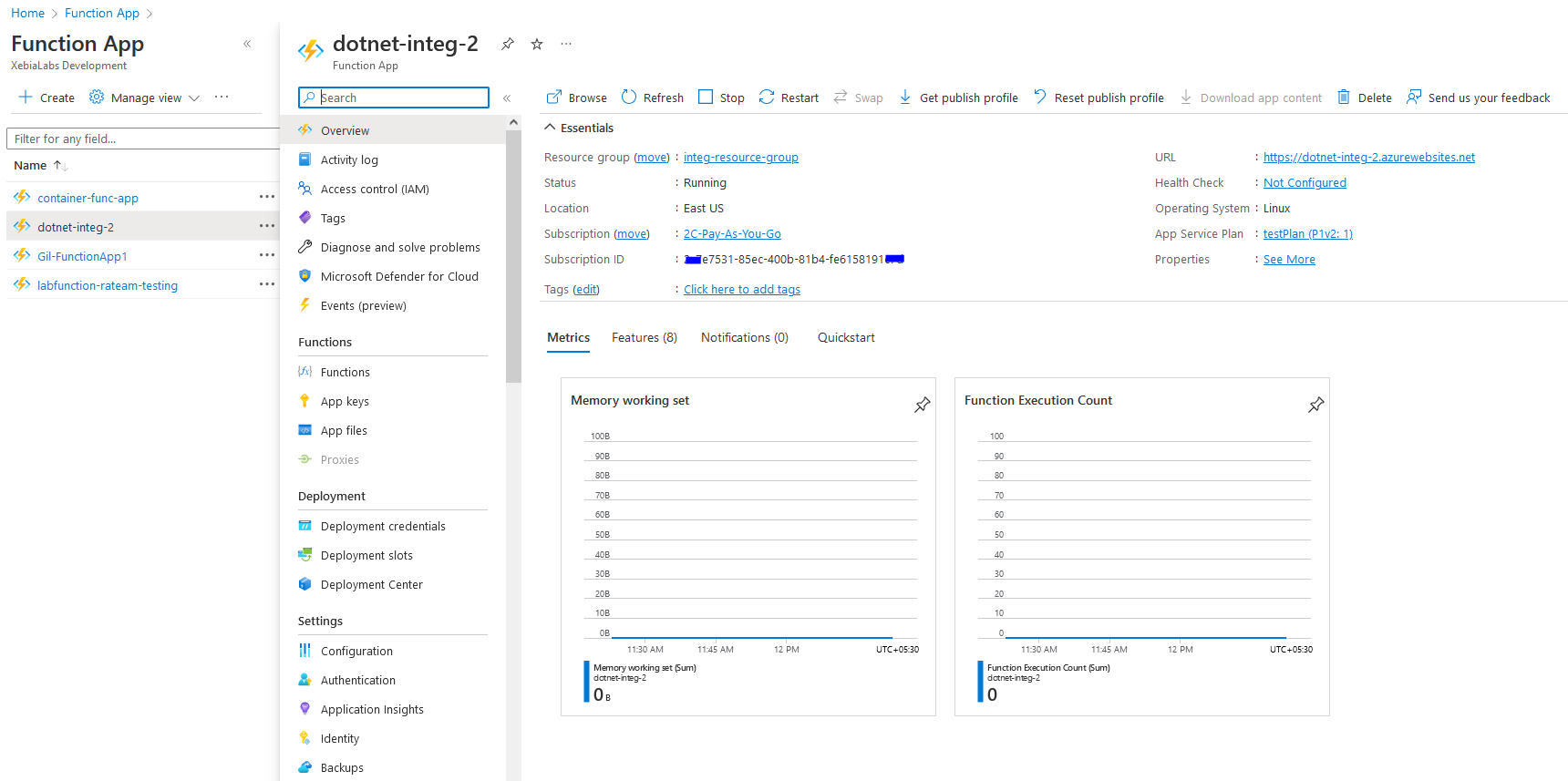
Verify the created Azure FunctionApp in Azure portal
After the deployment is successful, verify the newly created FunctionApp in the Azure portal.
Azure Create Container Group in Azure Resource Group with Instance spec
The Deploy Azure ContainerGroupSpec and ContainerInstanceSpec provides functionality in Digital.ai Deploy to create and deploy Container with an image in Azure Container Instances under a resource group.
