Setup ActiveMQ Artemis HA with UDP
This topic outlines the procedure to setup Active Messaging Queue (MQ) Artemis in a highly available configuration with UDP protocol. It also describes how Digital.ai Deploy can be connected to Artemis nodes.
Prerequisites
In the example setup that follows we have used CentOS release 8.1.1911 operating system.
| Hostname | IP Address | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| node1 | 192.168.10.1 | Artemis master (live server) |
| node2 | 192.168.10.2 | Artemis slave (backup server) |
To test or setup a cluster, You must have at least two physical or virtual machines. However, you can always add more machines to your cluster environment.
If you are setting up the cluster in a development environment, use the following commands to disable the firewalld service:
systemctl stop firewalld.service
systemctl disable firewalld.service
However, if you want to continue using the firewalld service you need to allow multicast traffic with firewalld.
Allowing IGMP traffic
IGMP traffic must be allowed through the firewall so that the system can respond to multicast queries for general group memberships, and for specific groups:
Use the following commands to enable IGMP traffic:
firewall-cmd --add-protocol=igmp
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-protocol=igmp
Allowing UDP Multicast
The actual multicast traffic itself must be allowed through the firewall so that the system can actually receive the traffic carrying the data payload.
Use the following commands to enable multicast traffic
firewall-cmd --direct --add-rule ipv4 filter INPUT 10 -d 231.7.7.7 -j ACCEPT
firewall-cmd --permanent --direct --add-rule ipv4 filter INPUT 10 -d 231.7.7.7 -j ACCEPT
Enabling the port
Use the following commands to enable the multicast UDP port in the firewall:
firewall-cmd --add-port=9876/udp
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=9876/udp
Configuring a multicast listener
A service XML file can be defined or created in the /etc/firewalld/services/ directory for enabling a multicast listener.
vi /etc/firewalld/services/multicastlistener.xml
A sample XML file looks like this, you need to replace the values by actuals based on your environments.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<service>
<short>My Multicast Listener</short>
<description>A service which allows traffic to a fictitious multicast listener.</description>
<port protocol="udp" port="9876"/>
<destination ipv4="231.7.7.7"/>
</service>
Once you have created the file, the service can be applied:
firewall-cmd --reload
firewall-cmd --add-service=multicastlistener
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=multicastlistener
sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --permanent --add-port=61616/tcp
sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --permanent --add-port=8161/tcp
firewall-cmd --reload
Preparing the brokers and connecting to Artemis
In this example, we will setup the master broker on node1.
- Download the latest distribution of apache from the below link and unzip it:
https://activemq.apache.org/components/artemis/download/
-
wget https://downloads.apache.org/activemq/activemq-artemis/2.15.0/apache-artemis-2.15.0-bin.zip -
unzip apache-artemis-2.15.0-bin.zip
-
Create a message broker using the following commands:
cd /root/apache-artemis-2.15.0/bin./artemis create /opt/master-broker/Provide the username and password for the user during the broker creation.
-
Change the
jolokia-access.xmlandbootstrap.xmlfiles to access the Artemis UI. Navigate to/opt/master-broker/etc, the location of thejolokia-access.xmlfile, and use an editor to edit its contents.
cd /opt/master-broker/etc
vi jolokia-access.xml
Contents of the jolokia-access.xml file used in this example setup are shown below:
<cors>
<!-- Allow cross origin access from localhost ... -->
<allow-origin>*://localhost*</allow-origin>
<!-- Options from this point on are auto-generated by Create.java from the Artemis CLI -->
<!-- Check for the proper origin on the server side, too -->
<strict-checking/>
</cors>
In this file, replace the value in the <allow-origin>*://localhost*</allow-origin> tag to look like this:
<allow-origin>*://*</allow-origin>
In the bootstrap.xml file, replace value in the <web bind="http://localhost:8161" path="web"> attribute to look as follows:
<web bind="http:// 0.0.0.0:8161" path="web">
Contents of the bootstrap.xml file used in this example setup are shown below:
<!-- The web server is only bound to localhost by default -->
<web bind="http://localhost:8161" path="web">
<app url="activemq-branding" war="activemq-branding.war"/>
<app url="artemis-plugin" war="artemis-plugin.war"/>
<app url="console" war="console.war"/>
</web>
- Remove the existing
broker.xmlfile, using the following commands:
cd /opt/master-broker/etc
rm broker.xml
Create a new broker.xml file.
Note: Download the sample broker.xml file. Copy and paste the contents of the sample file to the newly created broker.xml file. Remember to replace the value node1_ip by your host's IP Address and fill in the actual values for these attributes:
<cluster-user>ACTIVEMQ.CLUSTER.ADMIN.USER</cluster-user>
<cluster-password>CHANGE ME!!</cluster-password>
- Preparing the slave broker on
node2
To setup the slave broker on node2, follow the steps 1-4 and replace the node2_ip with the node2 IP Address and fill in the actual values for these attributes:
<cluster-user>ACTIVEMQ.CLUSTER.ADMIN.USER</cluster-user>
<cluster-password>CHANGE ME!!</cluster-password>
Here's a sample broker.xml file for node2. You can replace the existing file with this and modify the IP address with the IP address of node2.
