Deploy Terraform Enterprises Plugin
The Deploy Terraform Enterprises plugin supports:
-
To deploy the
terraform.Moduleon Terraform Enterprise as the same manner as targetingterraform.TerraformClient -
To defines the
terraform.ConfigurationSpec. It gathers references on Terraform modules and manages the output->input connections between them. -
Offers a new extension point to define new structured-type CI based on existing Terraform modules.
-
It exposes the mapper API to allow creating new Infrastructure CI based on the execution of the
terraform.Configuration.
Requirements
The Deploy Terraform Enterprises plugin requires the following:
- Deploy 9.5 or higher.
| Terraform Version | AWS Artifacts | GCP Artifacts | Azure Artifacts | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S3-Bucket | S3-Content | AWS Stack | AWS Multi | GCP-Module | Azure-VM | |
| 0.14.6 | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 0.13.2 | Not Supported | Not Supported | Yes | Not Supported | Not Supported | Not Supported |
| 0.12.6 | Not Supported | Not Supported | Not Supported | Not Supported | Not Supported | Not Supported |
- xld-terraform-enterprise-plugin-10.1.0 onwards is compatible with Java 11
- xld-terraform-enterprise-plugin-10.0.0 and xld-terraform-enterprise-plugin-9.7.0 are compatible with Java 8
AWS Stack Deployments
-
AWS Stack 1.0.1
Works with Terraform 0.13.2
-
AWS Stack 1.0.2
Works with Terraform 0.13.2
Workspace should be created using Terraform 0.13.2
-
AWS Stack 1.0.3
Works with Terraform 0.13.2
Workspace should be created using Terraform 0.13.2
AWS Multi Deployments
-
AWS Multi 2.0.1
Works with Terraform 0.14.6
-
AWS Multi 3.0.3
Works with Terraform 0.14.6
-
AWS Multi 3.0.4
Works with Terraform 0.14.6
Replace Output variables and Secret Output variables with correct key-value pairs in s3-bucket-backup module.
-
AWS Multi 3.0.5
Works with Terraform 0.14.6
-
AWS Multi 3.0.6
Works with Terraform 0.14.6
-
AWS Multi 3.0.7
Works with Terraform 0.14.6
Create a terraform.EmbeddedModuleArtifact module inside stack.
Use this artifact.
Provide tags in key-value form in input HCL Variables of module1 and module2.
Provide bucket name in key-value form in Input Variables of module2 and move connect_string key-value pair from input HCL Variables to Output Variables of module2.
Azure Deployments
Works with Terraform 0.14.6
Sample artifacts for azure deployment can be found here under azure directory.
Installation
- Copy the latest JAR file from the Releases page into the
XL_DEPLOY_SERVER/pluginsdirectory. - Restart Deploy server.
Features
The Deploy Terraform Enterprise features and its overview:
Infrastructure
-
Describe the connection to Terraform Enterprise using
terraformEnterprise.OrganizationConfiguration Item. -
Then add the workspace definition using
terraformEnterprise.Workspaceconfiguration item as a child of the create Organization. -
Add a provider using
terraformEnterprise.Provideror dedicated Cloud Public Provider `-
Amazon Web Service
terraformEnterprise.AwsProviderand fill the associated properties -
Microsoft Azure
terraformEnterprise.AzureProviderand fill the associated properties -
Google Cloud
terraformEnterprise.GCPProviderand fill the associated properties
-
it's possible to create your own provider or to enhance the default types to add or to remove properties
Manage Certificates
By Default, the certificates aren't verified on HTTPS connection (terraformEnterprise.Organization.verifyCertificates property). In this case, on each connection to Terraform, you'll get the following display:
__pyclasspath__/urllib3/connectionpool.py:846: InsecureRequestWarning: Unverified HTTPS request is being made. Adding certificate verification is strongly advised. See: https://urllib3.readthedocs.io/en/latest/advanced-usage.html#ssl-warnings
To remove this message and enforce the certificates validation:
-
set
terraformEnterprise.Organization.verifyCertificatestoTrue -
set
terraformEnterprise.Organization.pathToCAFileto a file./ca/certifi/cacert.pemor to an archive (zip or jar) using this pattern./plugins/my-certificates.jar/certifi/cacert.pem.