Before you create Azure Container, you must have the following:
- Azure Cloud Infrastructure configured with a valid resource group
- Environment CI that points to the Azure resource group configured
Azure ContainerGroupSpec to create Container Group
This section describes how to configure Azure ContainerGroupSpec.
Step 1 – Configure the required Prerequisites.
Step 2 – Fill the required fields in the azure.ContainerGroupSpec configuration item.
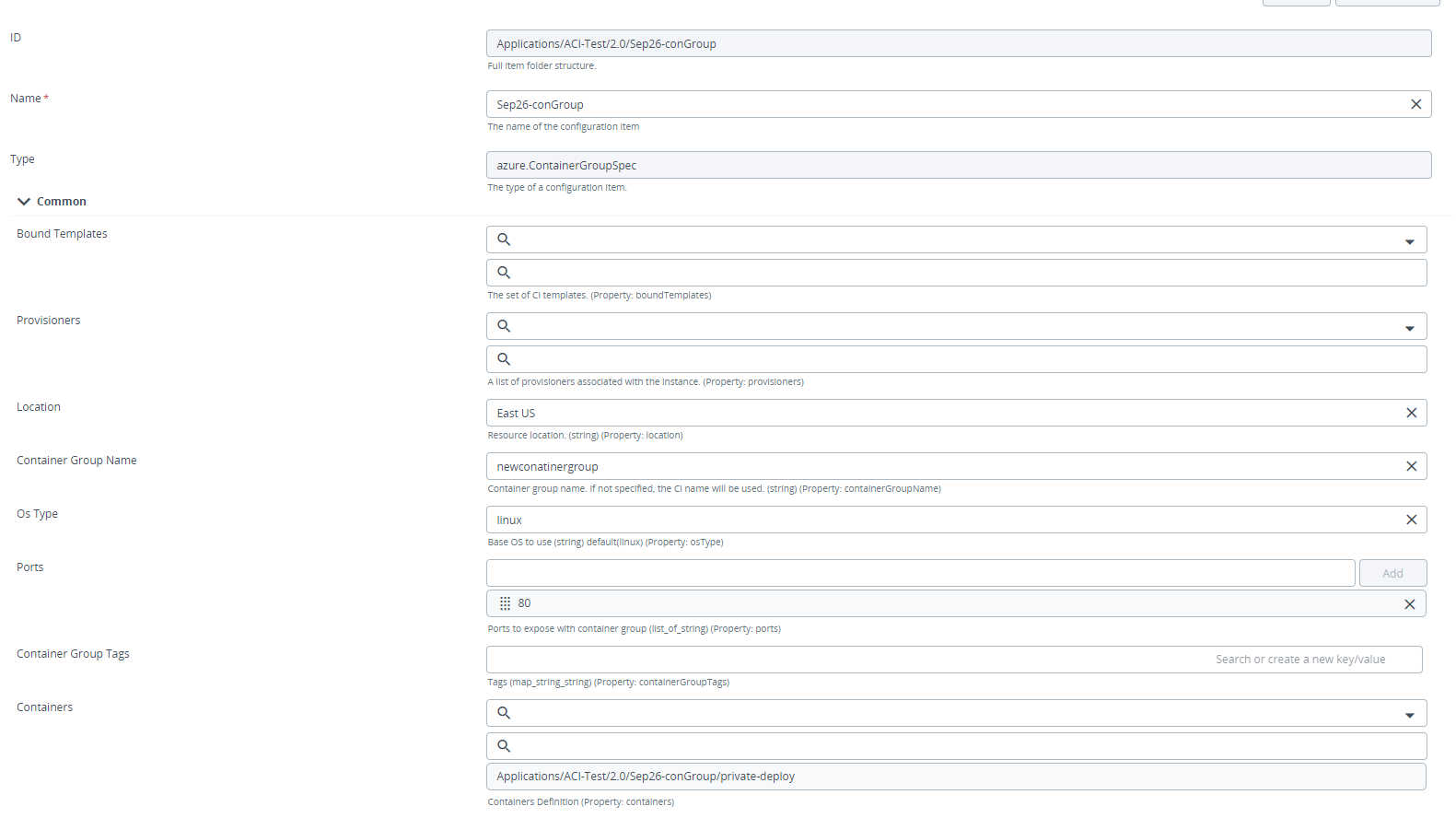
Step 3 – Hover over created azure.ContainerGroupSpec configuration item, click  , and select New > Azure > ContainerInstanceSpec.
, and select New > Azure > ContainerInstanceSpec.
Step 4 – Fill the required fields in the azure.ContainerInstanceSpec configuration item.
