AWS plugin
This topic outlines the AWS plugin for Deploy, which supports launching, managing, and configuring various AWS services.
The Amazon Web Services (AWS) plugin for Deploy supports:
- Launching and terminating AWS Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) and Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) instances
- Deploying applications to AWS cloud-based instances
- Using Amazon's Elastic Load Balancing feature for EC2 instances
- Creating and using Simple Storage Service (S3) buckets for file storage
- Provisioning EC2 Container Service (ECS) clusters, tasks, and services
- Using the Relational Database Service (RDS) for databases
- Using the Elastic Block Store (EBS) for persistent block storage
- Provisioning AWS Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) instances and deploying applications to those instances
- Deploying network configurations such as Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) instances, subnets, routing tables, and network interfaces
- Deploying load balancing configurations to AWS Elastic Load Balancing (ELB)
- Deploying storage configurations such as Elastic Block Store (EBS) volumes and Simple. Storage Service (S3) buckets for file storage
- Deploying content to S3 buckets
- Deploying tasks and services to ECS clusters
- Provisioning and working with EC2 Container Registry (ECR) repositories
- Provisioning and working with Relational Database Service (RDS) instances
- Deploying AWS Lambda functions
- Provisioning AWS API Gateway to invoke Lambda functions
- Authenticating via SSO credentials instead of access keys
- Launching AWS Service Catalog products
Note: Deploy AWS Plugin does not support deploying to AWS Auto Scaling Groups (ASGs).
For information on AWS requirements and the configuration items (CIs) that the plugin supports, see AWS Plugin Reference.
Note: To avoid warning when you check the connection for aws.Cloud, enable Verify SSL to true in aws.Cloud CI.
Features
- Create virtual machines on Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) with a specified Amazon Machine Image (AMI).
- Automatically destroy EC2 instances during undeployment.
- Provision a Simple Storage Service (S3) bucket.
Attach an elastic IP address with a non-VPC EC2 instance
Create and attach an elastic IP address with a non-Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) EC2 instance:
- Go to the Elastic IP tab.
- Set Attach Elastic IP to
true. - Set Elastic IP Domain to
standard. A new elastic IP is created and attached to the non-VPC EC2 instance. Note: If the EC2 instance is stopped state, the elastic IP is detached and is reattached by the plugin when you restart the EC2 instance.
Detach an elastic IP address with a non-Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) EC2 instance:
- During a MODIFY operation, set the Elastic IP property to
false. - Alternatively, perform an undeployment to release the elastic IP.
Attach an elastic IP address with VPC EC2 instance
Create and attach an elastic IP with a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) EC2 instance:
- Go to the Elastic IP tab.
- Set Attach Elastic IP to
true. - Set Elastic IP Domain to
standard. A new elastic IP is created and attached to the default network interface connected to the EC2 instance ateth0. Note: If the EC2 instance is restarted, the elastic IP will remain attached to the default network interface and does not need to be reattached.
Detach an elastic IP with a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) EC2 instance:
- During a MODIFY operation, set the Elastic IP property to
false. - Alternatively, perform an undeployment to release the elastic IP.
Create AWS CloudFormation resources
With the Amazon Web Services (AWS) plugin for Deploy, you can create AWS CloudFormation templates and stacks.
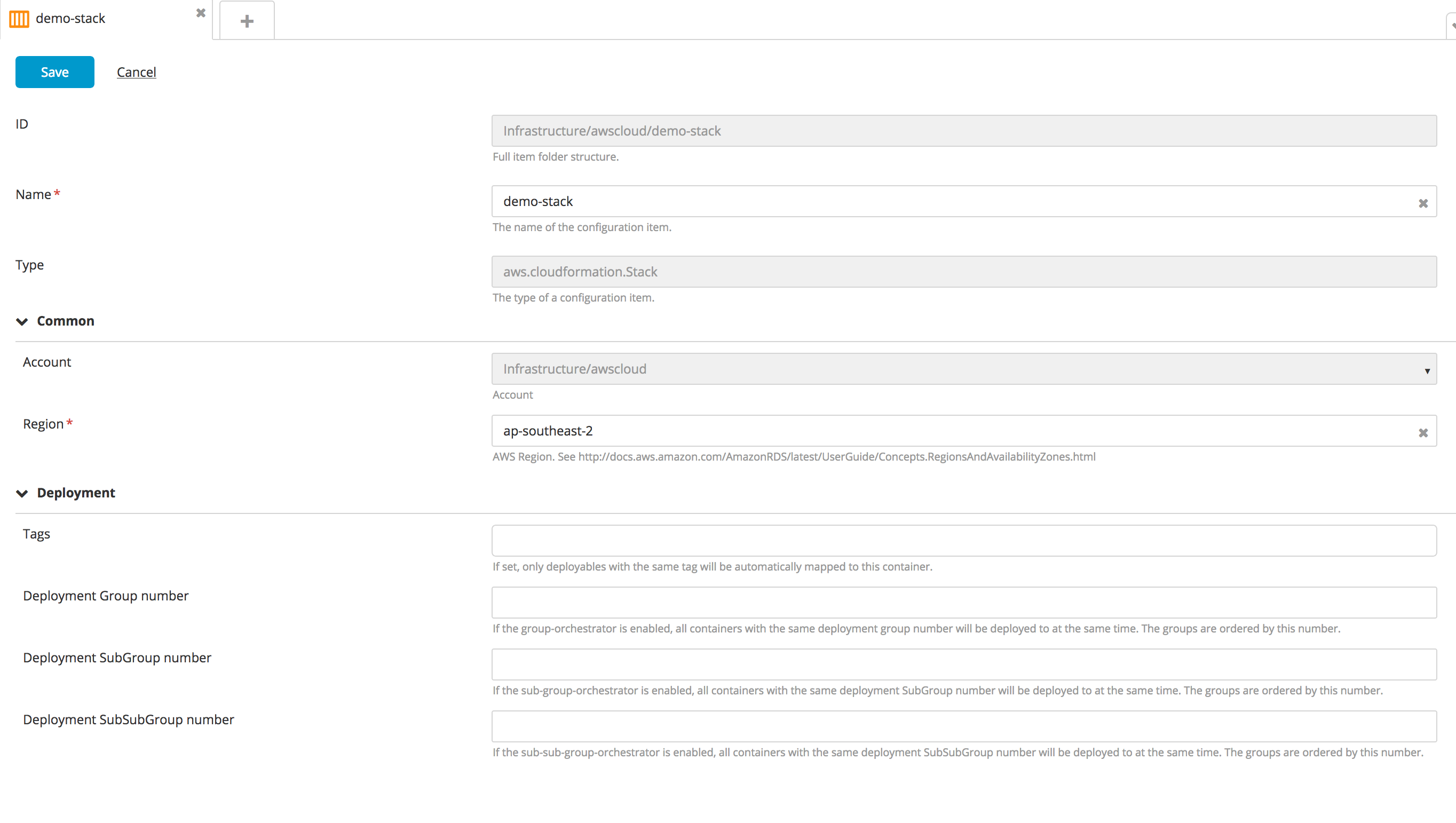
Create a new Stack type embedded infrastructure CI:
- In the top navigation bar, click Explorer.
- Expand the Infrastructure CI list.
- Navigate to a CI of AWS Cloud type, click
, and select New > aws > cloudformation > Stack.
- Specify a name region for the CI.
- Click Save.
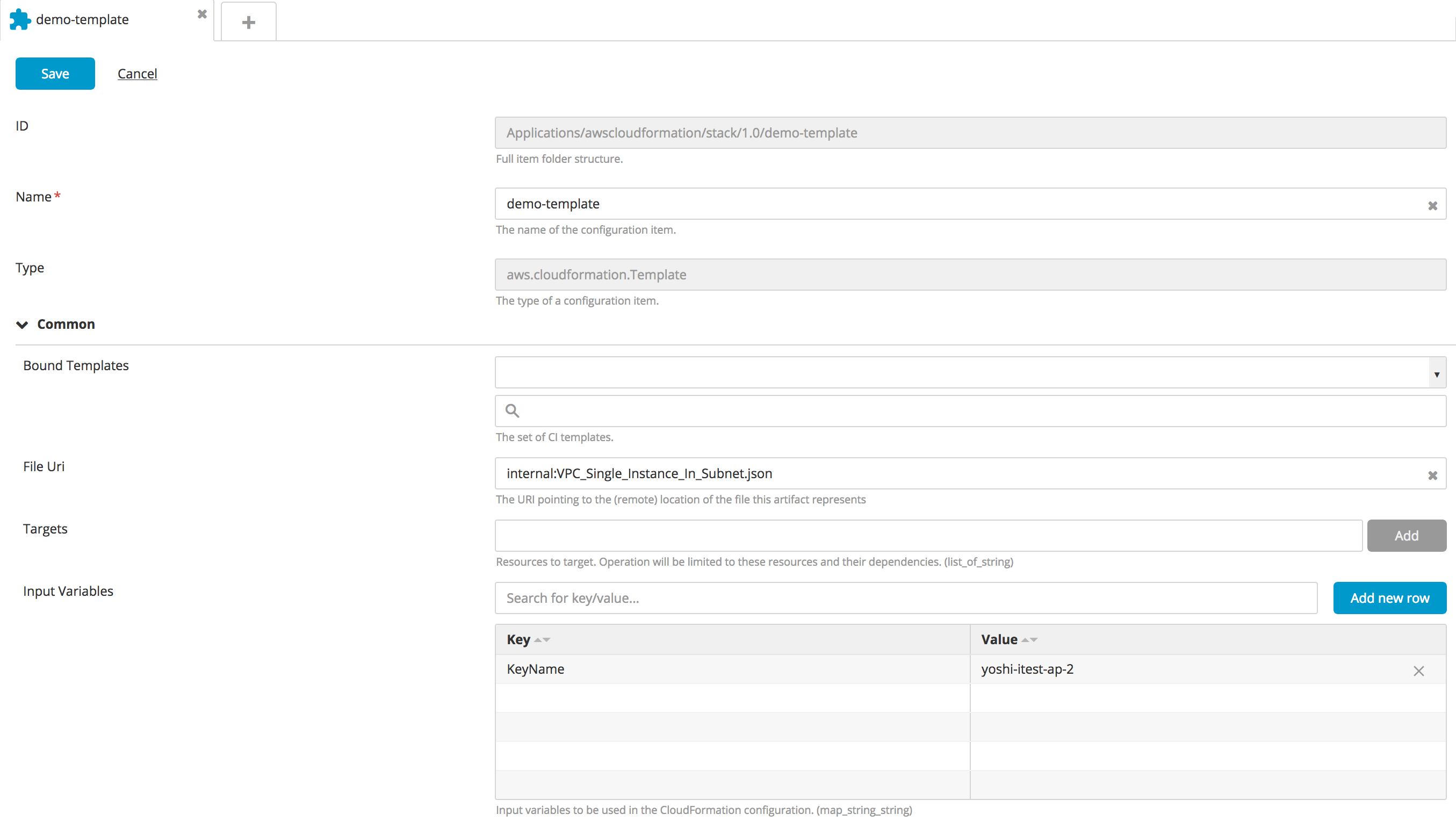
Create a new Template type CI:
- In the top navigation bar, click Explorer.
- Expand an application in the Applications list.
- Hover over a package, click
, and select New > aws > cloudformation > Template.
- Specify a name for the CI, the Json File as per AWS configuration, and the Input variables.
- To bind the templates with output variables, configure the Bound Templates.
Note: You can also create the Deploy resources by configuring them in METADATA section.
"Metadata" : {"XLD::Infrastructure":[{"id":"cloud","type":"core.Directory"},{"id":"cloud/webserver","type":"overthere.SshHost","os":"UNIX","connectionType":"SFTP","address":"{Address}","port":"22","username":"admin"}],"XLD::Environments":[{"id":"cloud-dev","type":"udm.Environment","members":[{"ci ref":"Infrastructure/cloud/webserver"}]}]} - Click Save.
Launch AWS Service Catalog resources
With the Amazon Web Services (AWS) plugin for Deploy, you can launch AWS Service Catalog product.
