SSL Options for HttpRequest
This topic covers SSL options for HttpRequest, which are settings that enable secure communication between clients and servers.
The code here is sample code only and it is not officially supported by Digital.ai. If you have questions, please contact the Digital.ai Support Team.
Release uses HttpRequest, a underlying base class for HTTP requests which is used in webhooks and is available in custom tasks. HttpRequest is based on Apache HTTP Components.
The Apache HC default SSL configuration aims for security, however, hostname mismatches between a target host and its certificate can occur.
The following is an example of how to configure the Apache HC client in HttpRequest with different SSL options. These examples are based on a fresh installation of Release that has SSL has enabled, and a self-signed certificate for localhost has been generated.
Step 1 - Configure HttpRequest.py to disable certificate handshake
From Release version 10.1 if you want to disable the certificate handshake, just pass req = HttpRequest(server, verify=False)
Step 2 - Extract HttpRequest to the extensions directory
- Create the following directory, if it does not already exist:
XL_RELEASE_SERVER_HOME/ext/xlrelease. - Extract the
HttpRequest.pyclass fromXL_RELEASE_SERVER_HOME/lib/server-<version>.jarinto the directory. This will override theHttpRequest.pyclass provided in the JAR file. You can do this by copying the JAR file to a temporary directory, opening it with a ZIP file browser, changing the file extension to.zipif necessary, and extracting the file from thepythonutilorxlreleasedirectory.
Step 3 - Set up a sandbox template with a test task
Create a simple sandbox release template with a single script task to test the various settings:
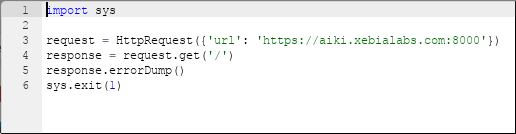
This fails on two counts, as expected: first, it is a self-signed certificate and, secondly, the certificate is for localhost, not nb-aphillips, which is the machine's hostname:

Step 4 - Configure HttpRequest to trust self-signed certificates
Configure HttpRequest to trust the self-signed certificate. This means changing HttpRequest to not use the Apache HC default HttpClient object, but one that is configured with the required SSL options.
In this example, the original client = HttpClients.createDefault() call is commented out and a createHttpClient method that returns a client configured to trust all certificates has been added. An additional import statement for the required classes to the initial section of HttpRequest.py has also been added.
from org.apache.http.conn.ssl import SSLContextBuilder, SSLConnectionSocketFactory, TrustSelfSignedStrategy
...
def executeRequest(self, request):
client = None
response = None
try:
# replace the original default client with a call to our new method
#client = HttpClients.createDefault()
client = self.createHttpClient()
...
# we're adding this method to the class
def createHttpClient(self):
# see the Javadoc for SSLConnectionSocketFactory for more options
builder = SSLContextBuilder()
builder.loadTrustMaterial(None, TrustSelfSignedStrategy())
socketfactory = SSLConnectionSocketFactory(builder.build())
# print 'DEBUG: Created custom HttpClient to trust all certs\n'
return HttpClients.custom().setSSLSocketFactory(socketfactory).build()
Step 5 - Configure HttpRequest to ignore hostname mismatches
Configure the HTTP client to ignore hostname mismatches by adding an additional configuration option in the new createHttpClient method:
def createHttpClient(self):
builder = SSLContextBuilder()
builder.loadTrustMaterial(None, TrustSelfSignedStrategy())
# now also adding ALLOW_ALL_HOSTNAME_VERIFIER here
socketfactory = SSLConnectionSocketFactory(builder.build(), SSLConnectionSocketFactory.ALLOW_ALL_HOSTNAME_VERIFIER)
# print 'DEBUG: Created custom HttpClient to trust all certs and allow hostname mismatches\n'
return HttpClients.custom().setSSLSocketFactory(socketfactory).build()
Additionally, can also configure the client to ignore hostnames but not to ignore trust self-signed certificates:
def createHttpClient(self):
socketfactory = SSLConnectionSocketFactory(SSLContextBuilder().build(), SSLConnectionSocketFactory.ALLOW_ALL_HOSTNAME_VERIFIER)
# print 'DEBUG: Created custom HttpClient to allow hostname mismatches\n'
return HttpClients.custom().setSSLSocketFactory(socketfactory).build()
If you configure the client to ignore hostnames but not trust self-signed certificates. Remove TrustSelfSignedStrategy from the org.apache.http.conn.ssl import ... line, as it is not used.
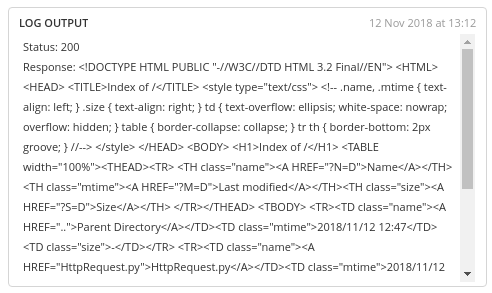
The test task will now call the server successfully:
Code samples are based on this Stack Overflow post.
Considering the POODLE SSL vulnerability, you may wish to consider to allow only TLS connections. For information ON how to construct the socket factory to achieve this, see Javadoc for SSLConnectionSocketFactory