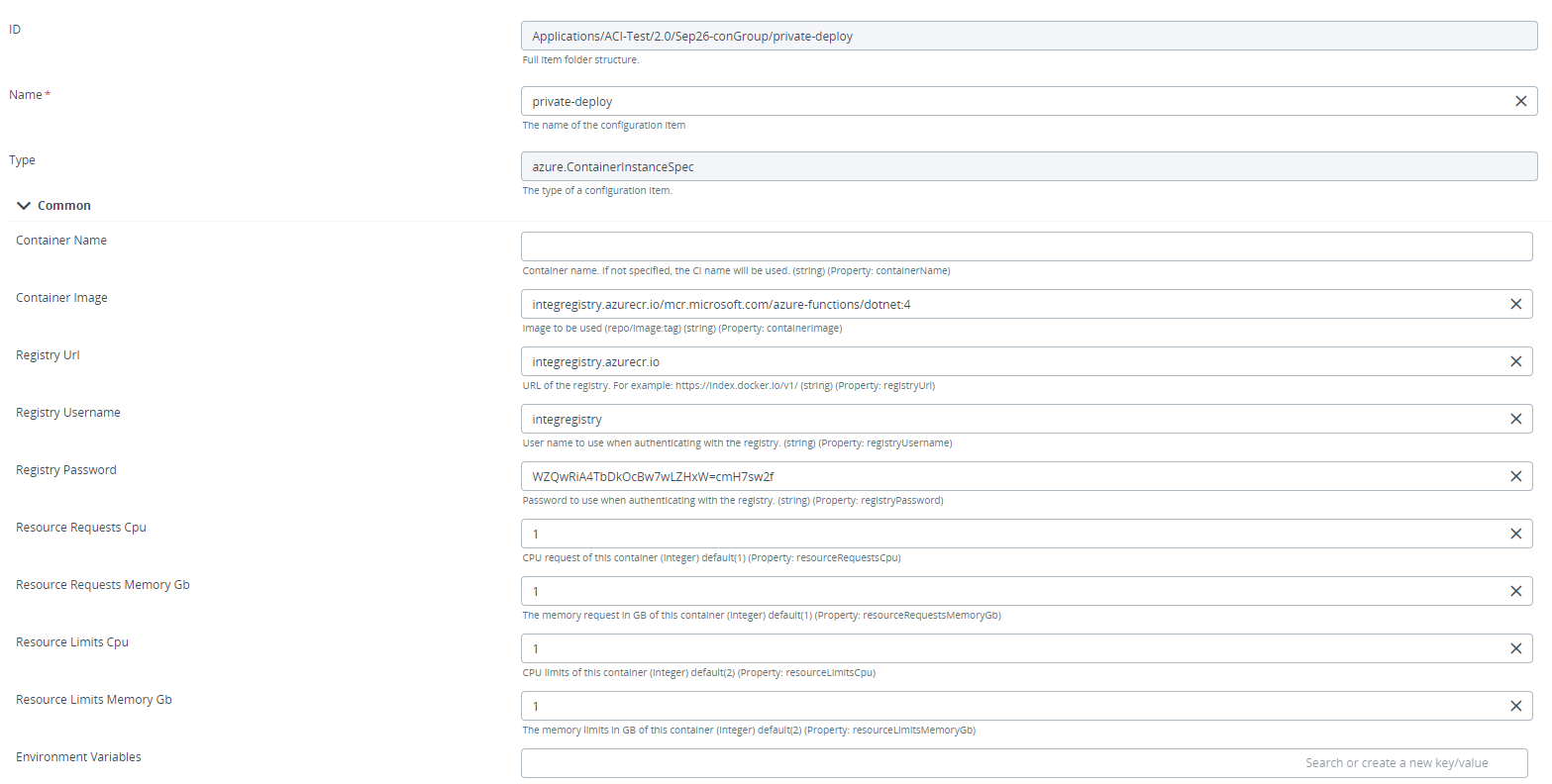
Step 5 – Deploy the Configuration Item to the Deployable.