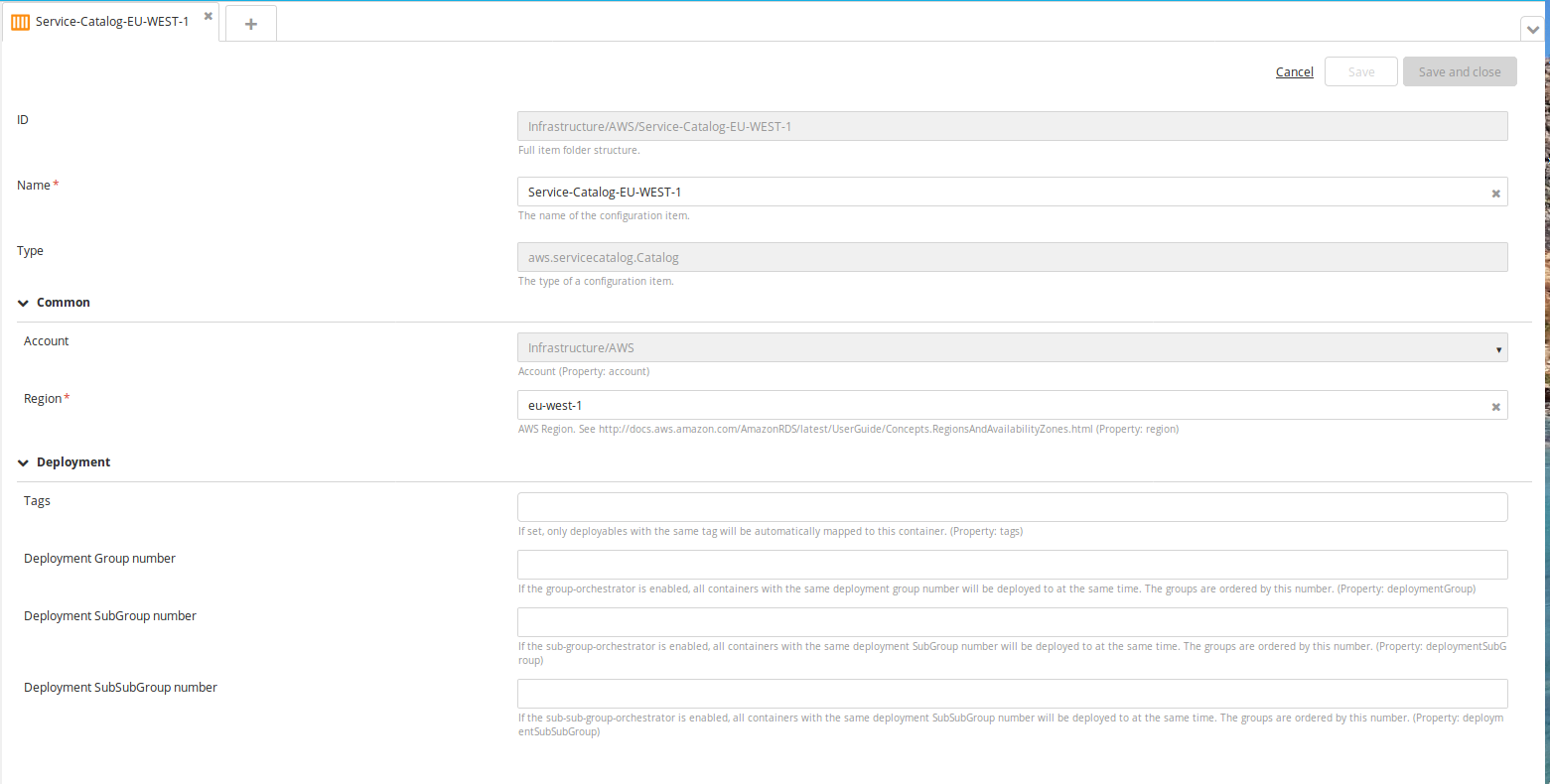
Create a new Catalog type embedded infrastructure CI:
- In the top navigation bar, click Explorer.
- Expand the Infrastructure CI list.
- Navigate to a CI of AWS Cloud type, click
, and select New > aws > servicecatalog > Catalog.
- Specify a name region for the CI.
- Click Save.
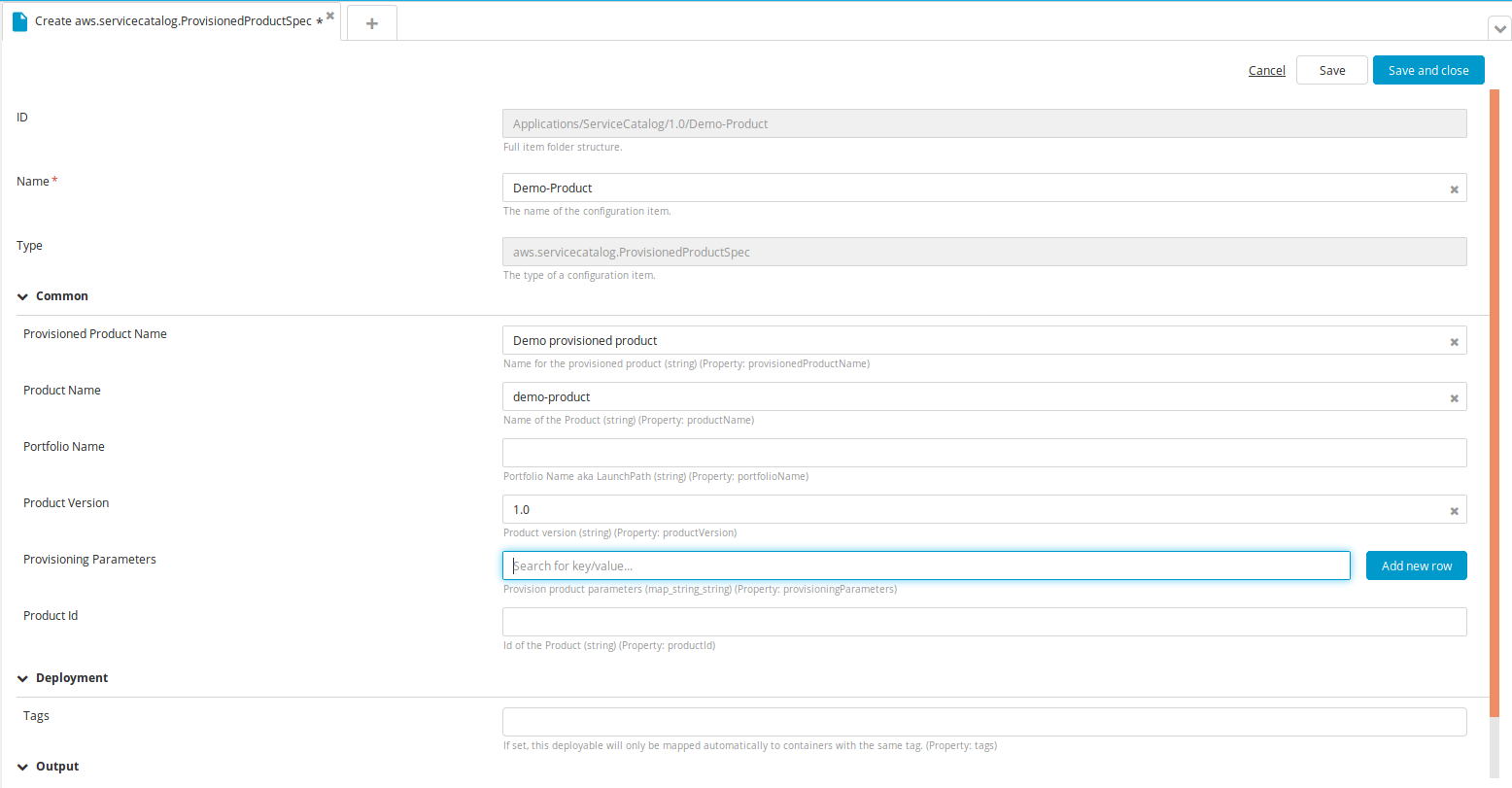
Create a new ProvisionedProductSpec type CI:
- In the top navigation bar, click Explorer.
- Expand an application in the Applications list.
- Hover over a package, click
, and select New > aws > servicecatalog > ProvisionedProductSpec.
- Specify a name for the CI, Product Name, Product Version, and Provisioning Parameters, if there are any. Note: When the CI is deployed on the deployed type (ProvisionedProduct), you can see the output of the stack that the product created. It will be empty if there are no outputs on the stack.
- Click Save.
Create AWS ECS resources
With the Amazon Web Services (AWS) plugin for Deploy, you can create cluster instances and ECS task and services. The ECS task and services are deployed over an AWS cluster and run on the instances of the cluster. Amazon specifies the AMIs which are optimized for ECS For more information, see Amazon ECS-Optimized Amazon Linux AMI.
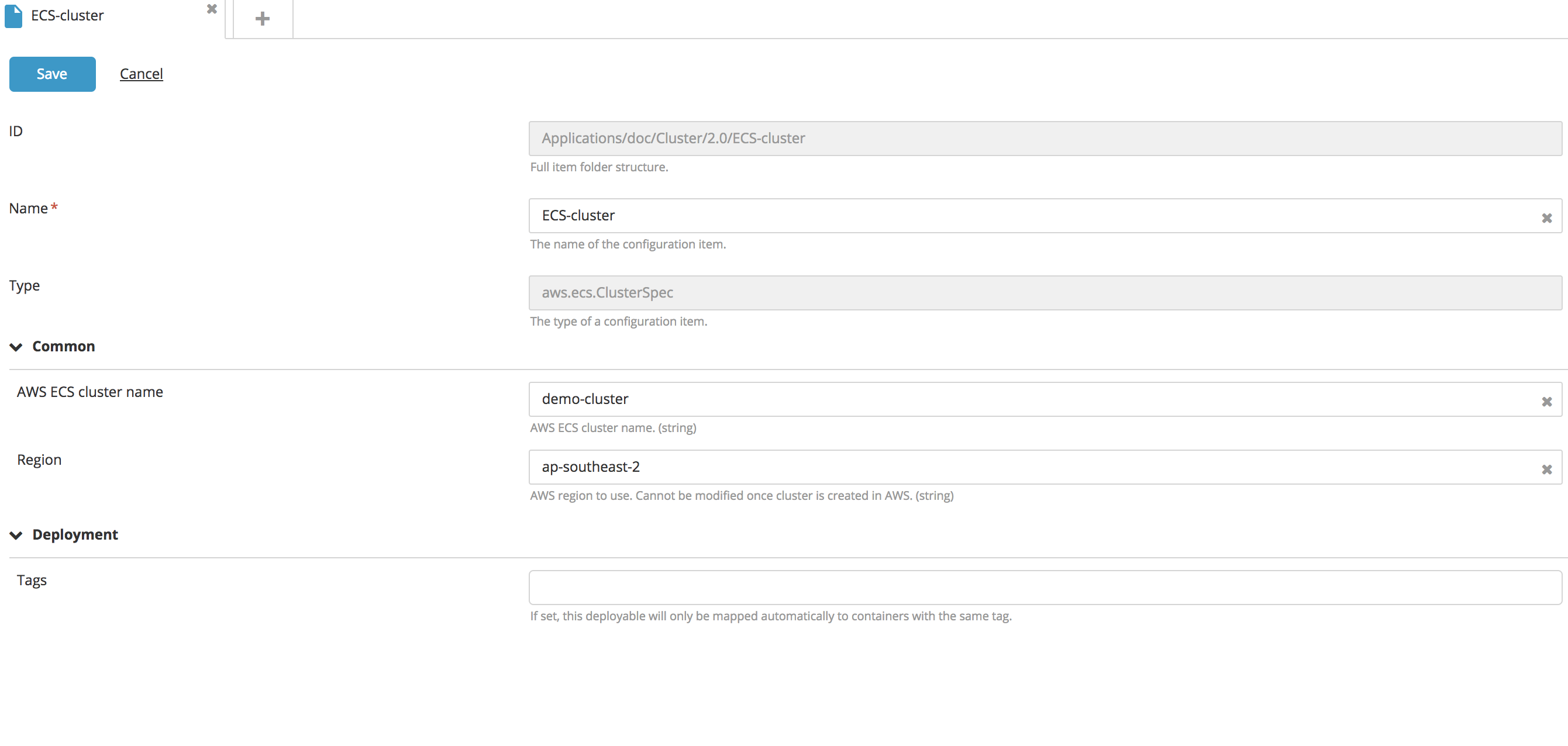
Create a new Cluster type CI:
- In the top navigation bar, click Explorer.
- Expand an application in the Applications list.
- Hover over a package, click
, and select New > aws > ecs > ClusterSpec.
- Specify a name for the CI, the AWS ECS Cluster Name, and the Region.
- Click Save.
