Setting Asset State
Asset state defines the system-known life-cycle for an asset. The UI, for example, will typically query assets that are not = 'Dead' to automatically exclude those items from the return results. The AssetState attribute is the internal state of an asset, accessible only through operations.
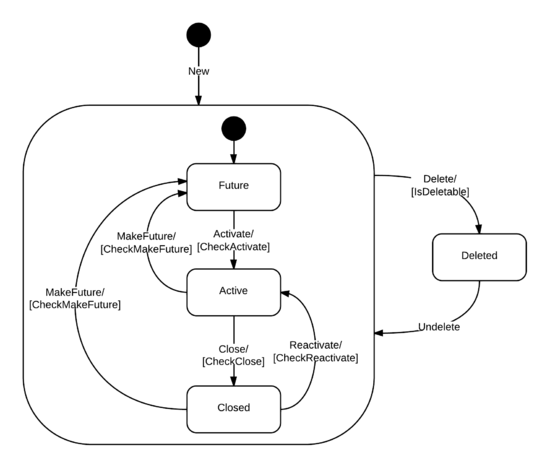
As an example, we can progress a Timebox through the life-cycle states.
Getting Started
- Have an HTTP Client.
- Obtain an API token.
1. New Schedule
Create a new asset for a sandbox Schedule, named Digital.ai Agility API Sandbox. The following is a representative response.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<Asset href="/v1sdktesting/rest-1.v1/Data/Schedule/14635/22321" id="Schedule:14635:22321">
<Attribute name="Name">VersionOne API Sandbox</Attribute>
<Attribute name="TimeboxLength">1 Days</Attribute>
<Attribute name="TimeboxGap">0 Days</Attribute>
</Asset>
2. New Timebox
Create a new asset for a Timebox using the newly created Schedule. Using the OID Token from the schedule above as the ctx parameter, create a new asset for a Timebox, named VersionOne Timebox Lifecycle. From the example above, we would use ctx=Schedule:14635. The following is a representative response.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<Asset href="/v1sdktesting/rest-1.v1/Data/Timebox/14636/22322" id="Timebox:14636:22322">
<Attribute name="Name">VersionOne Timebox Lifecycle</Attribute>
<Attribute name="BeginDate">2013-09-02</Attribute>
<Attribute name="EndDate">2013-09-03</Attribute>
<Relation name="State">
<Asset href="/v1sdktesting/rest-1.v1/Data/State/100" idref="State:100" />
</Relation>
<Relation name="Schedule">
<Asset href="/v1sdktesting/rest-1.v1/Data/Schedule/14635" idref="Schedule:14635" />
</Relation>
</Asset>
3. List the Timebox Operations
Use meta.v1 to list the operations on the Timebox asset type.
<Server Base URI>/meta.v1/Timebox?xsl=api.xsl
The response should include something similar to the following list.
Activate : operation — validated by CheckActivate
Close : operation — validated by CheckClose
Delete : operation — validated by IsDeletable
MakeFuture : operation — validated by CheckMakeFuture
Reactivate : operation — validated by CheckReactivate
Undelete : operation — validated by IsUndeletable
Activate the Timebox
Send an HTTP POST with no body using the op parameter set to Activate.
<Server Base URI>/rest-1.v1/Data/Timebox/14636?op=Activate
The response should be similar to the following.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<Asset href="/v1sdktesting/rest-1.v1/Data/Timebox/14636/22329" id="Timebox:14636:22329" />
The returned Asset node indicates the asset was properly updated. To check the state progression, use HTTP GET on the returned asset, selecting Name and AssetState. The following uses this example's data.
<Server Base URI>/rest-1.v1/Data/Timebox/14636?sel=Name,AssetState
The response should be similar to the following.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<Asset href="/v1sdktesting/rest-1.v1/Data/Timebox/14636" id="Timebox:14636">
<Attribute name="Name">Sprint 1</Attribute>
<Attribute name="AssetState">64</Attribute>
</Asset>
From the asset state table, we can see the value 64 corresponds to Active.
5. Close the Timebox
Send an HTTP POST with no body using the op parameter set to Close.
<Server Base URI>/rest-1.v1/Data/Timebox/14636?op=Close
The response should be similar to the following.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<Asset href="/v1sdktesting/rest-1.v1/Data/Timebox/14636/22330" id="Timebox:14636:22330" />