If you are using Terraform Cloud, the CA PEM file is stored in the GitHub Repository.
Mappers
After the cloud infrastructure is generated and created, you must deploy the application. So the plugin offers to define customer mappers that allows you to create new containers and add them to the environment.
A mapper is a python class extending ResourceMapper with 2 methods:
-
the
accepted_typesmethod returns the list of the Terraform accepted_type. -
the
create_cimethod that build the list of the new CI that need to be created and added. The plugin managed to the updates and the deletions.
Then the mapper should be added to the terraformEnterprise.Provider using the additionalMappers map property. The key is a unique identifier, the value the path to the class. eg xldtfe.mapper.aws_s3_mapper.AWSS3Mapper
Structured Terraform Configured Items.
Even it's possible to package terraform.InstantiatedModuleSpec using a generic type, it's also possible to defined new CI based typed to help the user to fill the inputs & output properties.
Example If you want to package the jclopeza/java-bdd-project module using a structured type, this is the definition you can add to the synthetic.xml file
<type type="jclopeza.JavaDBProject" extends="terraform.AbstractedInstantiatedModule"
deployable-type="jclopeza.JavaDBProjectSpec" container-type="terraform.Configuration">
<generate-deployable type="jclopeza.JavaDBProjectSpec" extends="terraform.AbstractedInstantiatedModuleSpec" copy-default-values="true"/>
<property name="source" default="jclopeza/java-bdd-project/module" hidden="true"/>
<property name="version" required="true" default="4.0.0"/>
<!-- simple type -->
<property name="aws_region" default="us-east-1" category="Input"/>
<property name="environment" default="dev" category="Input"/>
<property name="instance_type" default="t2.micro" category="Input"/>
<property name="private_key_path" default="/dev/nul" category="Input" password="true"/>
<property name="project_name" category="Input"/>
<property name="public_key_path" category="Input"/>
<property name="instance_type" label="InstanceType" default="t2.micro" category="Input"/>
<!-- output-->
<property name="public_ip_bdd" category="Output" required="false"/>
<property name="public_ip_front" required="false" category="Output"/>
</type>
It's also possible to define structured types for terraform.EmbeddedModule helping to manage complex inputs & outputs.
<type type="myaws.ec2.VirtualMachine" extends="terraform.AbstractedInstantiatedModule"
deployable-type="myaws.ec2.VirtualMachineSpec" container-type="terraform.Configuration">
<generate-deployable type="myaws.ec2.VirtualMachineSpec" extends="terraform.AbstractedInstantiatedModuleSpec" copy-default-values="true"/>
<!-- simple type -->
<property name="key_name" label="KeyName" category="Input"/>
<property name="subnet_id" label="SubNet Id" category="Input"/>
<property name="vpc_id" label="VPC Id" category="Input"/>
<property name="secretPassword" category="Input" password="true"/>
<property name="memory" category="Input" kind="integer"/>
<property name="highLoad" category="Input" kind="boolean" default="true"/>
<property name="instance_type" label="InstanceType" default="t2.micro" category="Input"/>
<!-- complex type -->
<property name="terraformTags" kind="map_string_string" category="Input" required="false"/>
<property name="loadBalancerZone" kind="list_of_string" category="Input" required="false"/>
<!-- output-->
<property name="arn" label="ARN" category="Output" required="false"/>
<property name="private_ip" label="Private IP" required="false" category="Output"/>
<property name="security_group_id" label="Security Group Id" required="false" category="Output"/>
<property name="secret_password" label="Sensitive Info" password="true" required="false" category="Output"/>
</type>
<type type="myaws.ec2.BlockDevice" extends="terraform.MapInputVariable"
container-type="terraform.InstantiatedModule" deployable-type="myaws.ec2.BlockDeviceSpec">
<generate-deployable type="myaws.ec2.BlockDeviceSpec" extends="terraform.MapInputVariableSpec"/>
<property name="device_name" label="Device Name" category="Input"/>
<property name="volume_size" label="Volume Size" category="Input"/>
</type>
Annotation to link 2 modules
Typically, using input variables (module2) whose values is the output of the other one (module1).