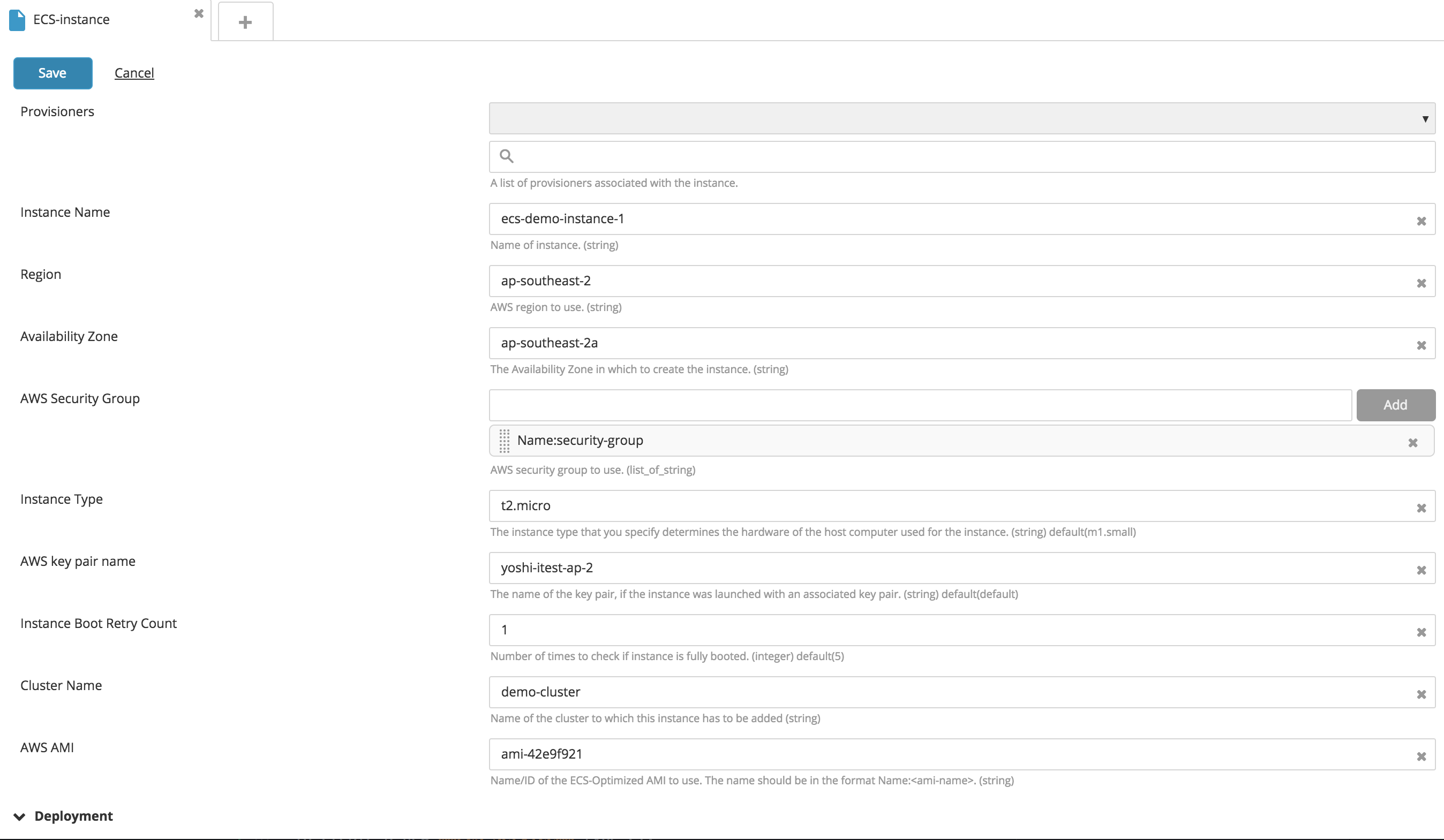
Create a new Cluster (Container) Instance type CI:
- In the top navigation bar, click Explorer.
- Expand an application in the Applications list.
- Hover over a package, click
, and select New > aws > ecs > ContainerInstanceSpec.
- Go to the Create EC2 instances section.
- Fill in the following fields: Instance Name, Region, Availability Zone, AWS Security Group, AWS ECS Cluster Name, AMI ID, and IAMRole. Note: Container instance is an extension of the EC2 instance type. It supports all properties supported by the instance type.
- Click Save.
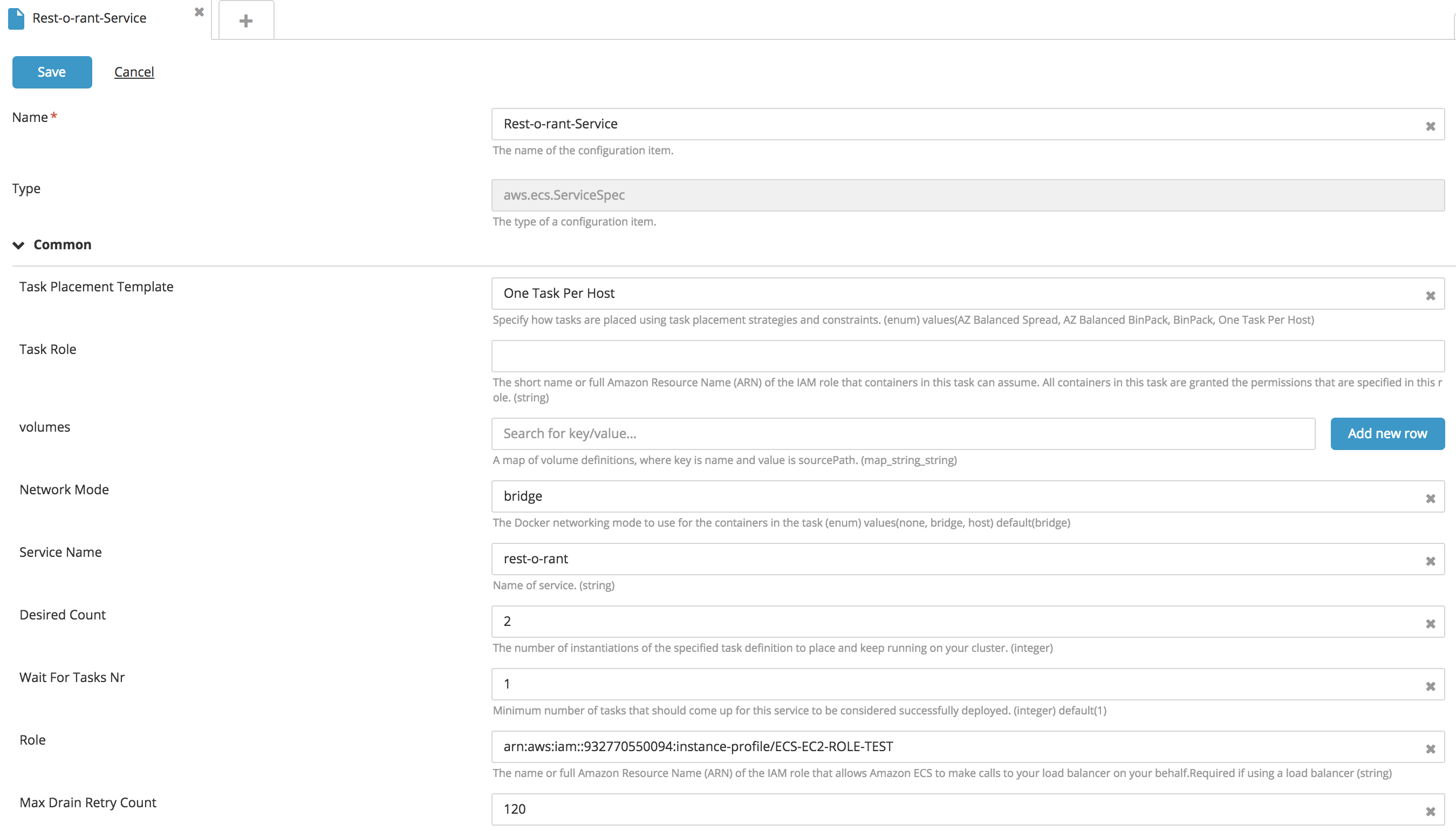
Create a new ECS Service type CI:
- In the top navigation bar, click Explorer.
- Expand an application in the Applications list.
- Hover over a package, click
, and select New > aws > ecs > ServiceSpec.
- Fill in the following fields: Name, Task Placement Template, Volumes, Network mode, and Service name.
- To configure the number of instances of a running task, enter a value for the Desired Count property.
- To attach the IAM Role to the EC2 instance, specify the IAMRole property.
- To configure a deployment configuration, specify values for the Maximum Percent and Minimum Healthy Percent properties. Note: The ECS Service contains an embedded CI for configuring Load Balancers and Container Definitions.
- To set the PidMode and IpcMode, choose an option from the corresponding drop down boxes.
- Click Save.
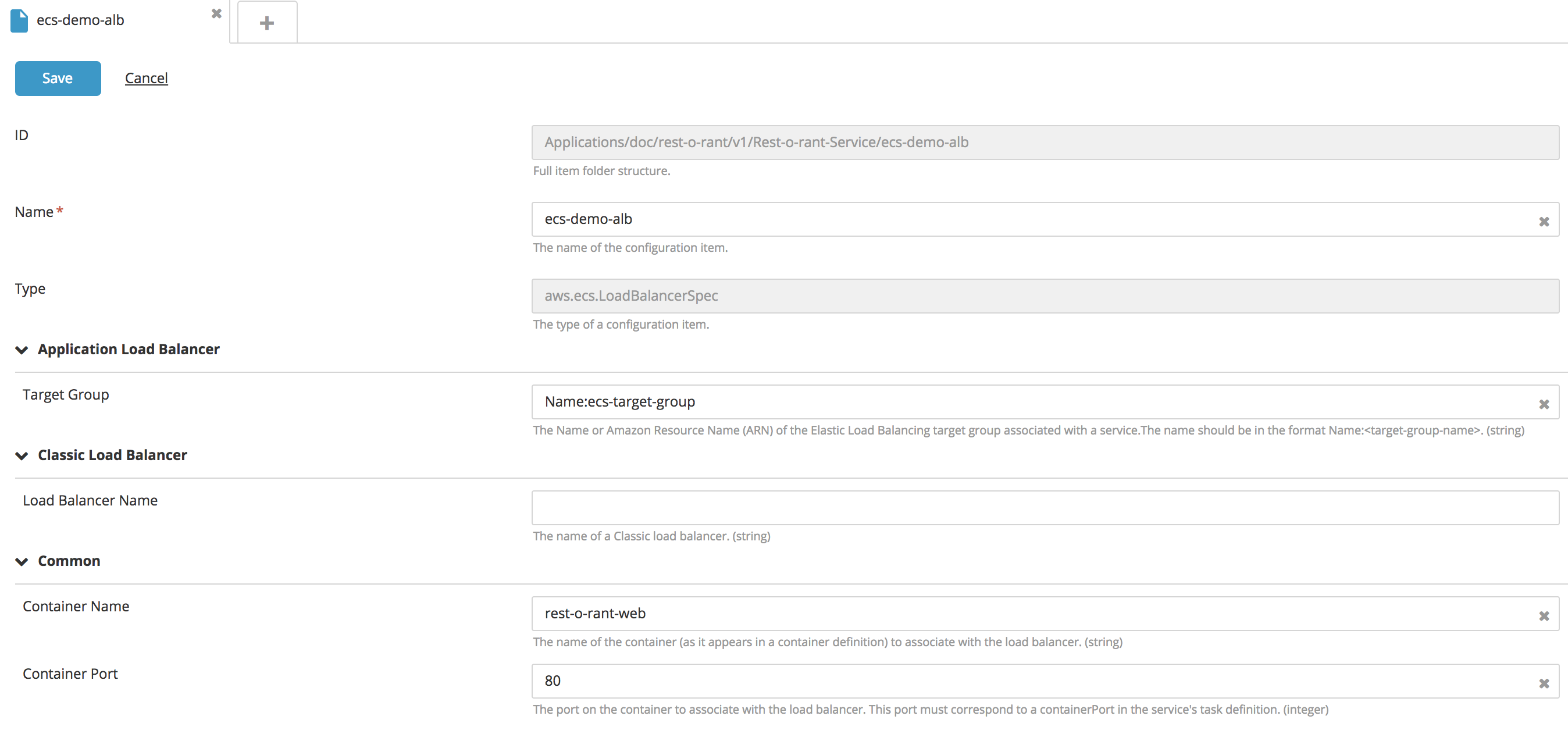
Create a new ECS Service Load Balancer type embedded CI:
- In the top navigation bar, click Explorer.
- Expand an application in the Applications list.
- Navigate to ECS Service, click
, and select New > aws > ecs > LoadBalancerSpec.
- Fill in the following fields: Name and Load Balancer Name.
- To configure the attached container configuration, specify the Container Name and Container Port properties.
- Click Save.