- From
node1, navigate to/opt/master-broker/bin/and run this command:
./artemis run
This will start the master broker (node1) and you should see something like this:
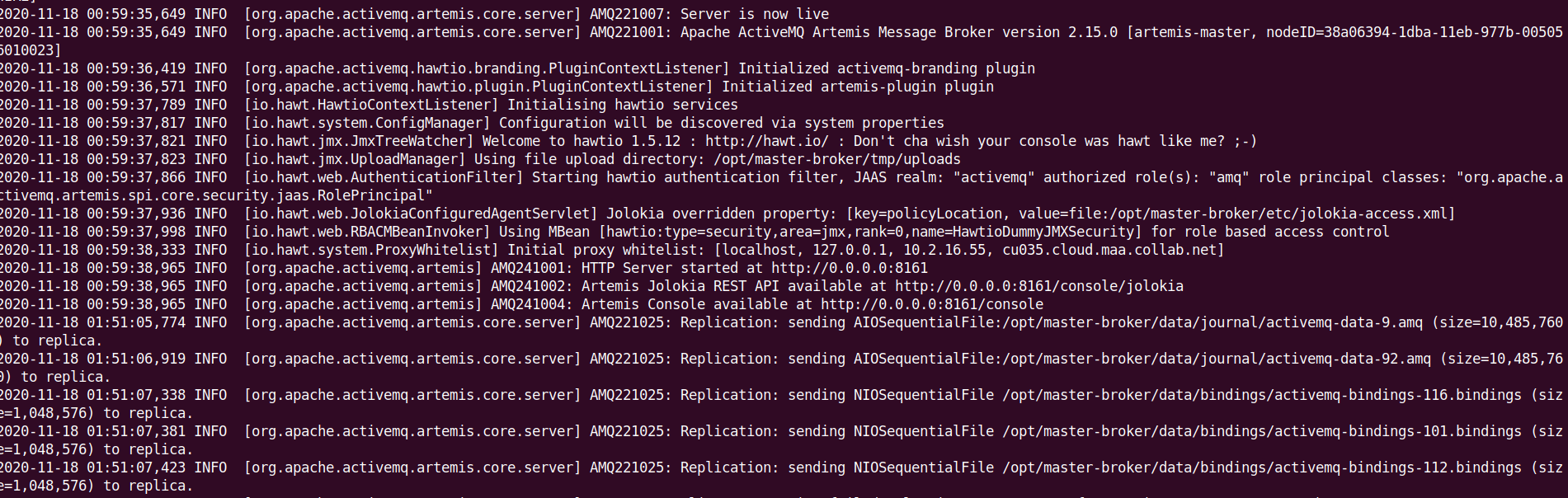
- From
node2, navigate to/opt/master-broker/bin/and run this command:
./artemis run
This will start the slave broker (node2) and you should see something like this:
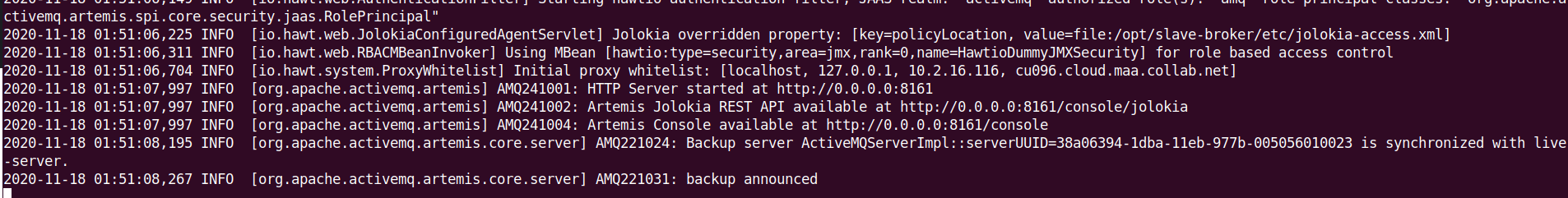 Note: You can test the fail-over scenario by stopping
Note: You can test the fail-over scenario by stopping node1 master node and checking if the slave takes control of the cluster.
- Navigate to
xl-deployrepository or workspace and run this command to get the dev build distribution:
./gradlew clean build -x test
From the build, remove xld-jms-cf-default.jar and replace it with xld-jms-cf-artemis.jar from libs/ directory. You can obtain this jar from xl-deploy/xld-jms/xld-jms-cf-artemis/build/libs.
Add the ActiveMQ .jar file to the lib folder to connect the Artemis cluster.
cd /opt/xl-deploy-9.x.x-server/lib
wget https://repo1.maven.org/maven2/org/apache/activemq/activemq-client/5.15.13/activemq-client-5.15.13.jar
- Modify
xl-deploy.confto include UDP protocol to connect to the cluster.
Connecting through UDP protocol:
task {
queue {
backoff {
attempts=25
timeout=5000
}
external {
# External task queue, used only if xl.task.in-process-worker=false^M
jms-driver-classname="org.apache.activemq.ActiveMQConnectionFactory"
jms-password="admin"
jms-url="udp://231.7.7.7:9876"
jms-username=admin
}
in-process {}
name=xld-tasks-queue
}
}
Here, the multi-cast group address 231.7.7.7:9876 binds to both nodes as we specified this configuration in the broker.xml for both nodes.
You can also have local-bind-address and local-bind-port in the xl-deploy.conf for the Artemis cluster. To learn more, visit:
https://activemq.apache.org/components/artemis/documentation/1.0.0/clusters.html
- Test the cluster setup with a Deploy Active-Active setup (recommended) or Active-Hot Standby setup.