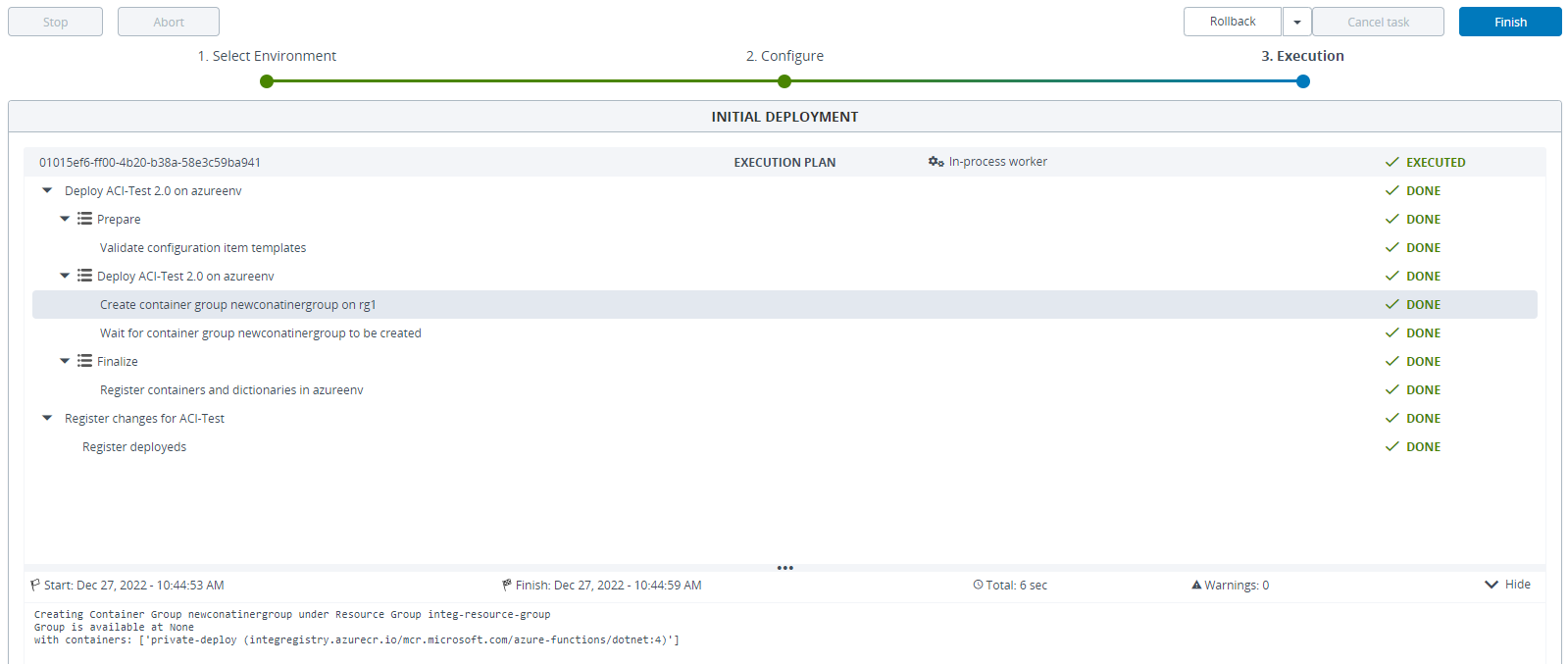
Step 6 – Verify the Newly Created Container Group in Azure Portal.
Step 7 – Update the webapptag Deployment.
Azure Create Resources in Azure Resource Group using Bicep Template
The Deploy Azure Bicep deployment provides functionality in Digital.ai Deploy to deploy Bicep template resources under a resource group.
Before you create Azure Container, you must have the following:
- Azure Cloud Infrastructure configured.
- Environment CI that points to the Azure Cloud configured.
Azure ContainerGroupSpec to create Container Group
This section describes how to configure Azure Bicep template configuration Item.
Step 1 – Configure the required Prerequisites.
Step 2 – Fill the required fields in the azure.bicep.Template configuration item.