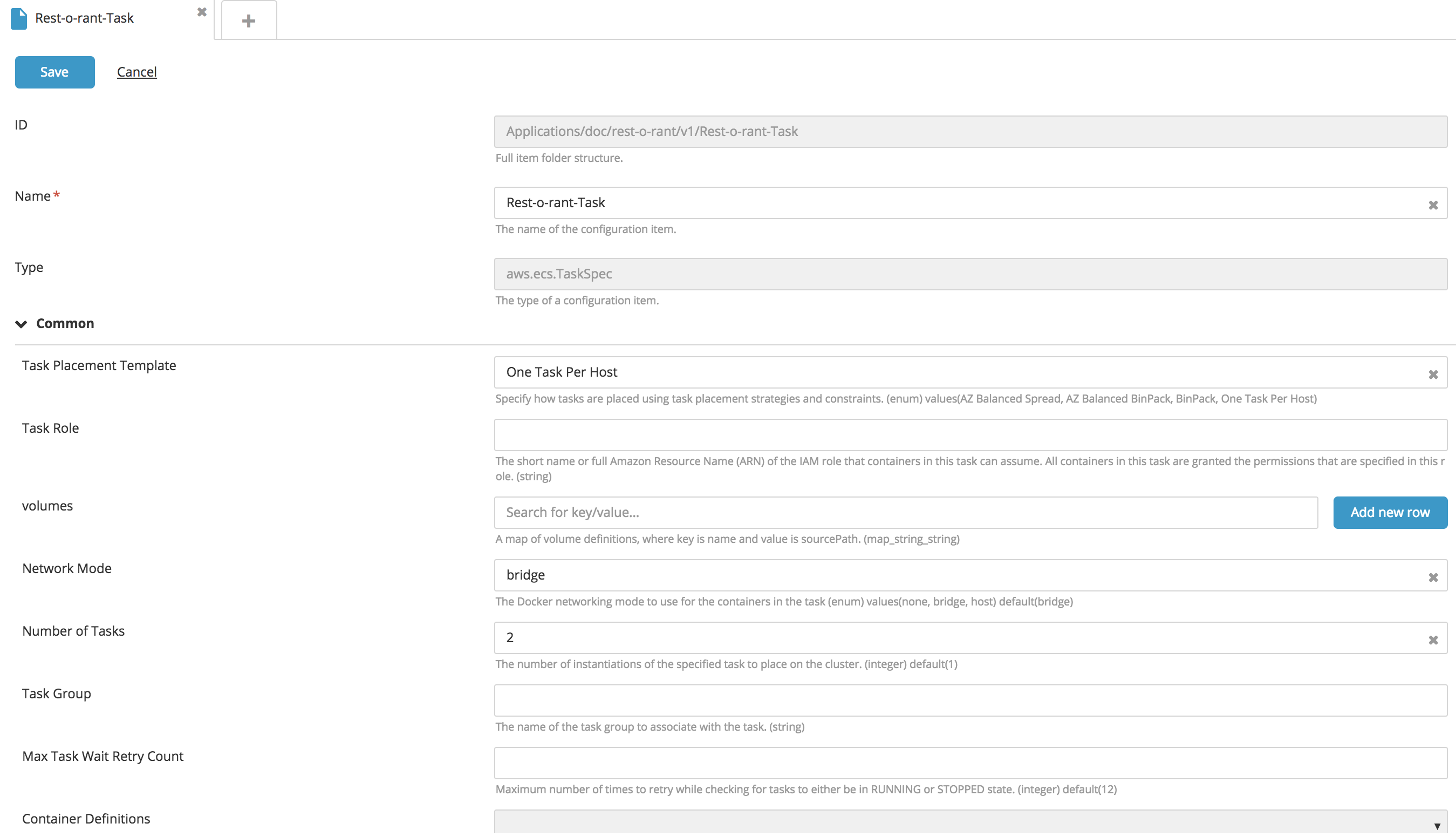
Create a new ECS Task type CI:
- In the top navigation bar, click Explorer.
- Expand an application in the Applications list.
- Hover over a package, click
, and select New > aws > ecs > TaskSpec.
- Fill in the following fields: Task Placement Template, Task Role, Volumes, and Network mode.
- To configure the number of tasks, enter a value for the Number of Tasks property.
- To attach the IAM Role to the EC2 instance, specify the IAMRole property.
- Click Save. Note: The ECS Service contains an embedded CI for configuring Container Definitions. To configure, see Create a new ECS Service/Task Container type embedded CI.
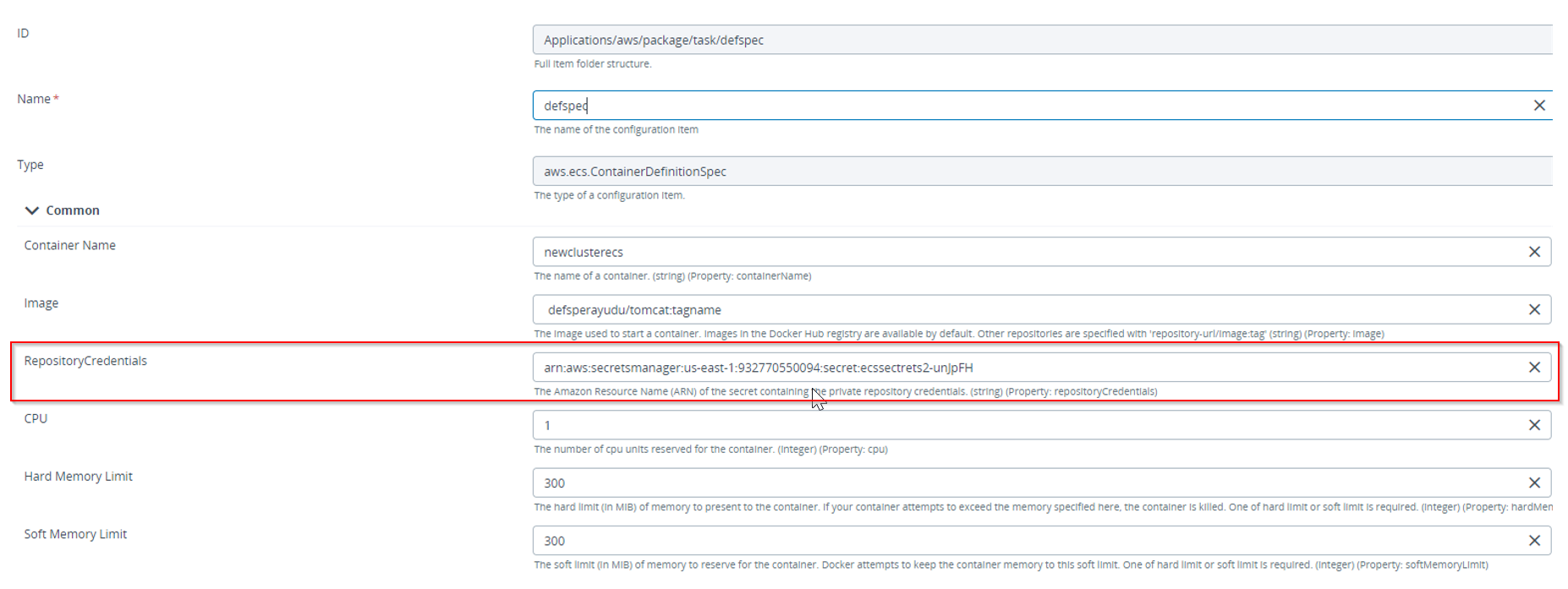
Create a new ECS Service/Task Container type embedded CI:
- In the top navigation bar, click Explorer.
- Expand an application in the Applications list.
- Navigate to an ECS Service or ECS Task, click
, and select New > aws > ecs > ContainerDefinitionSpec.
- Fill in the Container Name and Image fields.
- In the Repository Credentials field, enter the Amazon Resource Name (ARN) of the secret that contains the Private Repository credentials.
Note: The Private Repository Image used in TaskSpec should be provided with Private Repository credentials. - To configure the memory limit, specify values for the Hard Memory Limit and Soft Memory Limit properties.
- Optionally specify values for dnsSearchDomains, dnsServers, entryPoint, startTimeout, stopTimeout, essential, hostname, pseudoTerminal, user, readonlyRootFilesystem, dockerLabels and healthCheck
- Click Save.
Note: The ECS Container contains an embedded CI for configuring Mount Points and Port Mappings. Mount Points are used for mounting the volume and Port Mappings for mapping the ports. Other embedded CIs include environmentFiles, resourceRequirements, ulimits, secrets, extraHosts, systemControls, linuxParameters. For accepted values for these parameters please see AWS ECS Register Task Definition.
Create network resources
With the Amazon Web Services (AWS) plugin for Deploy, you can create various network resources: VPCs, subnets, internet gateway, routing tables, and others.
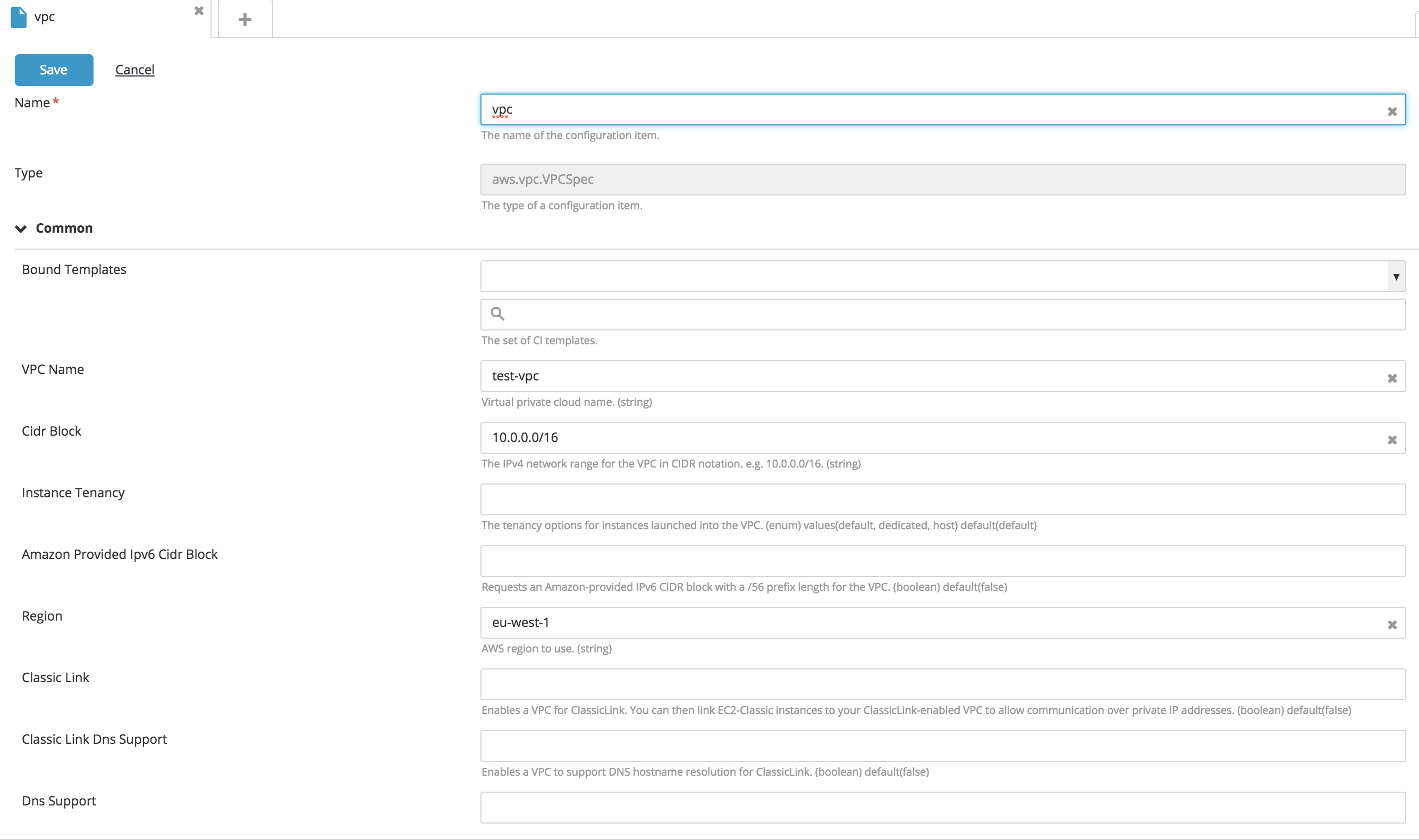
Create a new VPC type CI:
- In the top navigation bar, click Explorer.
- Expand an application in the Applications list.
- Hover over a package, click
, and select New > aws > vpc > VPCSpec.
- Fill in the following fields: VPC Name, CIDR Block, and Region.
- To make classic EC2 (non VPC) accessible through this VPC, set Classic Link to
true. - To assign EC2 with hostname, set DNS Support to
true. - To connect privately to other VPCs, in the Peering Connections section, specify IDs or VPC names in Peer VPCs field.
- Click Save.
Note: You can specify the VPC resource ID from the AWS console or specify the Name:
<vpc_name>when the VPC belongs to the package that is to be deployed. Connectivity across VPCs within the same account is supported.
Create an Internet Gateway network resource:
- In the Gateway section of the
aws.vpc.VPCSpecCI, set the Create Internet Gateway property totrue. The internet gateway is used when you require a subnet for public access. - Optionally, to specify a name for internet gateway, enter a name into the Name field.
- Click Save.