modules:
- name: module2
type: terraform.InstantiatedModuleSpec
source: s3
inputVariables:
anothervar1: module.module1.anothervar1
inputHCLVariables:
region: module.module1.region
The plugin offers an annotation if the 2 variables (input/output) have the same name: <<module this annotation can be used with the inputVariables and inputHCLVariables properties.
This annotation is also manage to new types inheriting from terraform.MapInputVariable type. (cf samples/synthetic.xm)
modules:
- name: module2
type: terraform.InstantiatedModuleSpec
source: s3
inputVariables:
anothervar1: <<module1
inputHCLVariables:
region: <<module1
MapInputVariable
Often it's necessary to provide complex values as input variables. Either it's possible to use
-
InstantiatedModule.inputHCLVariablesto provide the value as text. -
terraform.MapInputVariableSpecto provide values as, easier to display and to manage values using dictionaries.-
all item sharing the same value of the
tfVariableNamewill be merged the others to turn the value into a array of map[{...},{....}] -
if you have one single item matching the
tfVariableName, the output will be transformed to a single map"{...}"instead of an array containing only one item[{...}]. If you don't want this behavior, setreduceSingleToMaptoFalse
-
Example
mapInputVariables:
- name: anotherBlock
type: terraform.MapInputVariableSpec
tfVariableName: myVariableName
variables:
size: 500Mo
fs: FAT32
- name: aBlock
type: terraform.MapInputVariableSpec
tfVariableName: myVariableName
variables:
size: 2G
fs: NTFS
- name: tags
type: terraform.MapInputVariableSpec
tfVariableName: tags
variables:
app: petportal
version: 12.1.2
The plugin generates the following content:
module "s3-bucket" {
source = "./s3"
name="benoit.moussaud.bucket"
region="eu-west-3"
myVariableName=[{"fs": "NTFS", "size": "2G"}, {"fs": "FAT32", "size": "500Mo"}]
tags={"app": "petportal", "version": "12.1.2"}
}
These 2 properties can be set and set as hidden=true if you extend the type.
<type type="myaws.ec2.BlockDevice" extends="terraform.MapInputVariable"
container-type="terraform.InstantiatedModule" deployable-type="myaws.ec2.BlockDeviceSpec">
<generate-deployable type="myaws.ec2.BlockDeviceSpec" extends="terraform.MapInputVariableSpec" copy-default-values="true"/>
<property name="tfVariableName" hidden="true" default="tf_block_device" />
<property name="device_name" label="Device Name" category="Input"/>
<property name="volume_size" label="Volume Size" category="Input"/>
</type>
Control task : Process Module
On the terraform.Module deployable CI, a Process Module control task allows to automatically fills the terraform modules with the variables defined.
It fills only with the variables that has no default value or null value or empty value ( or []).
How to define a new provider
A provider gathers the properties used to configure and to authenticate the actions on a cloud provider as environment variables injected at deployment time.
-
create a new CI extending
terraformEnterprise.Provider -
add properties. Using the
passwordattribute to control if it's a sensitive value or not. -
fill the
credentialsPropertyMappingdefault value that map each property name with the environment variable name. -
Optionally you can set a dedicated
an SVG file
Sample: for AWS.
<type type="terraformEnterprise.AwsProvider" extends="terraformEnterprise.Provider">
<icon>icons/types/amazon-web-services-icon.svg</icon>
<property name="accesskey" kind="string" label="Access Key ID" description="The access key to use when connecting to AWS(AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID)."/>
<property name="accessSecret" kind="string" label="Secret Access Key" password="true" description="The access secret key to use when connecting to AWS (AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY)." />
<property name="credentialsPropertyMapping" kind="map_string_string" hidden="false" default="accesskey:AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID, accessSecret:AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY" category="Parameters"/>
</type>
Sample Configuration
Sample configurations are available in the project.