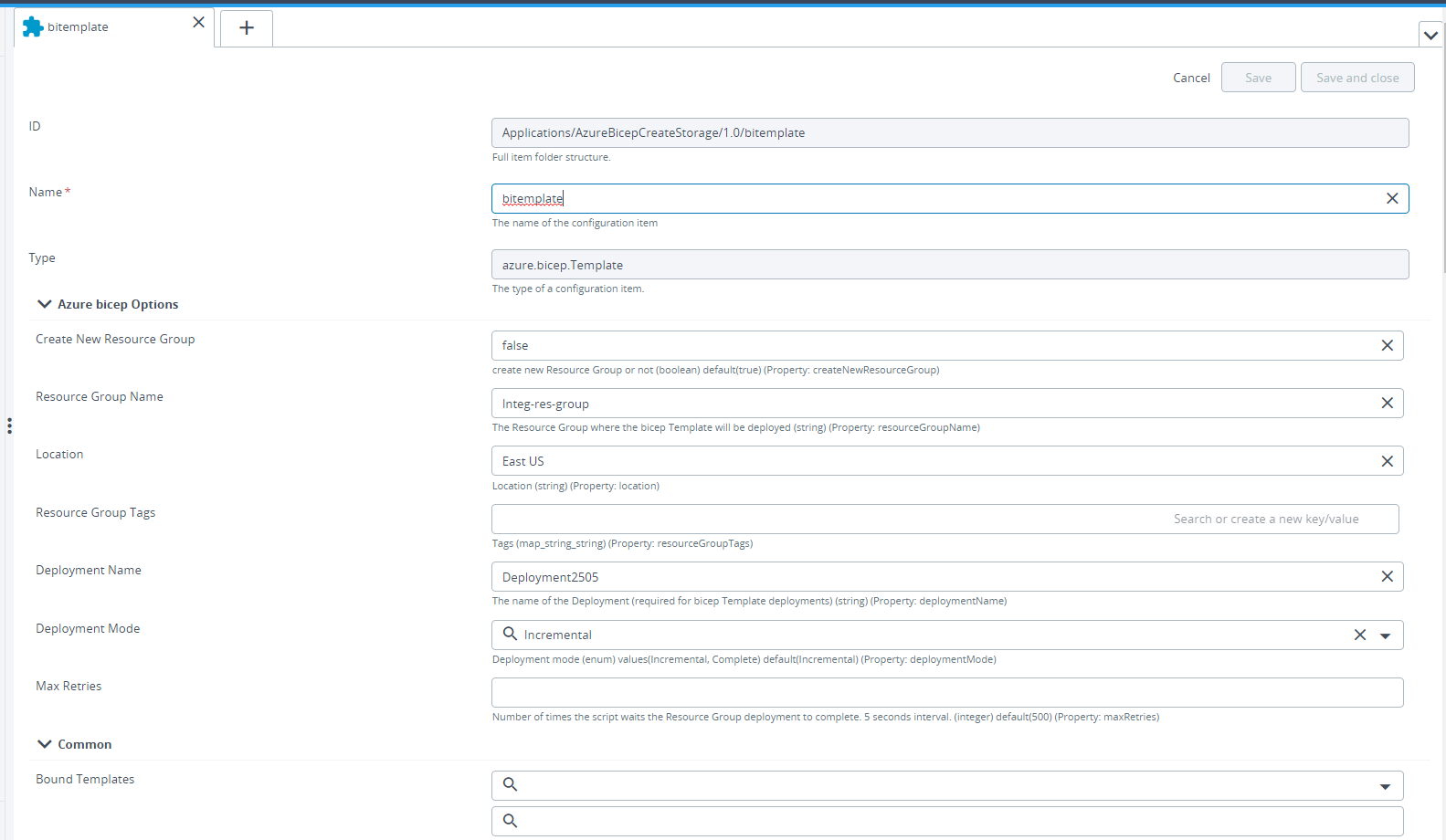
Input Variables can be added in the Input Variables field. For Object Type send a Dict String {'tag1':'value1'}
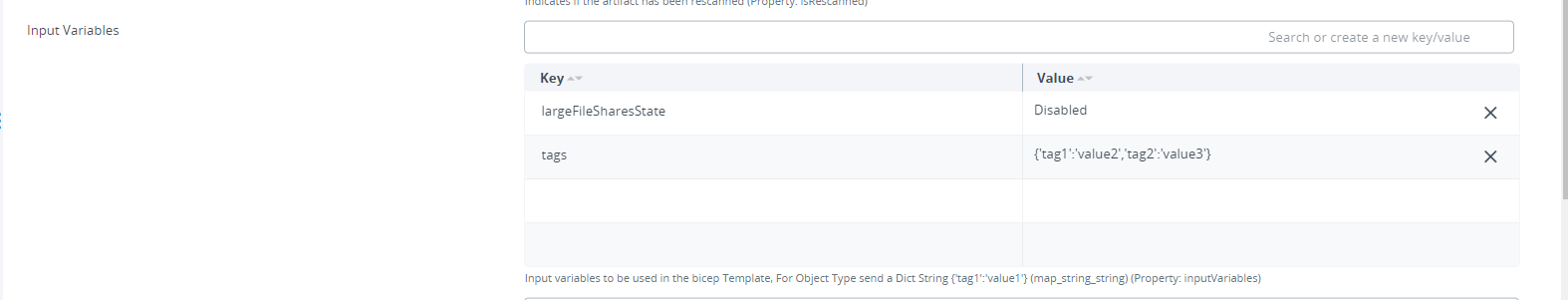
Step 3 – Deploy the Configuration Item to the Deployable.