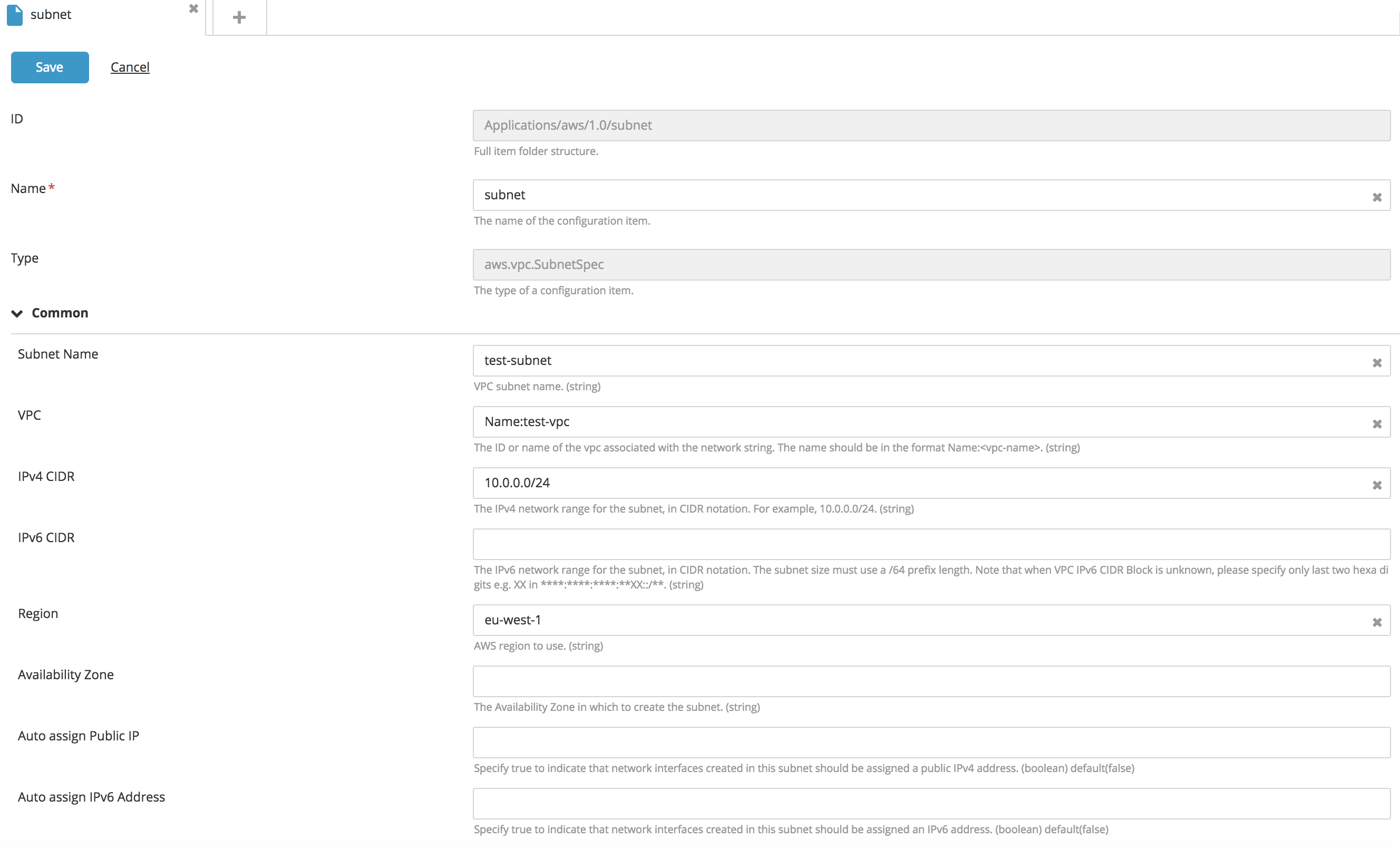
Create a new SubnetSpec* type CI:
- In the top navigation bar, click Explorer.
- Expand an application in the Applications list.
- Hover over a package, click
, and select New > aws > vpc > SubnetSpec.
- Fill in the following fields: Name, VPC, IPv4 CIDR, IPv6 CIDR, and Region.
- Click Save.
Notes:
- IPv4 CIDR and IPv6 CIDR represent the IP allocated to the subnet and is a unique subset of the target VPC.
- A VPC can be referred to by its VPC ID if the VCP already exists on AWS, or by Name:
<vpn_name>if the VPC belongs to the package that is to be deployed.
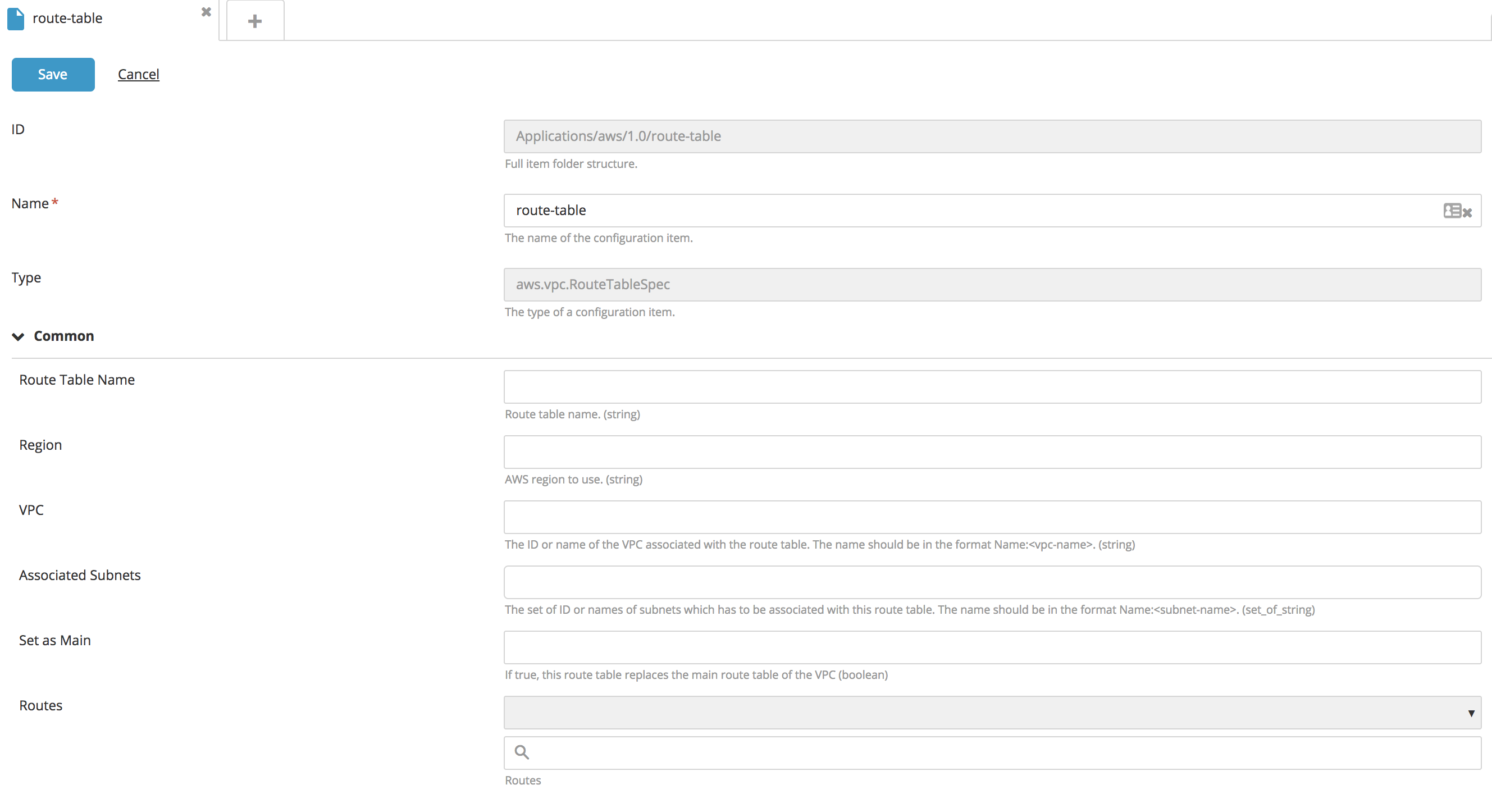
Create a new RouteTableSpec type CI:
- In the top navigation bar, click Explorer.
- Expand an application in the Applications list.
- Hover over a package, click
, and select New > aws > vpc > RouteTableSpec.
- Fill in the following fields: Name, VPC, Associated Subnets, and Routes.
- Click Save.
Notes:
-
A VPC can be referred to by its VPC ID if the VCP already exists on AWS, or by Name:
<vpn_name>if the VPC belongs to the package that is to be deployed. -
Subnets can be referred to by their subnet ID if the subnet already exists on AWS, or by Name:
<subnet_name>if the subnet belongs to the package that is to be deployed. -
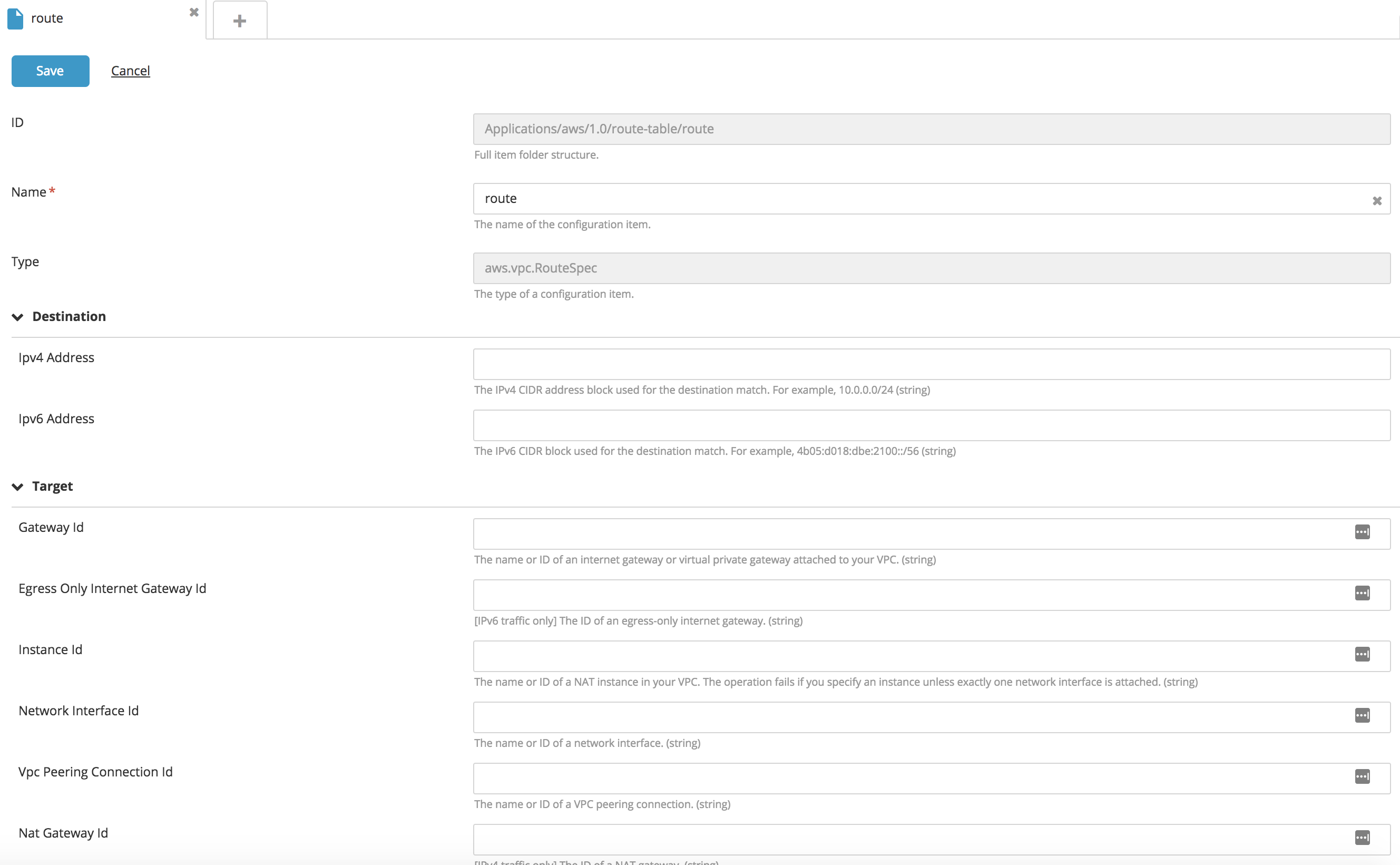
You can add a route as an embedded configuration item under Route Table with the following properties:
- Internet Gateway
- NAT Device
- Virtual Private Gateway
- VPC Peering Connection
- ClassicLink
- VPC Endpoint
- Egress-Only Internet Gateway
Create EC2 instances
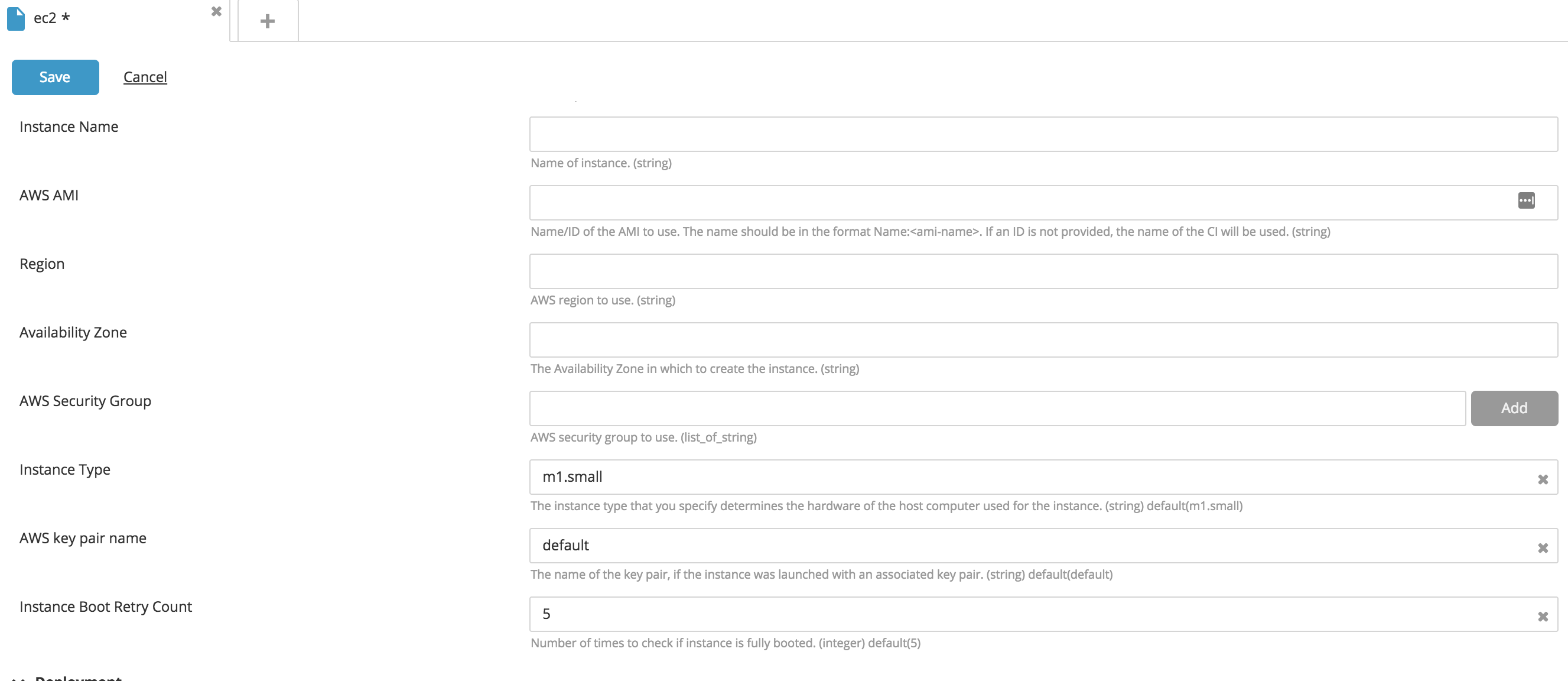
Create a new ec2.InstanceSpec type CI:
- In the top navigation bar, click Explorer.