Store you azure credentials into /.xebialabs/azure.secrets.xlvals(you can use dummy values)
cat ~/.xebialabs/azure.secrets.xlvals
subscriptionId: azerty-a628-43e2-456f-1f9ea1b3ece3
tenantId: qwerty-5162-f14d-ab57-a0235a2385e0
clientId: benoit-820a-404b-efed-4cf7c0a99796
clientKey: p/v-Mmoussauda0yry3W7L3OB
$cp ~/.aws/credentials ~/.xebialabs/aws.secrets.xlvals
$XL_VALUES_tfe_token="6SPlj2J5LMuw.atlasv1.Lm.........GWrnkSUZy1oCg"
$xl apply --xl-deploy-url http://localhost:4516 -f xebialabs.yaml
[1/6] Applying infrastructure.yaml (imported by xebialabs.yaml)
Updated CI Infrastructure/xebialabs-france/AWSProvider
Updated CI Infrastructure/xebialabs-france
[2/6] Applying environment.yaml (imported by xebialabs.yaml)
Updated CI Environments/dev
Updated CI Environments/dev.conf
Updated CI Environments/ec2-dictionary
[3/6] Applying applications.yaml (imported by xebialabs.yaml)
Updated CI Applications/micro-vm/1.0.1/ec2
Updated CI Applications/micro-vm/1.0.1
Updated CI Applications/micro-vm/1.0.0/ec2
Updated CI Applications/micro-vm/1.0.0
Updated CI Applications/micro-vm
[4/6] Applying applications-bucket.yaml (imported by xebialabs.yaml)
Updated CI Applications/s3-bucket/1.0.0/mybucket
Updated CI Applications/s3-bucket/1.0.0
Updated CI Applications/s3-bucket/1.0.1/mybucket
Updated CI Applications/s3-bucket/1.0.1
Updated CI Applications/s3-bucket
[5/6] Applying applications-content.yaml (imported by xebialabs.yaml)
Updated CI Applications/s3-content/1.0.0/content
Updated CI Applications/s3-content/1.0.0
Updated CI Applications/s3-content/1.0.1/content
Updated CI Applications/s3-content/1.0.1
Updated CI Applications/s3-content
[6/6] Applying xebialabs.yaml
Done
if you look for sample packages that instantiates several Terraform modules, please look at
xl apply -f xebialabs/aws_module.yaml
Troubleshooting
This section describes how to troubleshoot the issues when deploying the Terraform Enterprises plugin.
AWS Stack Update Failure
The stack update from AWS Stack 1.0.1 to AWS Stack 1.0.2 fails when executing the Create infrastructure items from resources deployed task.
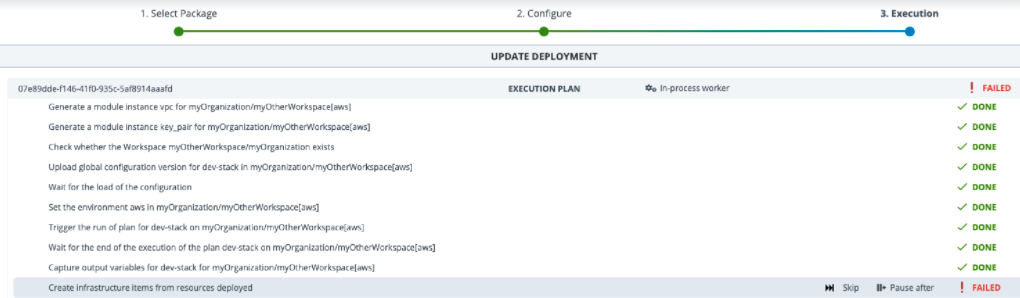
The stack update fails due to missing mappers. To troubleshoot the issue, ensure all the required customer mappers are added to the configuration items. If any mappers are found missing, use the additionalMappers map property to add the required mapper.