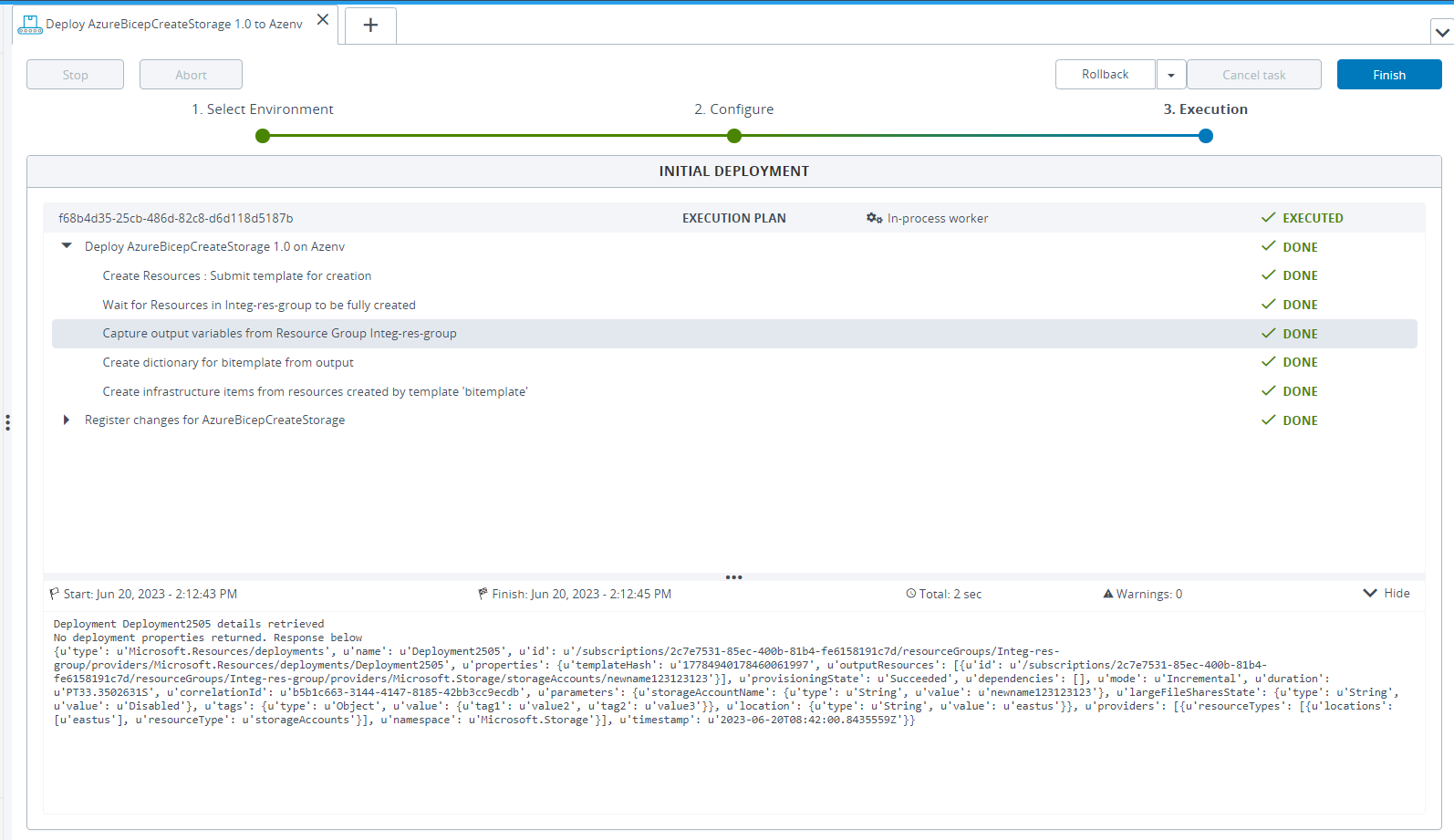
Step 4 – Verify the Newly Created resources in Azure Portal.