- Expand an application in the Applications list.
- Hover over a package, click
, and select New > aws > ec2 > InstanceSpec.
- Fill in the following fields: Name, AMI name, Region, and Instance Type.
- To attach the IAM Role to the EC2 instance, specify the IAMRole property.
- Click Save.
Notes:
- You can refer to a subnet by its subnet ID if it already exists on AWS, or by Name:
<subnet_name>if the subnet belongs to the package that is to be deployed. - The AWS key pair name associates the existing key pair name with the EC2 instance to be created, and is used to access the EC2 instance via SSH.
- Creating or destroying an EC2 instance behind a proxy server requires setting the
http_proxyandhttps_proxyenvironment variables in addition to providing proxy configuration on the Deploy infrastructure.
Attach a Network Interface to EC2 instances
You can attach multiple network interfaces to an EC2 instance by specifying the Network Interface map property. The key column is the index, and the value is the network interface ID, if the network interface exists on AWS, or Name:<ni-name> if the network interface belongs to the package to be deployed.
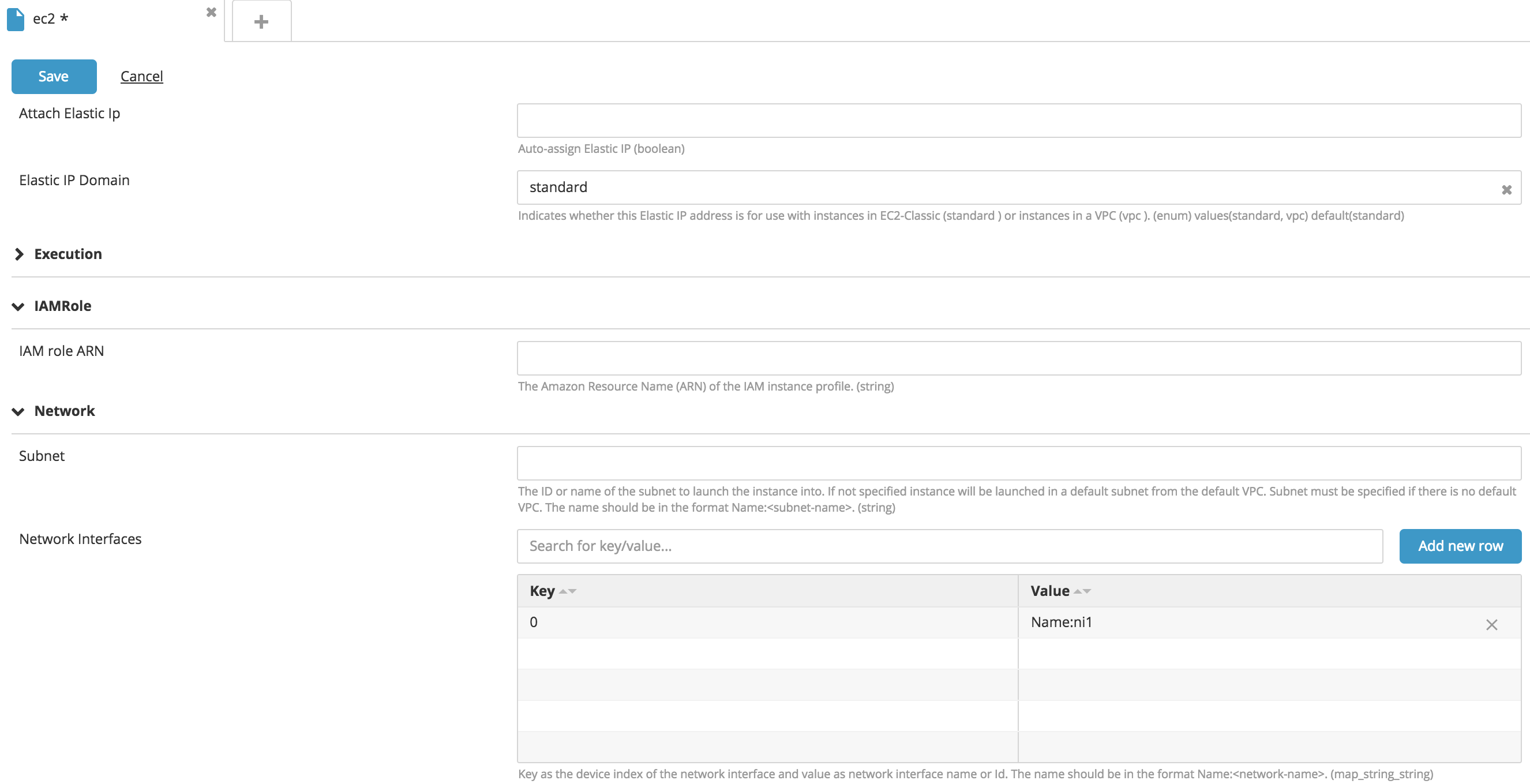
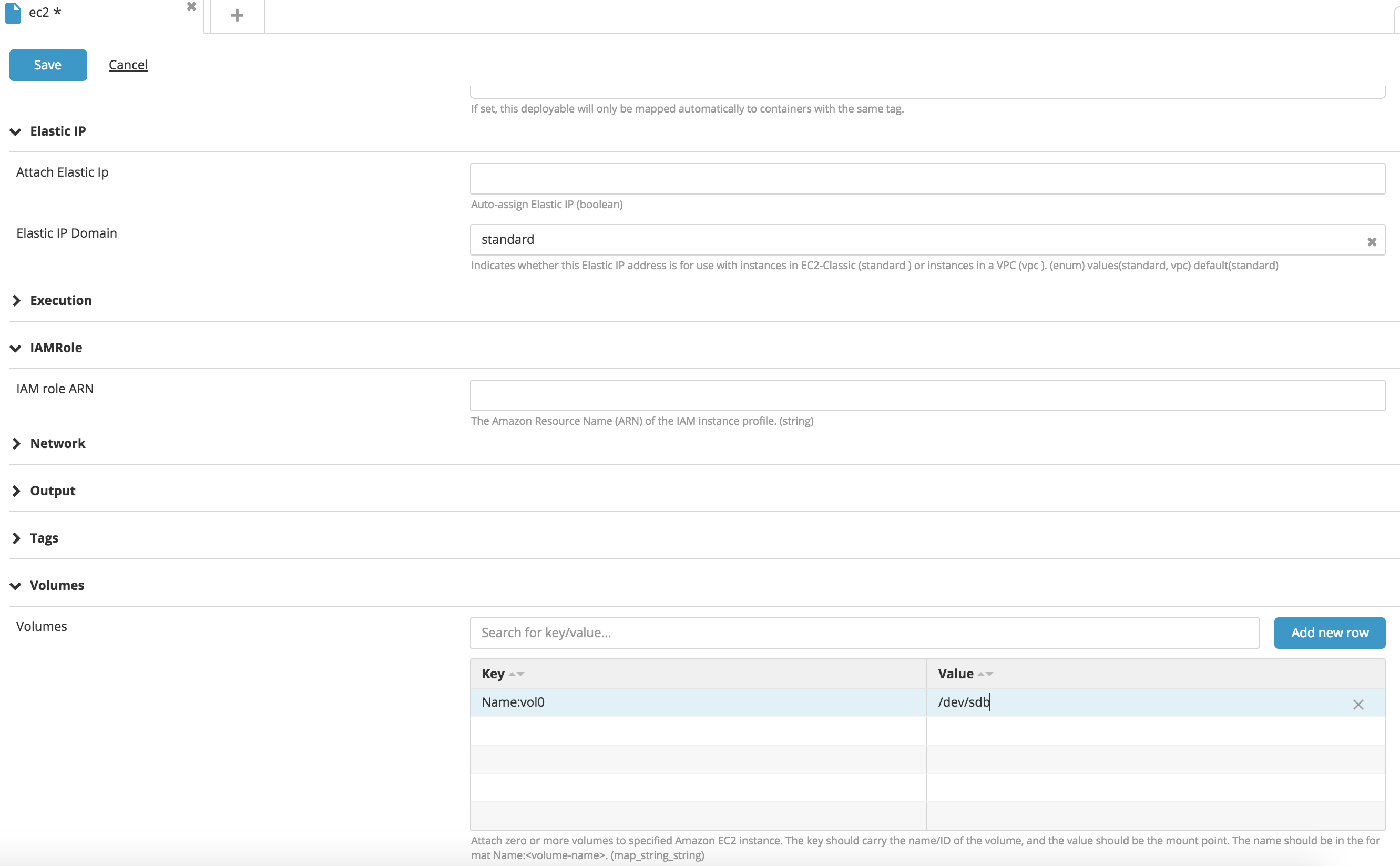
Mount volumes on EC2 instances
You can mount multiple volumes to an EC2 instance by specifying the Volumes map property. The key column is the volume ID if the volume exist on AWS, or Name:<vol-name> if the volume belongs to the package to be deployed, and the value is the device name. For more information, see Device Naming on Linux Instances.
