How Archiving Works
Archiving in Digital.ai Release is a two-stage process that manages completed and aborted releases:
- Pre-archiving: When a release is completed or aborted, an archiving cron job runs (by default, every minute) to scan for such releases. It copies them to the archive database, but leaves a copy in the operational (live) database. This allows for unified reporting and access to recent releases.
- Final archiving: According to the configured archiving schedule and age, the archiving cron job scans for completed/aborted releases that are older than the archiving age (see Archiving Job Configuration). These releases are then archived (if not already) and deleted from the operational database, leaving only the archived copy.
This process improves system performance and enables custom export hooks for integration with external databases or reporting tools.
Pre-archived releases (still present in the operational database) remain visible in dashboards, filters, and release overviews. Once a release is fully archived (removed from the operational database), it is available in the Archive tab of the Releases page.
- Archived releases are read-only. You cannot add comments to tasks in an archived release.
- Archived releases appear in reports.
- You can create a custom hook that runs when a release is archived (for example, to store the release in an external reporting database).
Archiving Job Configuration
The archiving process in Digital.ai Release is highly configurable. You can control when and how releases are archived, how often the archiving job runs, and how system resources are managed during archiving. The following sections explain the overall archiving flow and the key settings you can adjust to fit your organization's needs.
How Archiving Works
- Set up the archiving age:
- Go to System Settings > Releases and Triggers and configure the Archive executions older than setting. This is the minimum age (default: 30 days) after which completed or aborted releases are eligible for final archiving. For more information, see Archive and Clean-up Releases and Workflows.
- Pre-archiving:
- A cron job runs every minute by default. It scans for completed and aborted releases and copies them to the archive database, but keeps them in the operational database until they reach the archiving age.
- Archiving job schedule:
- Set the
xlrelease.ArchivingSettings.archivingJobCronScheduleproperty indeployit-defaults.propertiesto control how often the archiving job runs (using cron syntax). - When the archiving cron job runs, it scans for completed/aborted releases older than the archiving age, archives them (if not already), and deletes them from the operational database.
- Configure throttling and other properties:
- Adjust throttling and performance-related properties to control resource usage and job behavior.
Ensure the archiving job can process at least as many releases per day as are being completed or aborted. For example, do not run the job only once per week unless you adjust throttling properties accordingly. The pre-archiving service runs every minute by default, but the final archiving (deletion from operational database) depends on the archiving job schedule and age.
Throttling Properties
Throttling helps prevent the archiving job from consuming excessive system resources. Configure these properties in deployit-defaults.properties:
| Property | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
xlrelease.ArchivingSettings.maxSecondsPerRun | Max time (seconds) for one archiving job run. With the default, about 18 releases are archived per run. Set to 0 or -1 to remove the limit. | 20 |
xlrelease.ArchivingSettings.sleepSecondsBetweenReleases | Wait time (seconds) between archiving each release. Default: 1 release per second. Set to negative to remove wait. | 1 |
xlrelease.ArchivingSettings.searchPageSize | Number of releases found per search page. | 20 |
xlrelease.ArchivingSettings.enabled | Enables/disables the archiving job. Do not permanently disable. | true |
Adjusting Properties at Runtime
You can change throttling properties at runtime using the JMX managed bean at com.xebialabs.xlrelease:name=Archiving. Changes made via JMX are not persisted; after a server restart, file values are restored.
Search Page Size
The searchPageSize property controls how many releases are found per search. For example, if set to 5, the job finds five completed releases, archives them, then searches for the next five, and so on. Increasing this value can speed up archiving large numbers of releases, but may increase CPU usage.
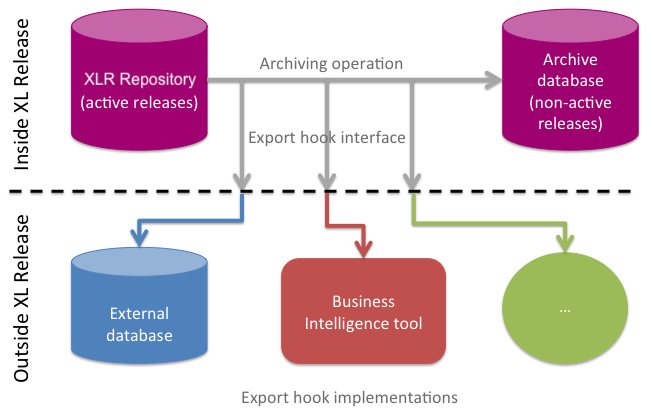
Export Hooks
Digital.ai Release supports custom export hooks to export information about completed and aborted releases. Hooks are triggered when a release is archived.
- Export hooks are written in Jython.
- Add them as JAR files or place them in the Release classpath.
You can define:
- Generic export hooks for exporting to any storage
- JDBC export hooks for exporting to SQL databases
A sample export hook implementation is available on GitHub.