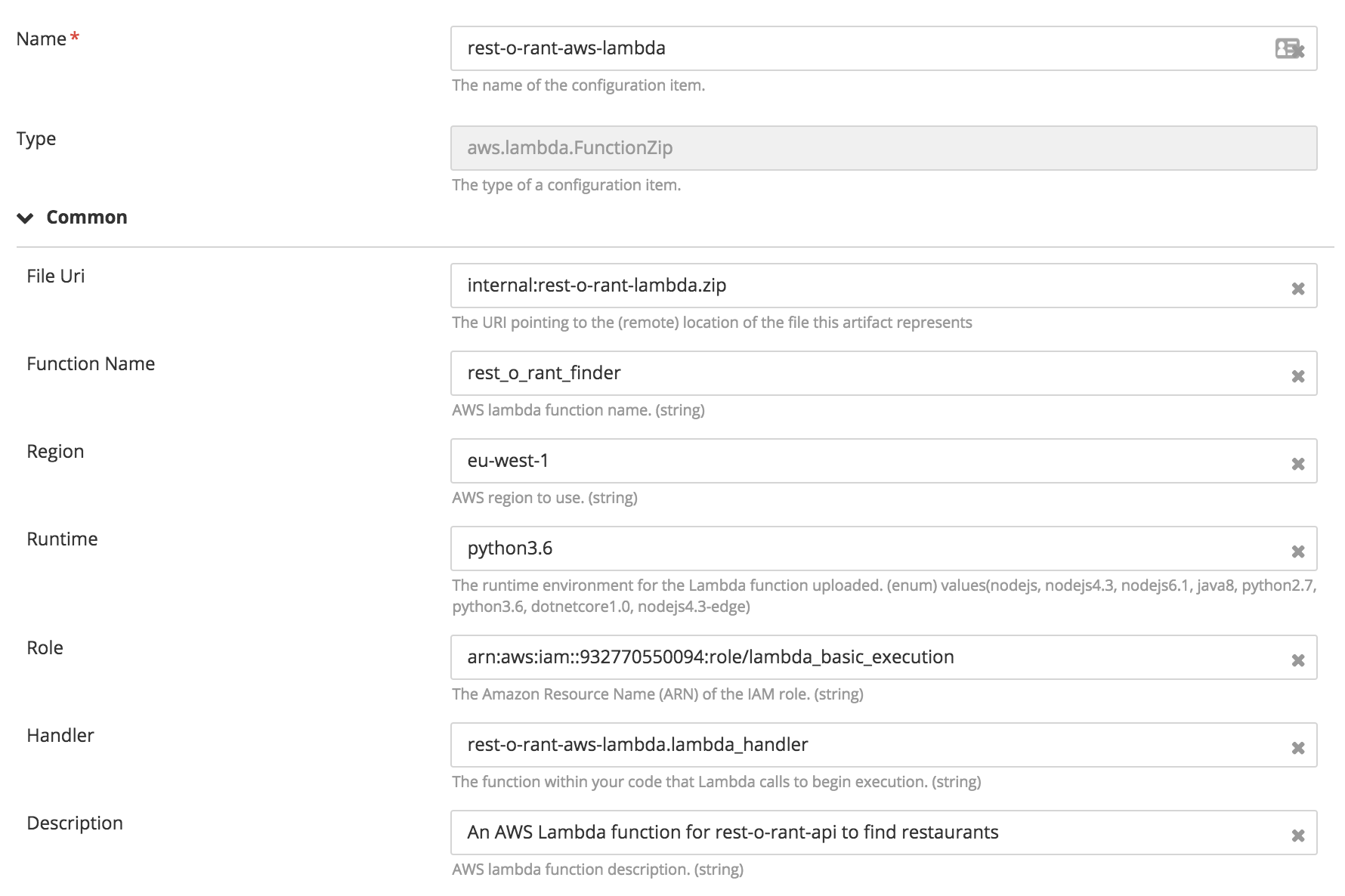
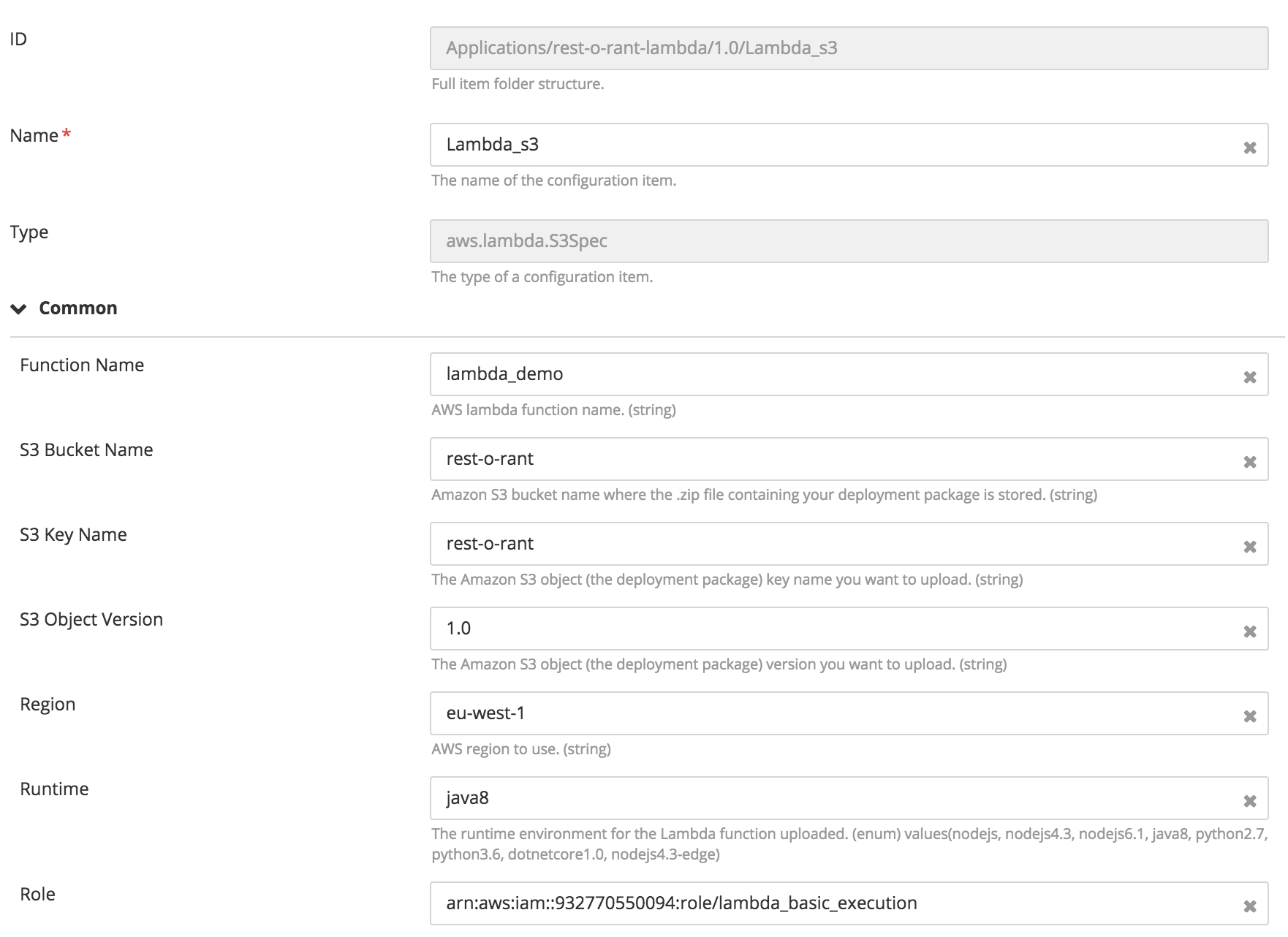
Creating Lambda function and run it in response to HTTP requests using Amazon API Gateway
Creating AWS Lambda function
There are two ways to create a Lambda function. The first is by providing the complete code in zip format and to use the aws.lambda.Function type, and the second is to upload the code to s3 and use the aws.lambda.Function type.
- Create an AWS Lambda function by specifying the functionName, region, runtime, role, handler.
- A role is the Amazon Resource Name (ARN) for the IAM role which has the rights to execute a Lambda function.
- Handler is the function within your code that Lambda calls to begin execution.
- Runtime is the runtime environment for the Lambda function uploaded (Example: python2.7, java8)
- If Lambda function code is uploaded on S3 we need to provide bucketName, s3Key, and s3ObjectVersion in addition to other properties.
- If Lambda function code is uploaded as an Image in Amazon Elastic Container Registry, then we need to provide functionName, imageUrl, region, and role in addition to other properties.
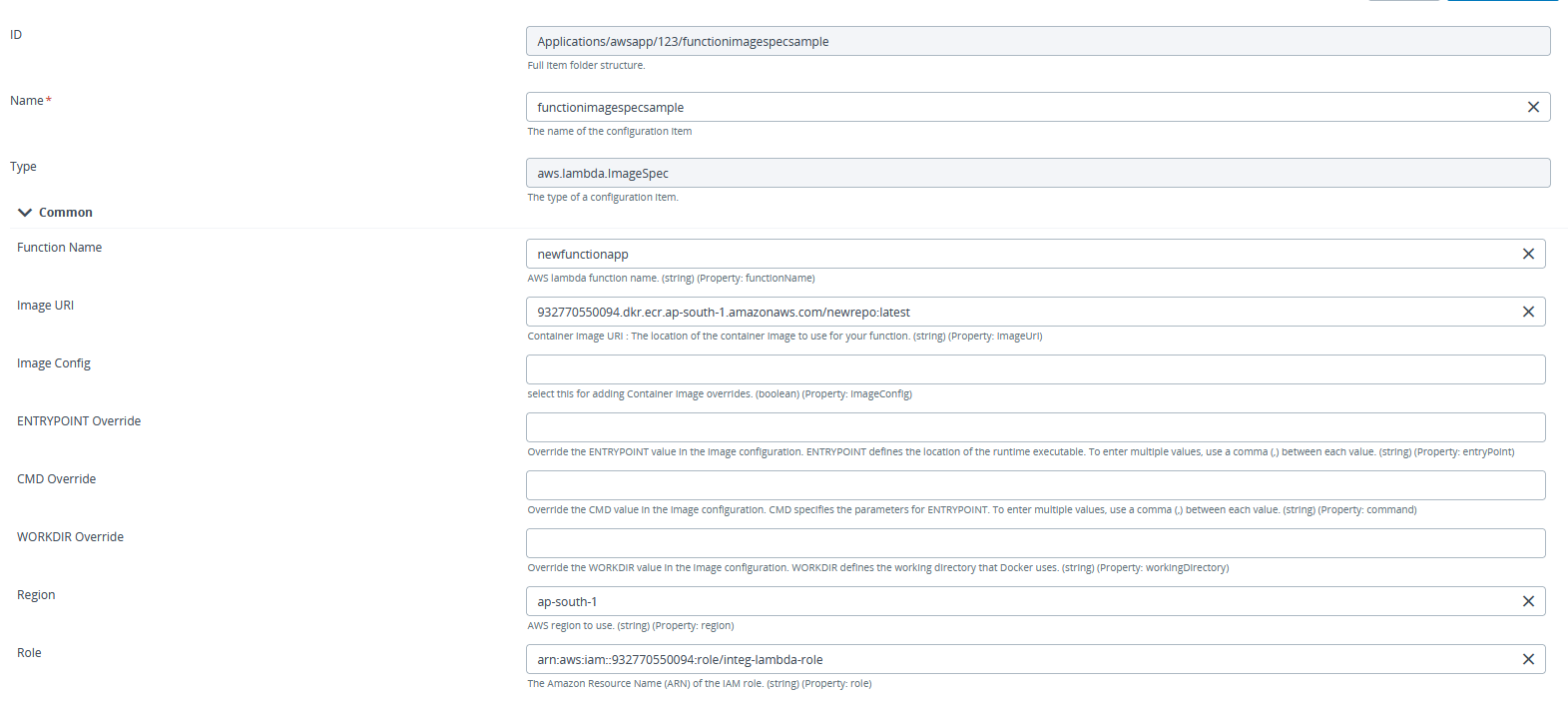
Create API Gateway
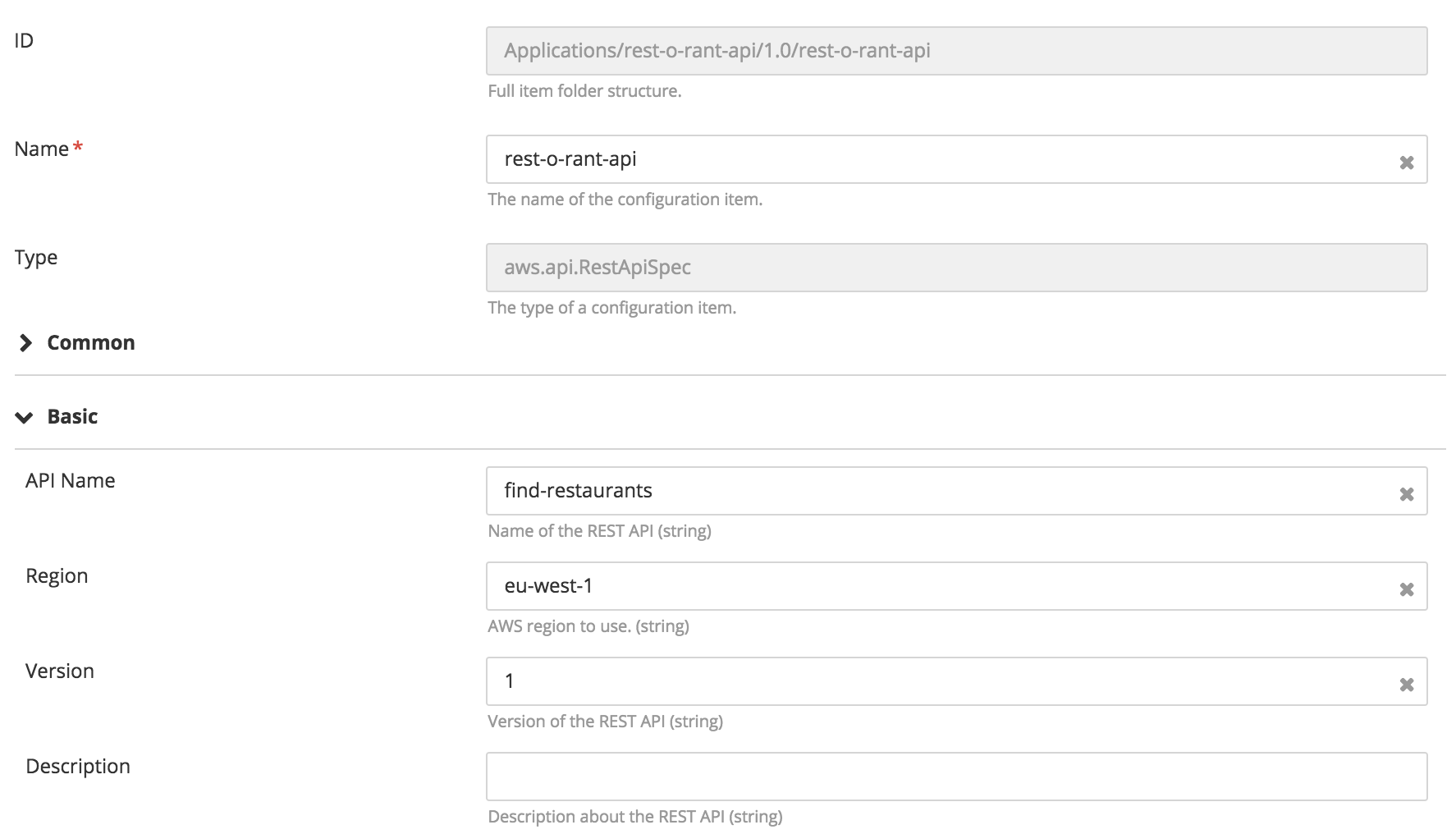
To provision an AWS API Gateway resource on AWS Cloud choose aws.api.RestApiSpec
- Create an
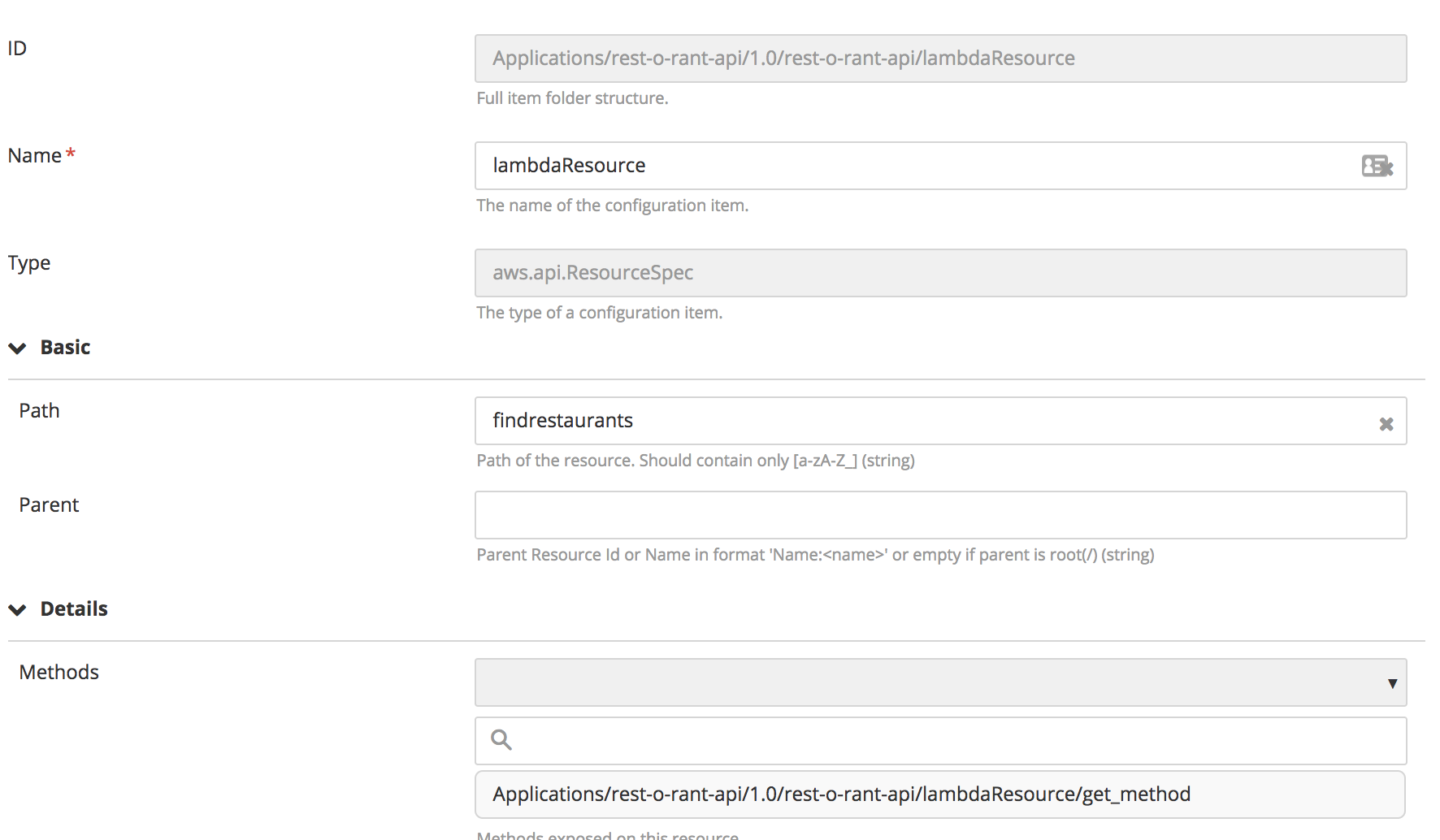
aws.api.RestApi, specify the apiName and region. - To bind a Lambda function to
aws.api.RestAPI, create aaws.api.ResourceSpec. Create aaws.api.ResourceSpec, specifying the path, parent, and methods. - Map multiple HTTP methods to
aws.api.ResourceSpecusingaws.api.MethodSpec. - To use the Lambda function with the API gateway in
aws.api.MethodSpec:- In the Type of integration field, select AWS.
- In the URI field, enter the Lambda name in the following format: Name:
<lambda_function_name>.


Use AWS with SSO federated login credentials
You can configure login to AWS with SSO (Single Sign On) instead of an AWS AccessKeyID and SecretKey.
- Deploy will communicate with the Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS) server and the AWS STS service to retrieve a temporary access token for performing operations.
- This access token is associated with a particular AWS IAM Role and carries its permissions.
- This token expires in 15 minutes, but a new token is retrieved for each resource that is deployed.
- ADFS will send a SAML 2.0 XML assertion to AWS to tell it what role the incoming user should have and to validate the authentication request.
- Only Microsoft ADFS 3.0 is currently supported.
Configuration requirements
- The AWS STS Service must be enabled in the region in which the AWS resource is being deployed.
- ADFS and AWS must be configured to trust each other according to the following article. Note the following:
- This article is for ADFS 2.0, but there are only minor differences in the ADFS 3.0 UI.
- This article suggests using AD Groups to map to AWS Roles. A different method can be used to map a user login to a role but the resulting SAML assertion produced by ADFS must contain AWS Role ARNs as Attributes.
- When setting up the AD user, they must have the Email address field filled.
When setting up the ADFS identity provider in AWS IAM, the name of the Identity provider in AWS must match the name of the saml-provider in the SAML assertion produced. For example:
arn:aws:iam::123456789012:saml-provider/ADFS30,arn:aws:iam::123456789012:role/ADFS-
In this example, the name is ADFS30 which must match the identity provider name in AWS.
- The ADFS server produces the SAML assertions and this name should be set when setting up the claim rules in ADFS.
- Remember to replace
123456789012above with your AWS account number.
Procedure
- Create an aws.Cloud infrastructure item.
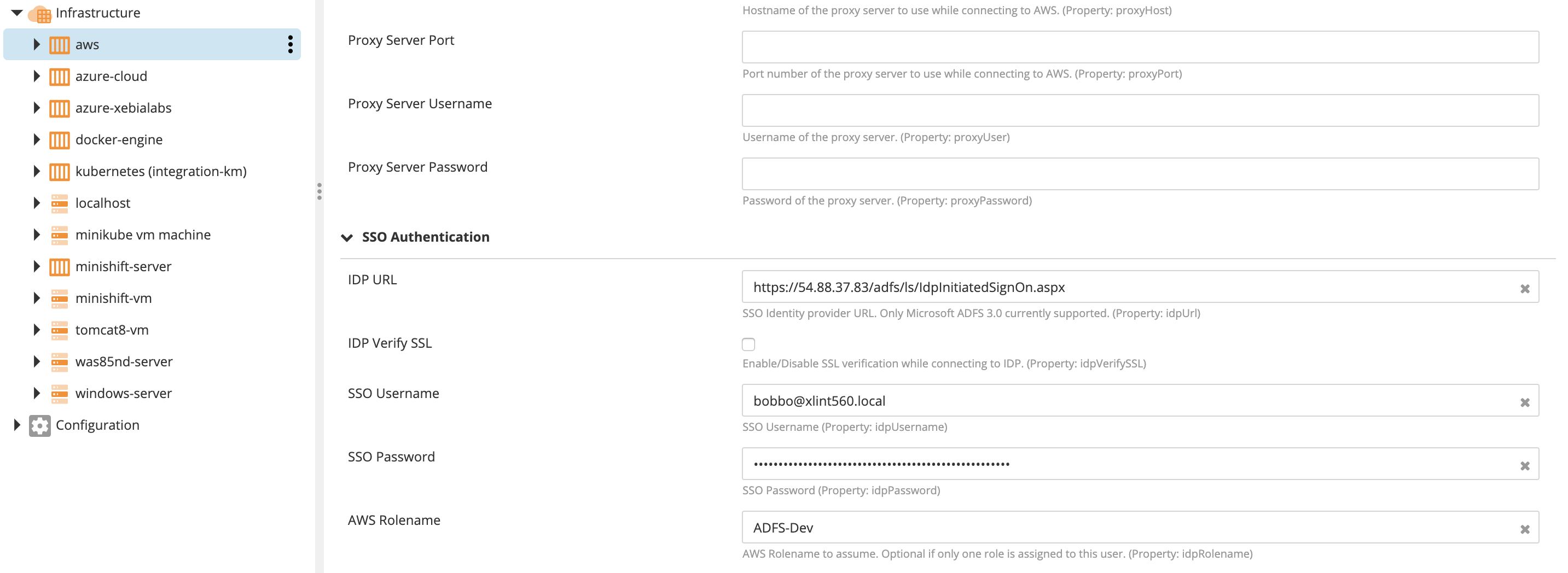
- Ignore the Access Key ID and Secret Access Key used with a normal connection and complete the authentication details in the "SSO Authentication" section.
-
The IDP URL is the URL to the ADFS 3.0 login page. For example:
https://<ADFS host name according to its SSL certificate>/adfs/ls/IdpInitiatedSignOn.aspx. -
ADFS is normally set up with an SSL certificate that specifies the hostname the ADFS server will have.
-
IDP Verify SSL: Check this option to verify the SSL certificate of the ADFS server. Uncheck if the certificate is self-signed.
-
SSO Username: AD login username. Example: bobbo@adfs.local
-
SSO Password: AD login password.
-
AWS Rolename: If the above user maps to more than one AWS role (more than one AWS role ARN in the SAML assertion), this specifies which AWS role to assume according to its role name. If there is only one role, this is field is optional as the plugin will automatically use the first one found in the SAML assertion.
For example: If the ARN of the AWS role is
arn:aws:iam::123456789012:role/ADFS-Dev, the Role name isADFS-Dev.
To check the configuration:
- Right click the aws.Cloud infrastructure item.
- Click Check Connection.
- Provide a region code to test with. This region must have the AWS STS service enabled in it. For example:
us-east-1. - Execute the task. If a failure occurs, examine the execution logs.
You have now successfully configured an AWS connection that uses SSO credentials.
Provide corporate user access to AWS Management through Active Directory Federation Services
To set up access to AWS using ADFS, configure the AWS infrastructure using SSO authentication.